AMD Ryzen APUs have proven to be extremely powerful and efficient, valid even for running some simple games. However, as they do not have dedicated VRAM, they reserve part of the system’s RAM for their tasks, sometimes leaving an insufficient amount for the rest of the system. In this article we are going to show you how you can reduce the RAM consumption of your AMD APU and thus leave more resources for the rest of the system.
Keep in mind that by reducing the amount of RAM reserved for the APU’s iGPU, you are potentially reducing its performance as it will have less reserved memory to lean on. However, if you have an APU but also a dedicated graphic (something frequent especially in laptops ) then you are not interested in the APU reserving RAM memory because you already have a dedicated graphic for it, so this tutorial will be tremendously useful.

RAM consumption with an AMD Ryzen APU
When you have an APU, inevitably part of the system RAM will be reserved for use, which means that the effective amount of memory on the PC will be depleted. On a desktop PC with 16 GB of RAM, this is probably not too much of a problem, but if you have a laptop with only 8 GB, the iGPU consuming slightly more than 2 GB can be a problem, since it will leave something less 6GB for everything else.
Unfortunately there is no direct way to modify the amount of RAM that the system reserves for the graphics integrated in the APU, but this is not something that we cannot modify; It is simply a bit more laborious, although as you will see below it is not complicated either.
How to reduce the RAM consumed by APUs
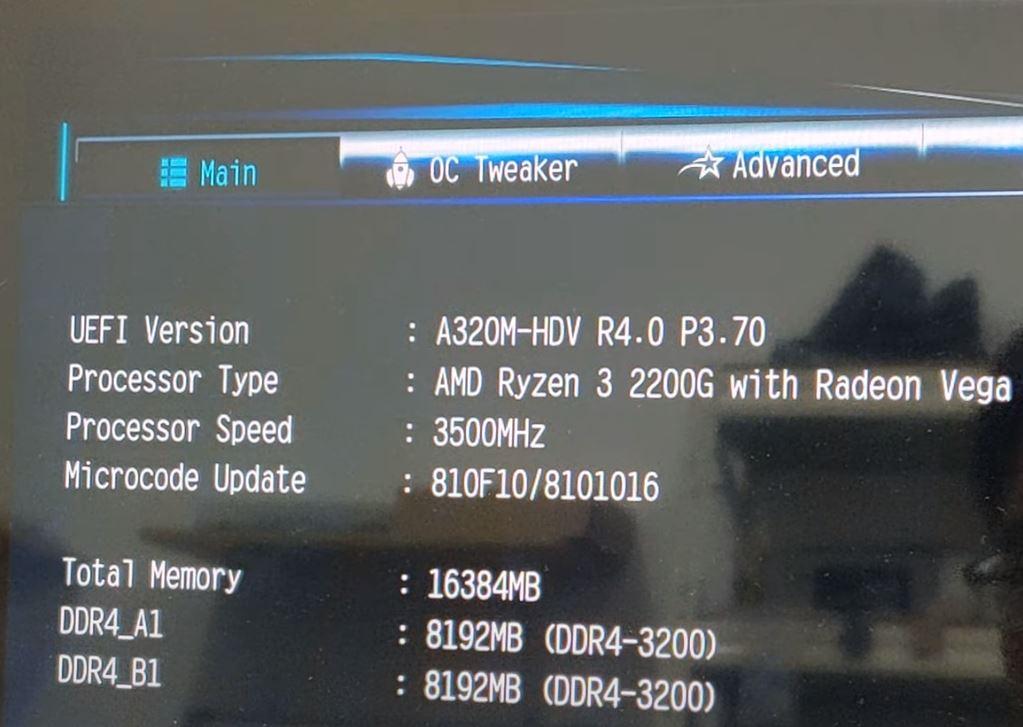
You must bear in mind that the procedure that we are going to tell you below may differ depending on the model and brand of your motherboard, and very especially in laptops you could find yourself in the position that you do not find this option (it is not frequent, but in some manufacturers have decided to eliminate it). In our example, we use a desktop computer with an ASRock motherboard and an AMD Ryzen 3 2200G APU with Vega graphics.
The first thing you should do is restart your computer and access the BIOS in the usual way.
