In the hardware world it is inevitable to use magnitudes when we talk about storage or capacity. Megabyte, Gigabyte, Terabyte and even Petabyte are very common terms that we use on a daily basis but how big is this? In this article we are going to put all these magnitudes in perspective so that you can get an idea of what they mean in a specific context.
It is easy to understand that 500 Gigabytes is more than 100 Gigabytes. You probably also know that a Terabyte is 1024 Gigabytes, but if you are not familiar with the architecture of computers, these terms are quite abstract. Although you can easily visualize magnitudes such as a meter or a liter, when we talk about a Terabyte or a Petabyte, things change, right?

To put this in perspective, let’s take a look at the storage sizes used by computers to see how large the quantities we handle on a daily basis are.
Bits and Bytes, the most basic units
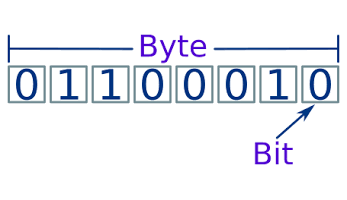
A bit is the smallest unit that can be stored in a computer. Since PCs use the binary system, each bit can be either a zero (0) or a one (1). To put this in perspective, one bit is enough to store whether a value is true or false; for example, in a PC game, a single bit can be 1 if the player has obtained a certain object, or 0 if he has not obtained it.
Eight bits together are called byte , which by calling it in an understandable way, are the “blocks” of storage. A byte can have 256 possible values depending on the bits it contains, and to give you an idea, a single character from the ASCII alphabet occupies one byte.
Kilobytes and Megabytes
A Kilobyte (KB) is the first of the main data groupings, and is equivalent to 1000 bytes (you will recognize it by its prefix “kilo” which means thousand, since it is used in other quantities such as kilometers). To give you an idea, a text file with 1000 characters occupies approximately 1 KB.
The last size before reaching the largest denominations is the Megabyte (MB), which is equivalent to 1000 KB or one million bytes. One megabyte contains approximately one minute of music compressed into MP3, or to give you another perspective, a normal audio CD occupies 700 MB. However, you have to keep in mind that a Megabyte (MB) is not the same as a Megabit (Mb), which is a million bits. Thus, a Megabyte is 8 Megabits .
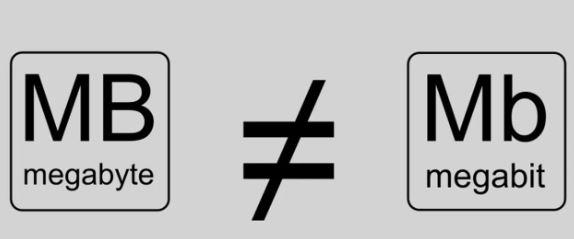
Before continuing, we must mention the difference between how computers and humans measure storage. Due to how the binary system works, a Kilobyte actually equals 1024 bytes, and not 1000. That variation increases as you move up the size scale, which is why a 250GB hard drive, for example, shows only 232 GB available.
Because the correct definition of prefixes such as “giga” is that it should be a multiple of 1000, for simplicity it is used even though it is actually 1024. The correct prefixes should be ” kibi ” or ” gibi “, but by standardization, it is not use.
Gigabyte, Terabyte and Petabyte
The terms Gigabyte and Terabyte are probably very familiar to you, and they are the most common storage units today. If you wonder how many bytes are in a Gigabyte or Terabyte, remember that the number is multiplied by 1000 each time you increase the magnitude.
We have already seen that there are 1000 bytes in a Kilobyte, and that there are 1000 Kilobytes in a Megabyte; Since a Gigabyte is 1000 Megabytes, then we have that in a Gigabyte there are no less than 1000 million bytes. In perspective, approximately 230 MP3 songs or three minutes of 4K video at 30 FPS enter 1 GB. A DVD is capable of storing 4.7 GB in total.

Moving on to Terabytes, following the same rule is 1000 GB. To put this in perspective, we would need 1,430 CDs or 213 DVDs to fill one Terabyte of storage. Another example would be that, as it has been calculated, the US National Library houses 74 TB of data, or at the end of 2019 Google announced that Google Books contained more than 40 million titles, occupying about 40 TB of storage.
As for Petabytes (PB) , it would have to be multiplied by 1000 again. To put this magnitude of storage in perspective, scientists estimate that the brain has room to store about 2.5 PB in memories. 1 PB would be enough space to store a 1080p resolution video recording 24 hours a day for 3.5 years.
There are of course other larger magnitudes: Exabytes, Zettabytes, and Yottabytes. To give you an idea, in 2004 1 EB of Internet traffic was exceeded for the first time in a single month, in 2017, the Internet managed 122 EB of data per month, or in 1 EB, 11 million movies would enter 4K resolution .
As for the Zettabytes, which we already talked about 1000 Exabytes, a curious fact is that the International Data Corporation calculated that all the data in the world stored in 2018 added up to 33 Zettabytes in total. Finally, with respect to Yottabytes, we are talking about 1000 zettabytes, and the comparisons with real-world terms are almost ridiculous, because we are talking, for example, of 257,054 thousand trillion DVDs.