When formatting a hard drive, SSD or pen drive , we will find a parameter called ” allocation unit size “, which is generally marked as default but in which we can choose different sizes. In this article we are going to tell you what this size of the file allocation unit is, what it influences and which one you should choose for each case.
This is one of those configuration parameters that we don’t pay too much attention to as a general rule, especially since Windows already offers us to choose a default value for it, but it can greatly influence the performance of your storage unit, so it deserves the It is worth doing a review and see what it is for so that you can make an informed choice.
What is the allocation unit size on a disk?
This parameter is used to designate the minimum capacity in which a file can be saved on the storage drive. It is also known as cluster size , as the PC’s file systems organize the storage unit according to the size of this cluster, so that when a file does not have a size that corresponds to a multiple of the size of the allocation, additional space is allocated to “square”.

In other words, suppose you have a file allocation size of 4 KB; This means that the minimum size that the files will have will be 4 KB and from then on always with their multiples, so that if you want to save a file that occupies only 1 KB, it will actually occupy 4 KB on disk, while if You try to save a 6 KB file, it will be 8 KB.
This is the reason why, if you click on any folder you have on the disk with the right button and select properties, you will see that the “Size” and “Size on disk” parameters never coincide, since the first one tells us what they occupy the files and the second tells us how much space it is actually occupying on the disk.
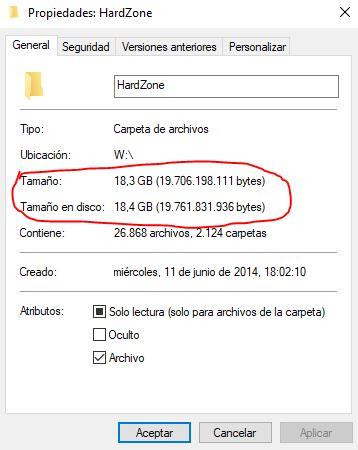
Doing this is necessary for the operating system and is especially important in mechanical hard drives, in which the sectors are physical, since a portion of the disk needs to be assigned to each file in order to find it later. As you will see, it is quite important to choose well because:
- Choosing too large an allocation unit size will waste a lot of disk space.
- Choosing an allocation unit size that is too small will impact performance and file fragmentation on disk.
You have to try to choose wisely, and for this, below we are going to give you a series of recommendations based on our own experience, so that you can choose what best suits you depending on both the type of unit you are using and the use you are going to give it. , a quite important factor and that in reality almost no user takes into account when formatting the disk.
Another consideration to take into account are the options you have, which depend on the type of format: for example, a drive formatted in NTFS format allows you to choose an allocation size ranging from 512 bytes to 2 KB, while if you choose format FAT32 options will be much smaller.
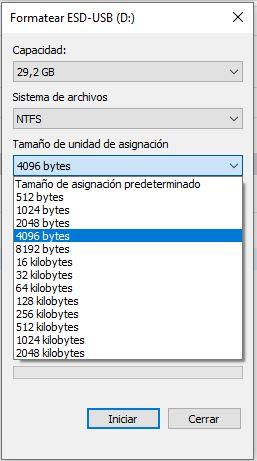
So what size is better to choose for each case?
Although modern operating systems are already prepared to always try to get the most out of the disk, sometimes they do not achieve an efficiency that we could achieve by configuring these types of parameters manually. Normally, if you leave this value in default you will be successful, because the operating system will look for an intermediate value that allows good performance without wasting disk space.
You have to be very careful with SSDs and flash drives like pen drives: we might think that choosing the minimum disk allocation size would be the right option because these devices have great performance, but you must remember that drives with NAND Flash memory do not they handle small files too well, as a simple ATTO Disk Benchmark shows us.
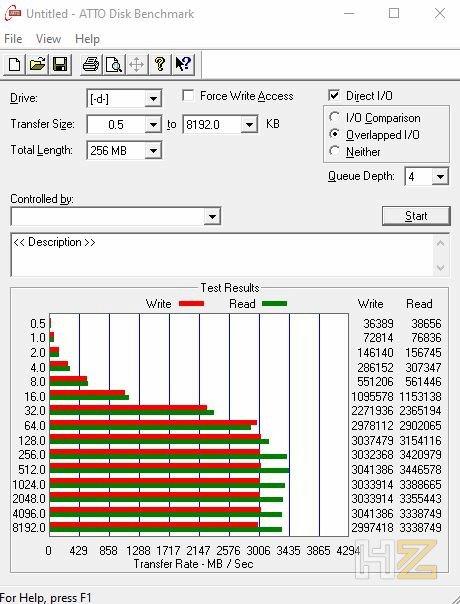
If you are using an SSD, the ideal is actually to benchmark with ATTO Disk Benchmark first to see from what file size it has the best performance; In the screenshot above, for example, we would choose 2 KB since from there it is already giving us a fairly good performance, although it is not until 32 KB that it begins to deliver its best face.
In any case, to choose well you must also take into account what type of content you intend to have on the disc. For example, for a large capacity disk that you are going to use to store very large files, such as series and movies, you want to have a large allocation file because you will not waste almost no space (since there will be few files very large) and by doing so you will be promoting better performance. However, for a system disk that is going to have a huge number of files, you want a smaller allocation size so as not to waste so much space.
Anyway, the main recommendation that we can give you on our part is that in case of doubt always leave the default value , and that only on secondary hard drives that you are going to use as mass storage (not to install programs or games) you modify the size of assignment to a larger value in order to encourage better performance.
Also bear in mind that choosing a very small allocation size will promote file fragmentation, that is, the same file could be spread over different parts of the storage unit and in order to use it the disk will have to work more than necessary, reducing your performance. You should always try to find an intermediate value, but as we have said before, choosing the default value will almost never go wrong.