NVIDIA has announced a collaboration with AyarLabs at Computex, which is very important for the company’s future graphics architectures. That is, the chips that they will launch in the future. Beyond the recently introduced H100 for servers and the future RTX 40. Why are light-based optical interfaces of interest to NVIDIA and what can it mean for the brand’s graphics cards in the future?
Dividing a chip into several with the same functionality combined between them is the future trend. We have talked to you at length about the so-called chiplets and it is more than proven that it is the bet for the future, at least from AMD and Intel. But what about NVIDIA?

It was speculated that Hopper would follow this trend, but in the end it has not been so. So the general feeling is that Jen Hsun Huang’s company is behind its rivals in this regard. Let us not forget that it has been necessary to create new types of interconnections to alleviate a common problem. And it is that in both semiconductor materials and metals, consumption increases with the length of the wiring. Well, a solution to this is the use of optical interfaces and this seems to be NVIDIA’s bet.
AyarLabs and NVIDIA agree on the use of optical interfaces on graphics cards
Through a press release, NVIDIA has announced its collaboration with AyarLabs for the creation of interconnections based on light for future artificial intelligence architectures. A statement that without the proper context may seem confusing, but it is very revealing. For some time now, the green company calls its graphics chips optimized for high-performance computing, AI chips . So we are talking about the design of what we know as Blackwell and that will replace the recently presented H100 chip with Hopper architecture.
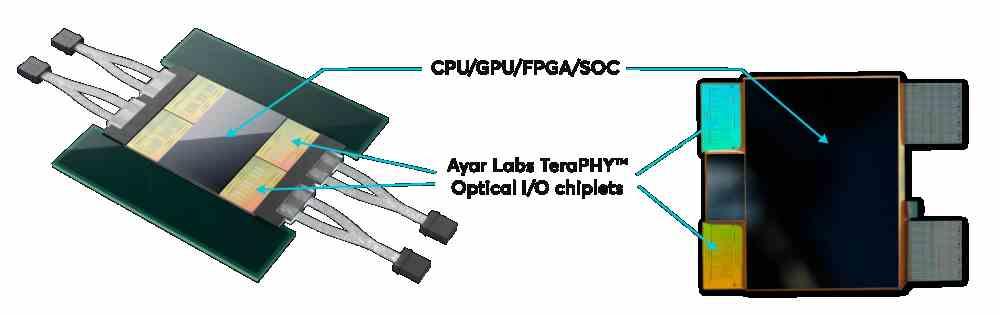
What is the idea? Well, in the fact that instead of communicating two chips with each other through copper interconnections, optical interconnections are used. To do this, a piece that converts electrical signals into light is used as a transmitter. And another that performs the reverse function as a receiver. The advantage of this is that the resistance that is created by the distance of the wiring disappears completely . In addition to other advantages, such as the fact that the number of interconnections per area increases up to 1000 times . Allowing simultaneous sends at very low clock speed. This allows the energy cost per transfer to be reduced by up to 10%.
In its current form, the AyarLabs technology, known as Tera Phy , is made up of 8 optical ports with the capacity to transfer 2 TB/s and an energy consumption per transmitted bit of 5 pJ . This is much higher than current interconnects at the processor level. However, it does give us a clue to what NVIDIA’s future plans are and what the application of this technology is.
Why does NVIDIA want this technology?
Although the advantage is not really found in the reduction of energy consumption. Something that has already been achieved with the TSMC CoWoS and Intel Foveros packages, if not that consumption does not increase with distance. This is key in HPC systems that use multiple GPUs at the same time. In other words, thanks to this, NVIDIA can create a large graphics card with dozens of chips arrayed and interconnected with each other through optical interfaces for intercommunication. Which let’s not forget that they can transmit hundreds of meters away without increasing consumption.

In any case, this should not take us by surprise. Since NVIDIA has already shown interest in the use of optical interfaces at the level of supercomputers and data centers made up of dozens of interconnected graphics cards. In any case, at the level of a graphics chip in chiplets. We believe that just as AMD has based its designs on TSMC’s technology, NVIDIA will do the same.
To finish, the optical interfaces are also key in the development of future video memories. Let’s not forget that your access is what consumes the most in a graphics card. A type of VRAM where its chips use optical ports to communicate would mean a huge step forward in reducing one of today’s biggest headaches. Something that only NVIDIA must solve and that also affects its rivals. In any case, we are talking about things in the future and we do not know if this technology will reach the domestic level.