Optical fiber reaches more and more homes in our country. Spain is already ranked third in the world in terms of fiber deployment. We can say that Spain is well connected and that, in a short period of time, before 2025, it will also reach rural areas that today lack fiber optic connection. But the qualities of fiber optics go beyond offering us a good connection, it has utilities that range from assessing the magnitude of earthquakes to detecting water or gas leaks.
The fiber installed throughout a city connected by sensors capable of making you feel the vibration of traffic or the presence of nearby machinery that can threaten to cut the cable connection is now a reality and is called FiberSense.

How does FiberSense work?
FiberSense ships its lasers and measures fiber tensions with a 3U box that is installed in large metropolitan data centers. Each installed unit can monitor 200 kilometers of fiber and house 20,000 virtual sensors. Each sensor can be configured as a hydrophone, microphone or any other vibration sensor
FiberSense uses sonar-derived techniques to detect vibrations in fiber cables. Through a laser that passes through the glass strands of the optical fiber, it is able to analyze the backscatter caused. FiberSense CEO Mark Englund clarifies that “vibration and sound modulate the tension in the fiber.” This company has discovered how to measure the changes in a fiber and find the reason that produced them. But, to what situations can this finding apply? Let’s go with some examples:
Traffic
FiberSense is capable of detecting traffic accurately enough to differentiate whether it is a truck, a passenger car or a cyclist. It is also capable of detecting the speed of said vehicle and the lane in which it is traveling. In addition to analyzing road traffic, in cities it is also used to detect leaks in pipes or detect vibrations caused by heavy machinery in construction areas.
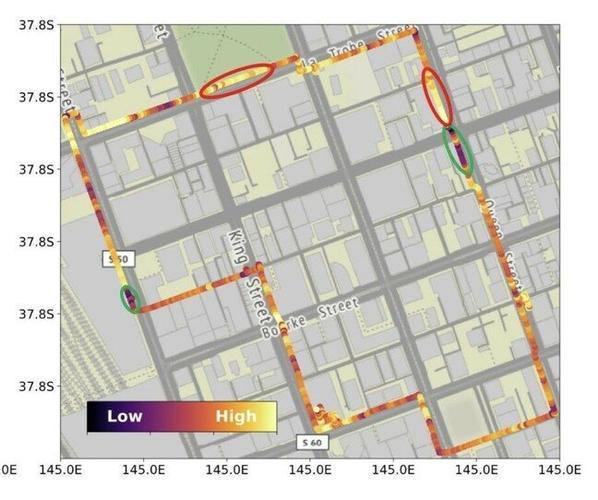
Earthquakes
The impact and magnitude of an earthquake can also be measured through fiber optics. Yesterday the Australian city of Melbourne suffered an earthquake measuring 5.9 on the Richter scale. FiberSense sponsor Bevan Slattery shared the following image where we can see how this technology works. The darkest segments show the points of greatest impact of the earthquake.
Sea
In a maritime environment, it is able to detect the dragging of ship anchors that can damage submarine fiber cables, as happened recently in the Australian city of Perth.
Cities that use this technology
FiberSense is already present in several Australian cities, in addition to London, Dublin, San Francisco, New York and Singapore. For example, in London, its chief executive, Mark Englund, sees water leak detection as a great opportunity, citing recent reports that the city’s Victorian-era pipes leak 500 million liters a day.
FiberSense aims to operate as a service in many other cities: it will install its kit in data centers and exchanges and provide a platform that telcos can rebrand or that end users can consume.
