Passive cooling in PC hardware components are the panacea for the most freaks of silence , since lacking fans and therefore moving parts, they do not emit any sound. However, as it lacks active cooling, a passive heatsink does not dissipate heat as efficiently and can lead to temperature problems , which is why special care must be taken in which model we choose for each component and, oddly enough, also Its orientation influences a lot and we are going to talk about this below.
When a manufacturer says, in the product specifications, that its passive heatsink is capable of dissipating a certain amount of heat watts, this value has been measured under optimal conditions, something that is almost never met once we install the device on our PC because Every box and hardware item is different. In a passive heatsink, in addition, it is doubly important to take into account the physical and environmental conditions since, lacking active cooling, it depends on its environment to be able to function efficiently.
Why choose a passive heatsink for your PC?
As we have mentioned before, this type of heatsinks are the ones that, whenever possible due to thermal conditions, are chosen by the most maniacal of silence. There are many users who do not care if their PC makes some noise, either because they have the box on the floor and they hardly notice it, or because they usually have headphones that isolate them from the noise of the PC and they do not notice it either, or because it just doesn’t bother them at all that the box makes a little noise.

However, there are also many users who do find noise a lot annoying, especially those who must work on the PC and need to have maximum concentration on what they are doing. This type of user ends up becoming maniacs for silence and any small noise, even that made by the fans running at a minimum, annoys them, and it is this type of user who often prefers to sacrifice thermal performance in their equipment in order to have the greatest possible silence.
A passive heatsink is obviously capable of dissipating much less heat than an active heatsink, since they lack an element that evacuates the heat itself (the fan in this case). That is why with the highest-end CPUs it is practically impossible to find a passive heatsink capable of maintaining a good temperature level, and this is even more true when you want to have a completely fanless case , without fans.
In other words, this type of heatsinks are not suitable (almost never, at least) for gaming or high-end PCs , but rather for low-power computers or equipment equipped with low or medium-low end hardware that do not generate much hot. Certainly there are models that are designed to dissipate a large amount of heat, but we again emphasize the fact that they are not ideal.
Let’s take an example: imagine a 95W TDP processor to which a normal heatsink is installed over the air, which as soon as it is moderately good will be able to dissipate 150W of heat. That processor could be at rest at a temperature of about 30ºC, reaching 65ºC under maximum load. If we installed a passive heatsink with the capacity to dissipate 95W of heat (and it would already be one of the best), the processor at rest is probably at a temperature of 50-55ºC, reaching 90ºC or even more when subjected to it. to load. This, obviously, will influence its performance (thermal throttling) and will also shorten its useful life, which is why it is not recommended.
The Importance of Orientation in a Passive Heatsink
Whether you are one of those who have a high-end PC and still want the maximum silence or you are one of the users who have a low-end PC that seeks the minimum necessary noise, if you have decided to go for a passive heatsink for your CPU you should know that the orientation of the heatsink is very important, and especially if your case is not completely fanless (that is, you have case fans to generate internal air flow).
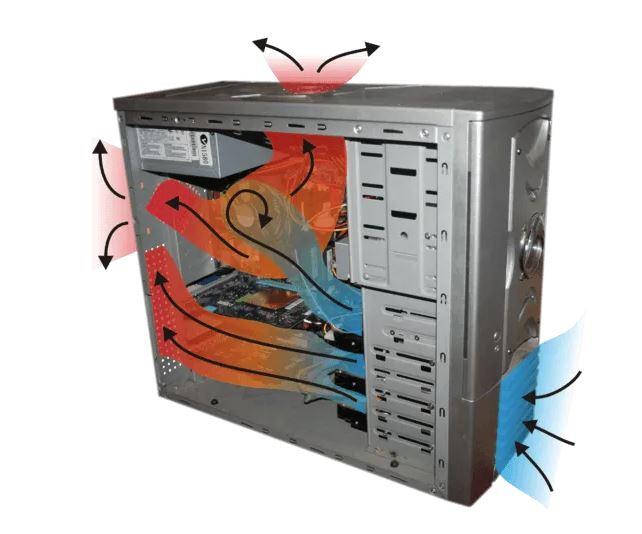

Passive heatsinks are generally made up of a copper core that makes contact with the processor’s IHS to maximize heat transfer, and then have a series of aluminum sheets distributed over a large surface area so that the heat passively dissipate. In the event that the heatsink itself does not have a fan, it will depend on the air flow of the case to better dissipate the heat generated by the processor, and therefore you must take into account where the air goes internally in your case. .
In the image above we have put a box with a conventional air flow, in which fresh air from outside enters through the front and hot air comes out from behind and above. In such a case, the orientation of the passive heatsink is extremely important because the idea is that the air passes through the aluminum fins (cooling them) in the largest possible area.
What orientation is the most appropriate?
Thus, the heatsink must be installed in such a way that the fins are in line with the air flow , so that fresh air can pass through most of its surface and thus cool the aluminum fins.
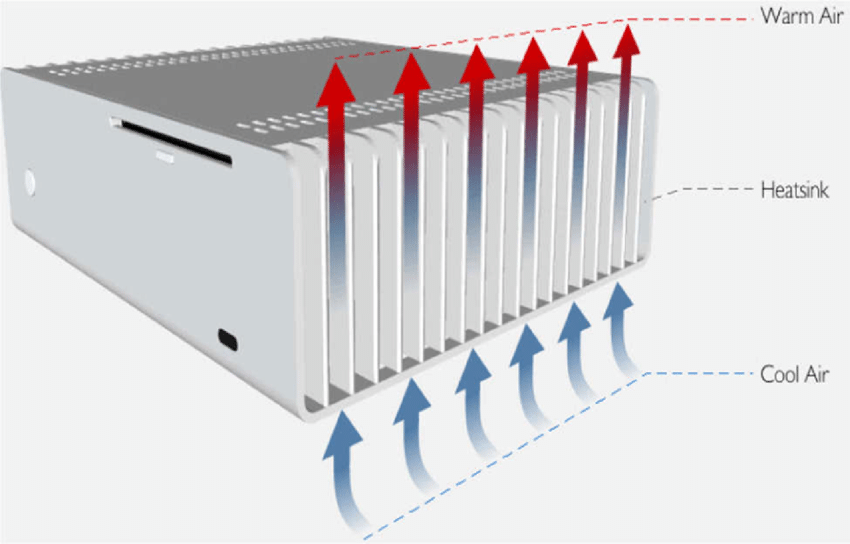
If we installed the heatsink rotated 90 degrees, what would occur is that the fresh air would hit the first of the fins directly, cooling only this one but without reaching the rest of the fins and of course without crossing its surface, something that would be harmful and not only in the thermal aspect as it is not using the maximum dissipation surface, but also noise would be generated by causing the air to collide with the “wall” of the first of the heatsink blades.
Therefore, the most suitable orientation to install a passive heatsink is with the aluminum fins in line with the internal airflow of the case. Even in cases that are totally fanless, that lack fans, you should make sure that the orientation of the heatsink is with the blades facing the vents because even without fans, some air always enters and leaves the case (finally, after all the air is always in motion).