Anyone who has ever assembled a PC knows that thermal paste should be applied between the processor and the heatsink and you probably know why this is necessary. However, what if we told you that you should apply thermal paste differently on Intel and AMD processors ? In this article we are going to explain in depth why the use of thermal paste is necessary, and also why the application technique should be different in Intel and AMD CPUs.
In this article we are not going to tell you how you should apply thermal paste or what techniques there are (for that we have other tutorials), and in any case after all, each person has their own technique. What we are going to tell you is, in case you didn’t know, that AMD and Intel processors have a slightly different IHS and that, therefore, you should apply thermal paste differently in processors of one brand or another. .
Why is it necessary to use thermal paste between CPUs and heatsinks?
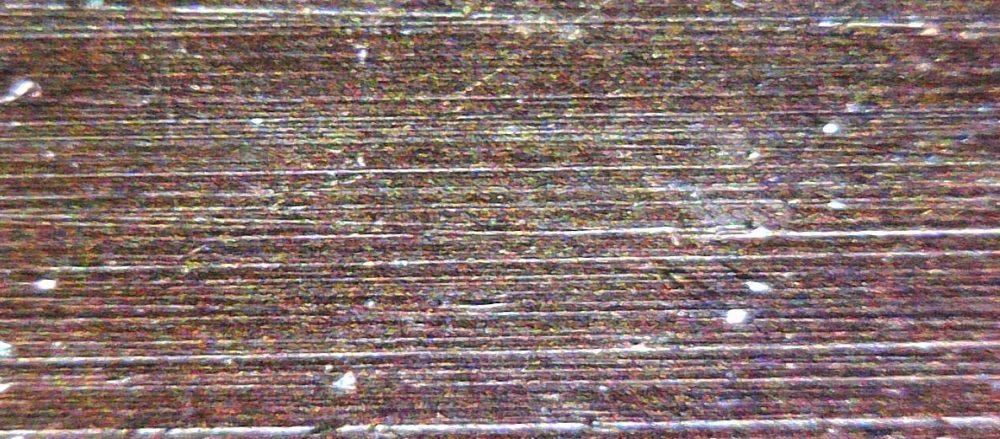
As you probably already know, perfectly flat surfaces do not exist, and even on surfaces like an IHS it is something that can be seen, many times, with the naked eye. For example, this is what an AMD Ryzen processor looks like under a microscope, zooming in just a little bit.

You can easily see that the surface is far from being completely smooth, and the exact same thing happens in Intel processors.

Exactly the same thing happens with the contact area of the heatsinks, there are certain protrusions, ridges and valleys that make the surface not totally flat. This means that, when we put the heatsink on top of the processor’s IHS, the contact is not total and therefore the heat transfer from one to the other cannot be produced efficiently.
This is the reason why it is necessary to use thermal paste, since as its name indicates it is a “paste” that will go through all these “valleys” of both the IHS of the CPUs and the heatsinks to fill those gaps. , and since they have a high thermal conductivity, it will make the heat transfer from the processor to the heatsink much more efficient.
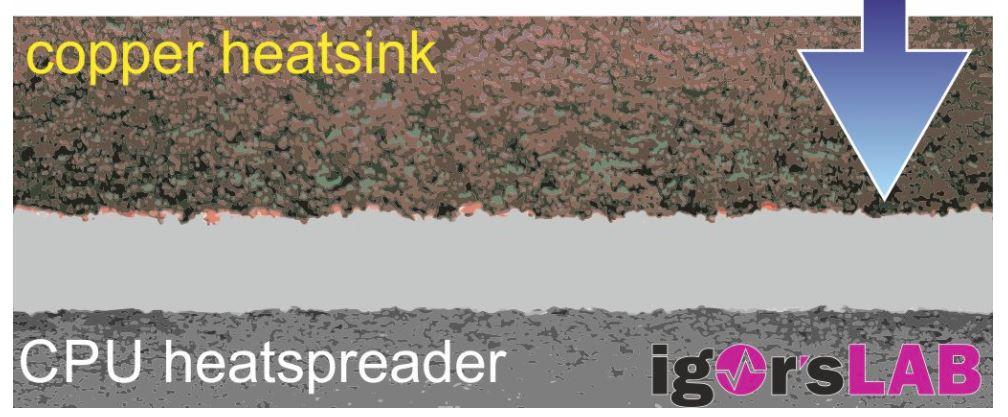