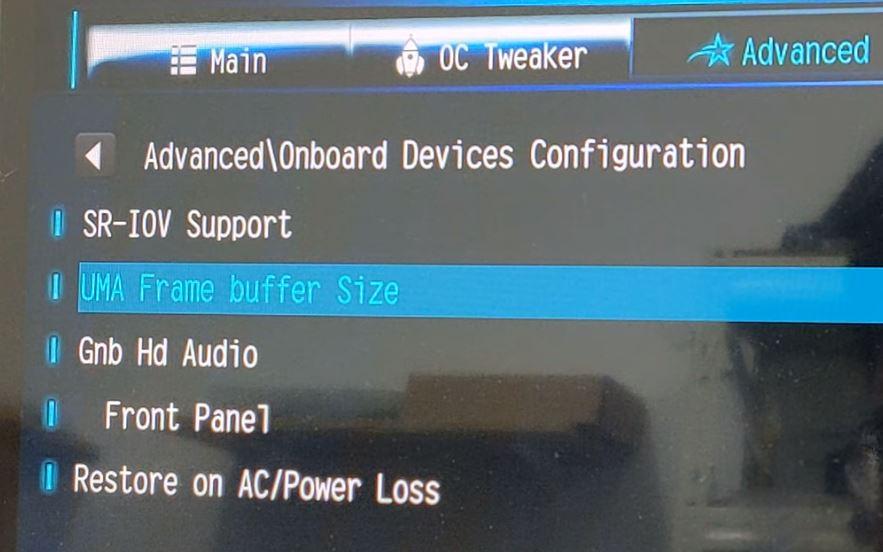
The option we are looking for will be found in the Advanced Options -> Onboard Devices Configuration, and is called “UMA Frame buffer Size”.
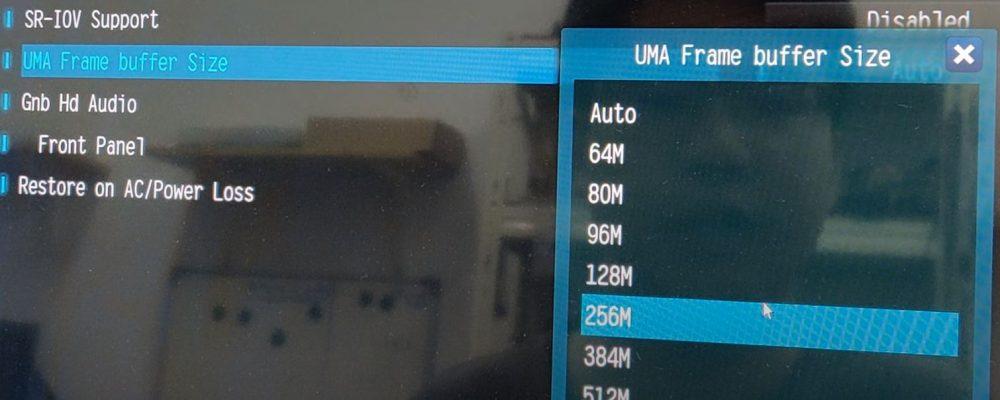
This is where we can select how much RAM we want to allocate by hardware to the integrated graphics. Obviously, if you have a dedicated graphic in your system, be it desktop or laptop, you are interested in assigning as much RAM memory allows you, although if the graphic you are using is the integrated one, we do not recommend assigning it less than 256 MB even if you do not use the PC. to play, since if you have a Full HD screen and want to play a video you will already be using up this amount of memory.
