We talk a lot in the world of NAND Flash memory hardware, and most of our readers surely know that it is the type of memory used, for example, SSDs or USB pen drives. But do you know what exactly this type of memory is and how it works? In this article we are going to tell you in depth.
When we handle so much data on our electronic devices, we always have to have a way to store it. In the past this was done using punched cards, and later magnetic discs arrived. Currently, the most widespread type of storage is NAND Flash, so let’s see what it is to understand it.
What is NAND Flash memory?
It is a type of non-volatile memory, and this means that it does not need power to retain data. In other words, contrary to what happens with RAM, the data is not erased when you turn off the PC or disconnect the device, and can remain there for a long, long time.
NAND is an acronym that comes from the English “Not And”, and this is so because its function is to behave as a Boolean type logical gate . When it started to be manufactured, this type of memory was either NOR or NAND depending on the type of transistor that was used, but currently NOR memory was discarded because NAND is much easier and cheaper to manufacture, in addition to being able to count on higher densities.

Its operation consists in that inside they have transistors based on EEPROM technology of floating door, which, unlike the EPROM memory, can be erased and rewritten (that’s why it has an extra E at the beginning, for “erasable” (erasable)). Essentially, the data is stored in the memory cells according to their state and following the usual binary code: in the ones the logical “door” is open, and in the zeros it is closed. This is how the data is stored.
NAND memory types
As you know there are different types of NAND Flash memory, so let’s summarize what each of them consists of:
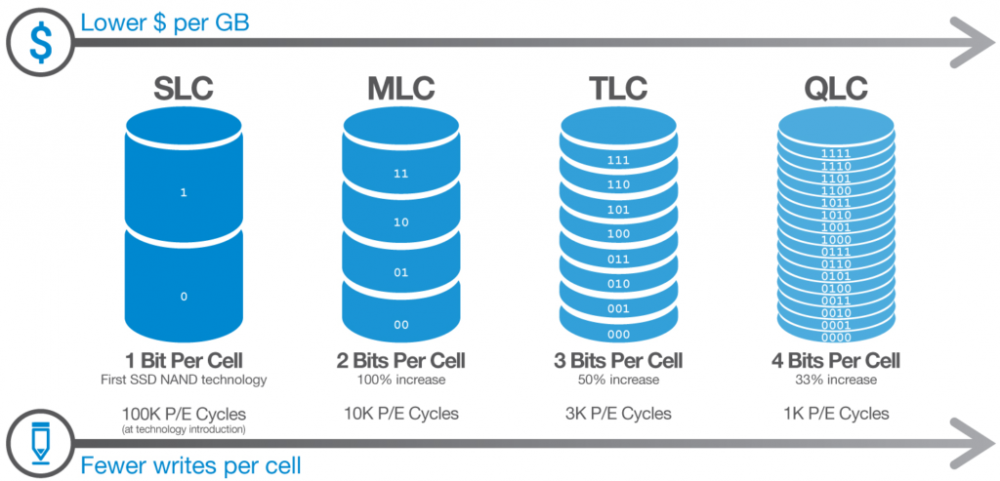
- SLC (Single Level Cell) : it is the first to hit the market; each one of its memory cells is capable of storing only one bit of information, and therefore it is the least wear and tear of all types of NAND Flash memory and the fastest when it comes to accessing data. However, because only one bit per cell fits, its density is extremely low.
- MLC (Multi Level Cell) : Its manufacturing cost is significantly lower than the SLC, and therefore it quickly gained importance. This NAND is capable of storing two bits per cell, so the density is literally doubled, although it also has considerably less durability because of it.
- TLC (Triple Level Cell) : The performance of this type is considerably lower than the previous ones since up to three bits can be stored in each cell, which also greatly increases its wear. The good news is that devices with this type of memory have very high densities.
- QLC (Quad Level Cell) : is the evolution of TLC memory, and up to four bits can be stored per cell. With the new generations and improvements in the algorithms, its wear was even lower than TLC.
NAND Flash 3D memory
In order to keep increasing the memory density more and more, for a long time you will have heard of NAND Flash memory in layers , or NAND 3D, in three dimensions. This is so because given the physical space limitations to put chips on the PCBs, in the end the solution to continue increasing the density and therefore the capacity of the devices was to stack layer after layer with high-speed interconnections.
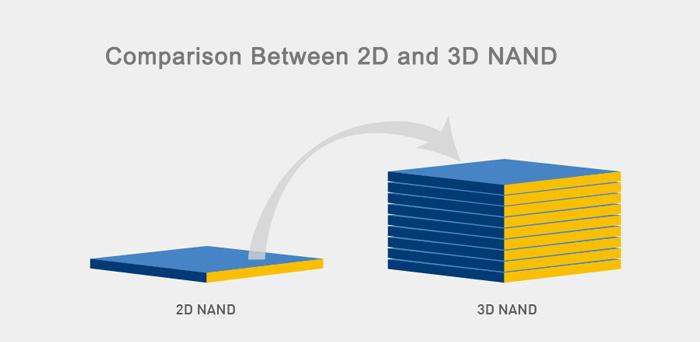
In this way, and regardless of the type of NAND used, the density can multiply, although of course to a certain limit, since as you will understand they cannot grow in height in an unlimited way. Currently, manufacturers already work with 128-layer chips, although Samsung has already announced that it has 160-layer NAND Flash memory in development.