If you’ve ever wondered if the amount of RAM in your PC influences performance , then you’ve come to the right article. And it is that we are going to explain to you in an easy and accessible way how having more or less memory installed on the PC gives more or less performance. As well as the cases in which this occurs and the reason for it.
Unless our system uses soldered memory, as is the case with LPDDR, all computers have expansion modules , DIMMs or SO-DIMMs, which allow us to place a larger amount of RAM memory. And in some cases even activate the dual memory channel, doubling bandwidth and reducing access conflicts. However, for the novice and inexperienced user, the value that you will see the most in the specifications is the amount of RAM.

And it is normal that it is a subject that is given turns. Since a greater amount increases the final cost and depending on the use and according to popular theory, more RAM than the account does not bring considerable benefits. However, this is partially false and depends on the type of use that we are going to give the computer and we must start from the fact that not all applications use RAM in the same way. Some are better optimized than others. This without forgetting that there are applications that, due to their simplicity, barely use RAM, but, on the other hand, others devour it.
Does the amount of RAM affect performance?
First of all, we must understand a very basic concept regarding access to memory by the processor. And it is that the so-called cache hierarchy stores only a partial copy of the files. The one that the different cores are currently looking at to execute their instructions. We don’t have all the program data inside. What does this mean? Since the processors execute the instructions in order and sequentially, if one points to another part of the memory and it does not have a copy in cache, then there is a drop in performance.

Have you ever wondered what happens if a file does not fit in RAM? Well, the same as if it does not fit in the cache. Only the part you are working with is stored and the rest is left at a lower level. Of course, on a PC today we can have several applications at the same time, each one generating many processes, apart from those of the operating system.
The normal thing when there are many active applications is that the operating system keeps a count of the most used. So it leaves the ones that are not used in the background and if necessary makes a copy of its state in RAM in storage. That is why some applications often take time to resume action and it seems to us that they have hung. The reason? The time to copy information back to RAM from media is much slower in access.
A little quick test
In order to test the performance according to the amount of RAM we have to force the situation to have a theoretical scenario. So the best way is to force the system with a very large image file. How about an image that takes up 25 GB? This is more memory than the RAM in many computers today . This will lead to the processor loading the image data in parts as it becomes necessary. To do this we will start with a small test using Adobe Photoshop.
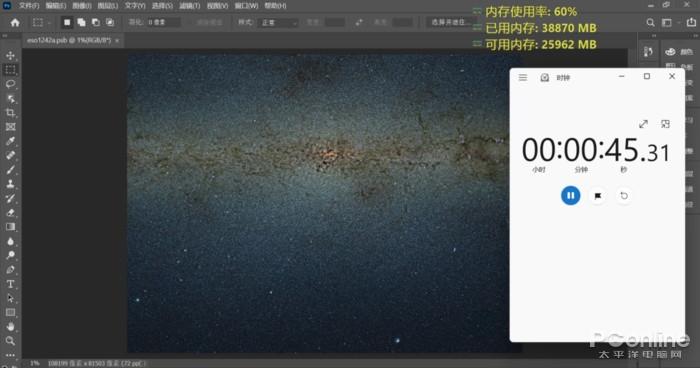
- On a system with a single 8GB RAM module , the file open time takes 4 minutes . Keep in mind that the system will only load a part of the image, so any movement on it beyond what is visible on the screen means a slowdown or a stop.
- On the other hand, if we use a 32 GB configuration, we will find that the file already fits in memory. The opening time of the file? 1 minute and a half.
- On the other hand, if the configuration is two 32 GB modules and, therefore, 64 GB of RAM capacity. The advantage ends up having the use of the double channel, leaving the time at 45 seconds .
The tests have been done on a laptop with an AMD Ryzen 5 5625U processor with the different memory configurations.