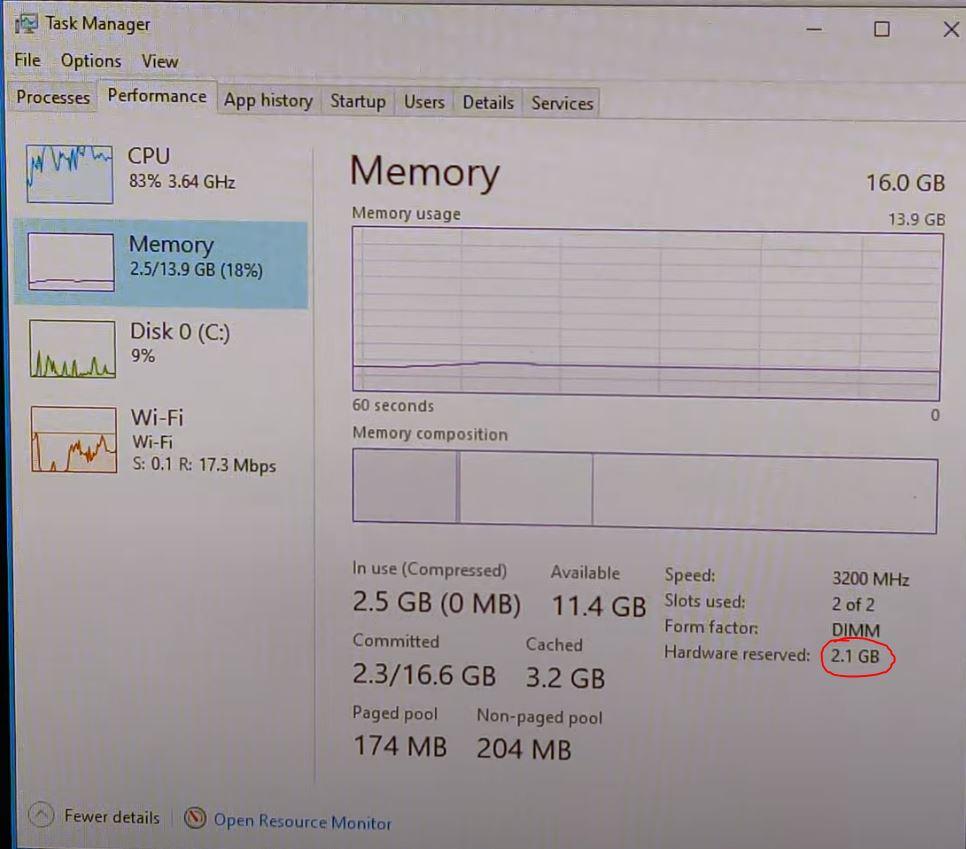
Once this modification is made, you will only have to save the changes in the BIOS and restart the computer. This parameter is set by default to “Auto”, and the maximum is assigned (2048 MB of RAM, which Windows interprets as 2.1 GB), but after having set it to 256 MB, Windows detects that it has 327 MB reserved by hardware ( why Windows detects that the allocated amount is more, we cannot say it) as you can see in the following image.
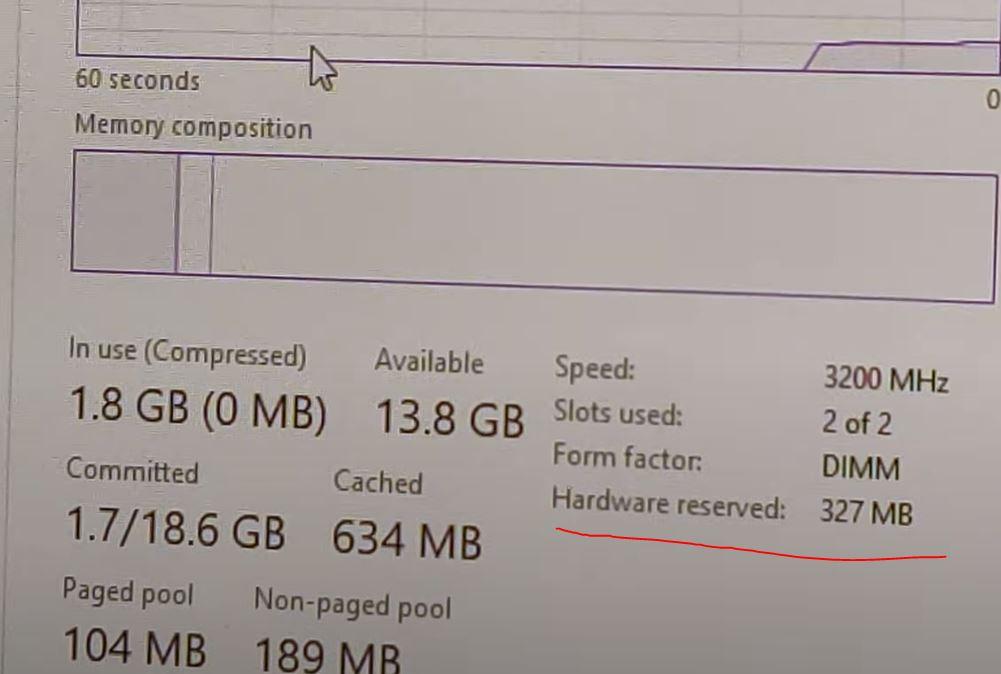
In this way we will have considerably reduced the amount of RAM consumed by the AMD Ryzen APU (for Intel it works more or less the same and the procedure is the same, actually), leaving more for the rest of the programs. Of course, as we have warned at the beginning, you should bear in mind that this can reduce the performance of the computer in activities that require the use of the computer’s graphic power, especially in games.