PCI Express 5.0 SSDs go beyond simply improving bandwidth and the amount of data transmitted. Since they bring with them quite interesting news that have been unpublished in previous versions. That is why we have prepared an article for you so that you can know everything that the latest generation of solid state drives brings with it.
Solid state drives or SSDs are based on the use of non-volatile RAM. And therefore, like a hard drive, they can store data that remains in memory even after the computer is turned off. However, their advantage is that they do not rely on a head and disk to access data. They do it the same way as conventional RAM. This allows them to access multiple data at the same time and do so in less time by not having to reposition the plate and needle. In addition, it brings with it the advantages of using an electrical interface for direct data transfer. As is the case with PCI Express 5.0 SSDs.

What does PCI Express 5.0 bring to NVMe SSDs?
The fifth generation PCI Express connection can transmit up to 4 GB/s of data in parallel per data pin. This means that M.2-type solid-state drives using a 4-lane variant of the standard will be able to transmit up to 16 GB/s of data . However, this must be qualified and make it clear from the outset that units designed for PCIe 4.0 or lower will not get an automatic increase in bandwidth.

This is because data access is managed by the flash controller, which performs the requests made by the processor to the SSD at a specific speed. Nor can we forget that for real purposes it is not possible to use 100% of the speed either. This is because there are certain requests that take longer than the rest and therefore end up adding access time in total. Therefore, if logically we add time when making a data transfer, then the bandwidth is reduced.
That is why the first NVMe PCIe Gen 5 SSDs promise transfer speeds between 12 and 13 GB/s despite 16 GB/s . On the other hand, we have yet to see any DRAM-Less drives. Which do not have RAM memory for the flash controller, which ends up affecting the total bandwidth.
Drives that support Compute Express Link
When we have two different memory wells, for example RAM and SSD. There must be a data transfer mechanism. This is done through direct memory drive access or DMA. Its operation is as follows:
- They read the data into source memory from the first DMA drive.
- They transmit the data to a second DMA unit through a secondary and memory-independent channel.
- The data is transmitted from the second DMA unit to the destination memory.
NVMe SSDs in PCs use the PCI Express data path to copy data from RAM to the solid state drive and vice versa. This opens up new possibilities such as the fact that graphics cards have direct access to information. Although that is already something that can be done with drives under PCI Express 3.0 and 4.0.
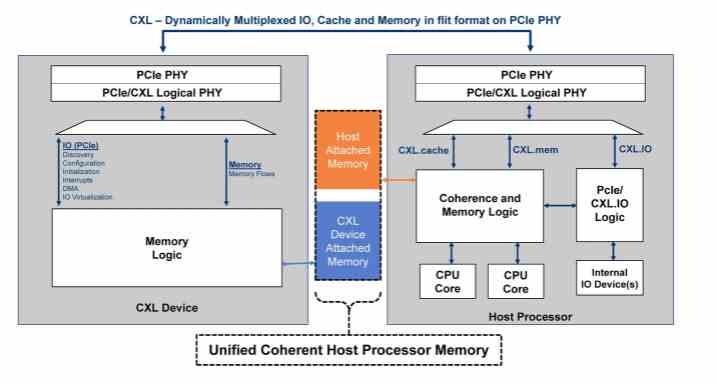
It must be taken into account that one reason why software does not make good use of the capabilities of the SSD is due to the fact that data transfers must be explicit in the program code. Well, the idea of Compute Express Link or CXL is to provide unified access between the system’s RAM and PCI Express devices. Thus the processor sees everything as a single homogeneous block of memory. Thus automating the process of accessing and copying from one data to another and giving all applications the power of an NVMe SSD without code changes.
PCI Express 5.0 SSD Drive Design Changes
Yes, and it is that until now we had different sizes of SSD units, but with the same width of 22 millimeters. So we had units ranging from 22 x 110mm to 22 x 30mm. Instead, it seems that the third generation units will increase their width to 25 mm .
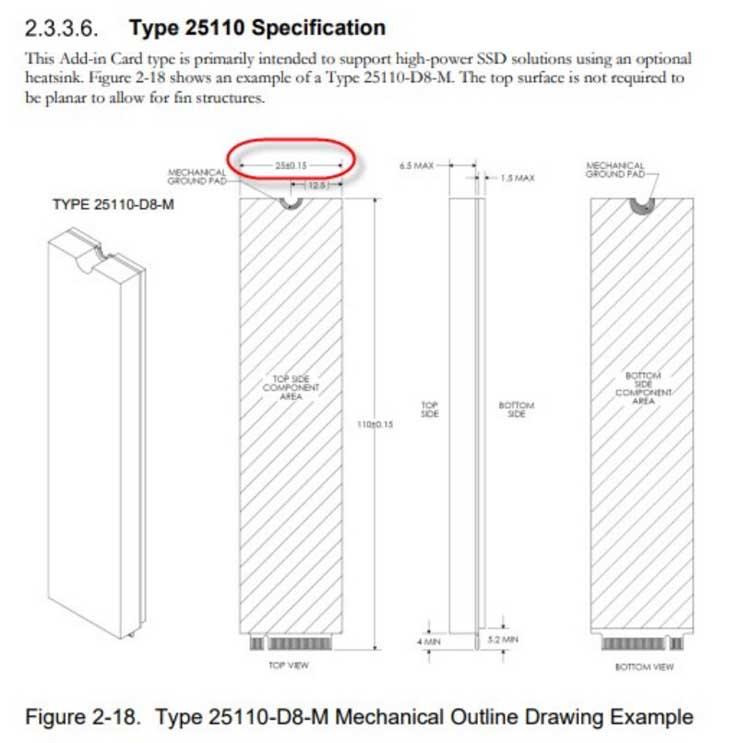
This is a problem for designs that have just enough room for such a unit. However, if your PC only supports M.2 under PCI Express 4.0 or lower. What is the advantage of having a PCIe 5 SSD if you cannot use its bandwidth? In reality, the extra 3mm of width will accommodate a larger heatsink. Let’s not forget that the higher the data transfer, the more temperature it generates and that these units are usually in a closed space.
They will not be usable on PlayStation 5
The change in width means that they cannot be used in the PlayStation 5 console or any other type of unit that uses an NVMe SSD of the M.2 type with a width of 22 millimeters. In any case, it is not a loss since they do not have the capacity to take advantage of the high
Changes in terms of processor, graphics card and RAM
One of the things we’re going to see in the future will be drives with the ability to compress and decompress data at high speeds. Which will be key to freeing the processor from said task and allowing storage to be increased. At the moment, PCs use hardware technologies such as NVIDIA‘s RTX IO and AMD Smart Access Storage through Microsoft‘s DirectStorage API.
However, not everyone is going to have a high-caliber graphics card in their computer, and it won’t be long before we’re seeing drives that provide virtually tens or even hundreds of extra gigabytes of storage. We will see these inside future Intel Core and AMD Ryzen processors.
Because DirectStorage also allows direct access to the drive state to the graphics card. Well, they will also include this type of support units inside. At the end of the day, it is recommended that all the power of the graphics is focused on achieving the best graphics at the highest possible frame rate.