However, you should also know that its conductivity is worse than that of metal, and therefore the thinner the layer of thermal paste that we put, the better the heat transfer will be since the materials of the IHS and the heatsink will be closer from each other.
Intel and AMD processors are shaped differently
Now comes the node of this article, and it is that as we told you at the beginning the technique to apply thermal paste in Intel and AMD CPUs should be different since their IHS are different. In addition to the fact that in both cases we find those peaks and valleys of which we have spoken in the previous section, and that obviously the size is different, there is a recurring “problem” in both brands and that is that AMD processors have a convex shape, while that Intel processors are concave in shape.
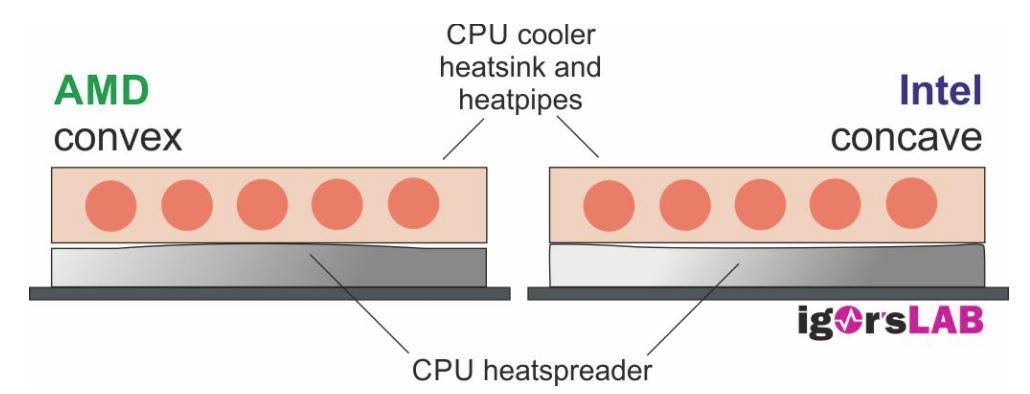
This means that, for example, when mounting an AMD processor and putting the heatsink on it, when we press it it is easy that if we have put extra thermal paste it will be “ejected” from the sides, something that does not happen in Intel processors because it remains accumulated in the center.
This means that when we mount an AMD processor, we should apply a very thin layer of thermal paste but with special emphasis on the outer perimeter, since that is where there will be greater contact distance between the IHS and the processor. On the contrary, if we are mounting an Intel processor we will have to influence more in the central area, since that is where there is a valley that will make contact with the heatsink not entirely good.
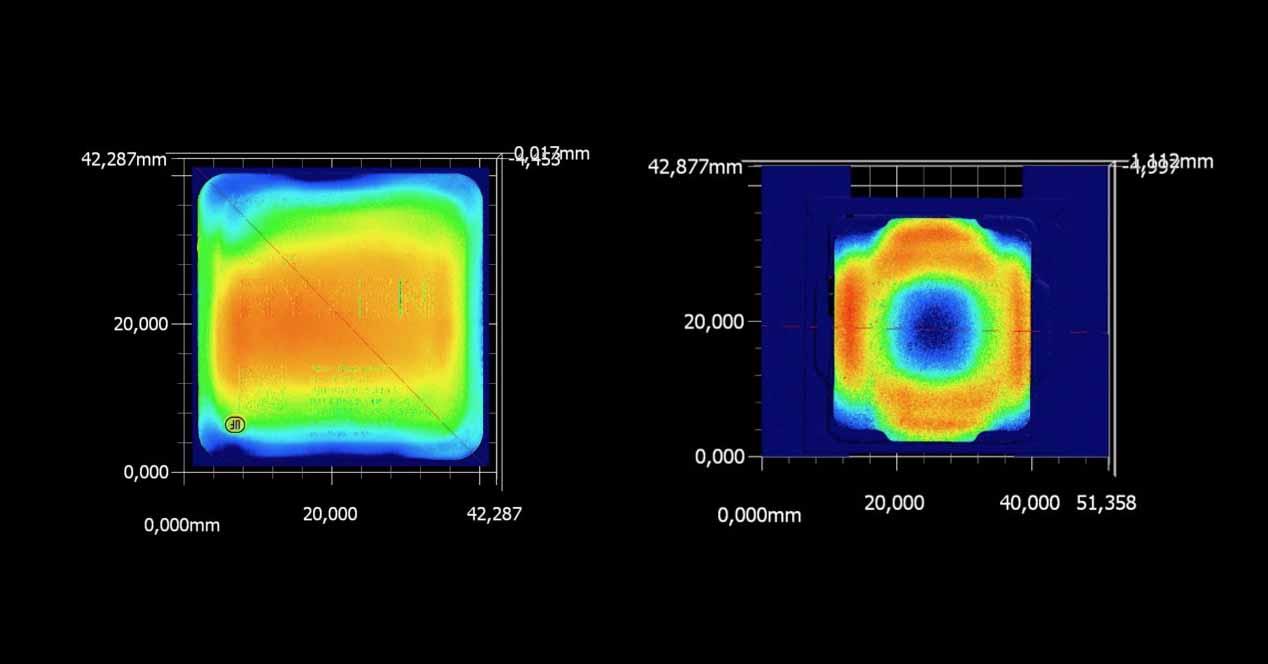
And, if we apply a very thin homogeneous layer, what happens when we analyze the heat of the IHS is the following:

On the left of the image above we have an AMD Ryzen processor, and you can see that there is more heat in the central area. This is because the contact with the heatsink is much better and therefore the heat transfer is also much better. To the right of the image we have the same with an Intel processor, where it is very clear that the best heat transfer occurs on the outer perimeter, denoting that it is in this area where the contact is best. In fact, in the case of the Intel processor, you can see that the center area can cause serious temperature problems because there is practically no heat transfer there.
In short, you should keep in mind that the IHS of AMD CPUs are convex, while Intel CPUs have concave IHS, so you should apply the thermal paste differently since, as we have shown in the image of heat from above, with a thin homogeneous layer you can have problems.