It is a term really heard by many and over the years it has ended up taking more and more force first among professional overclockers and finally among all types of users. Many still do not know it, so we are going to explain in depth what chip binning is and how it can help us improve the overclocking of our PC.
We start from the basis that we have more or less idea of how any current chip is created, and of course of concepts such as wafer, or perimeter cut, since this is basic to understand the final explanation. And it is that as we well know the chips are manufactured in a chain production, but they are never the same, they are not perfect and they will never be when compared, why?

A method of keeping a check on the quality of chips
This term is just a way of calling the processing of any chip and its classification according to a series of specific parameters. But if all the chips are made the same and the degree of perfection is practically 100%, the most obvious question is why classify them?
The answer is equally simple: no chip is identical to its brother, even if it was right next to it at the time of the cut. As much as manufacturers strive to perfect their creation, assembly, cutting, cleaning and soldering techniques , small defects always occur in wafers and later in chips.
Due to the way each wafer is built, we have a curious nuance that should be known, since the chips that are more in the center of it will always have a higher quality of construction, fewer impurities and therefore fewer failures, more perfect. As no other way to create them has been invented, this will continue until the paradigm changes.
Two types of binning, industrial and for overclocking
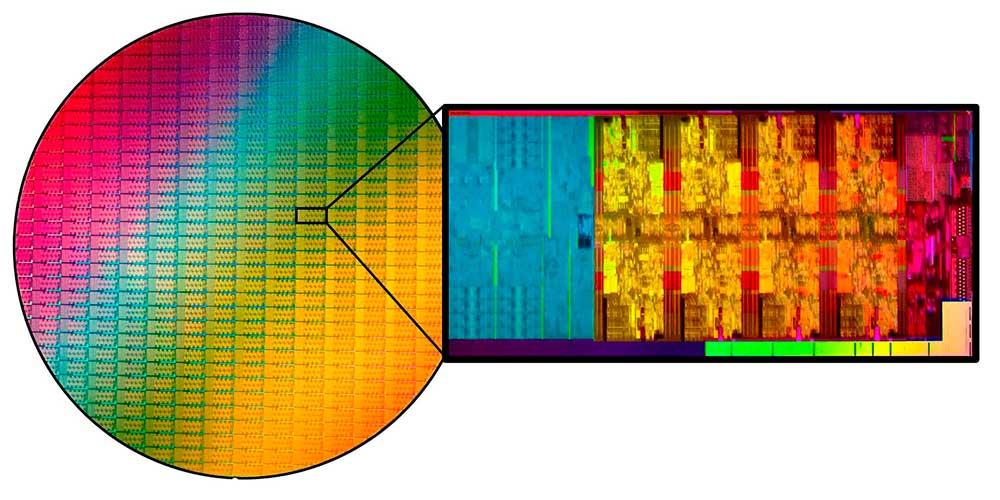
Having understood this, now we must approach binning from two perspectives: that of the manufacturer and that of the user . On the manufacturer’s side and as a rule, it creates matrices with which it designs the chips through a maximum specification, that is, with a number of specific cores, transistors, ALUs, etc …
Through preliminary tests, he has come to the conclusion that you will get a number of chips with that maximum specification, since they are very perfect, but the rest will not be able to pass the cut, that is, they will have shape defects, too large power leaks, transistors in bad condition and endless problems.
Therefore, this maximum specification always results in more expensive chips, but logically they are not going to throw away the chips that do not pass it, but rather they create lower specifications to output them as slower chips with fewer features, like this make wafers more profitable.
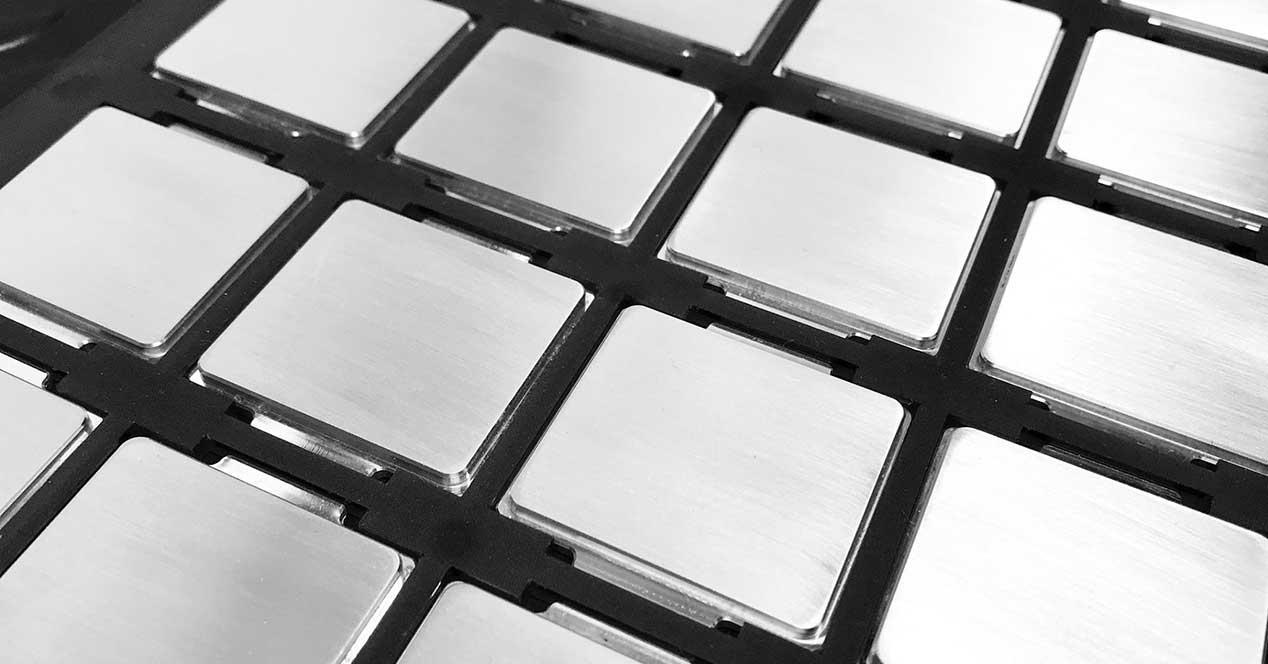

Logically, not everything starts from a single chip, from a single matrix, since there are limits, but in reality there are only four or five matrix models per architecture and all the chips come from there, both from Intel and AMD or NVIDIA.
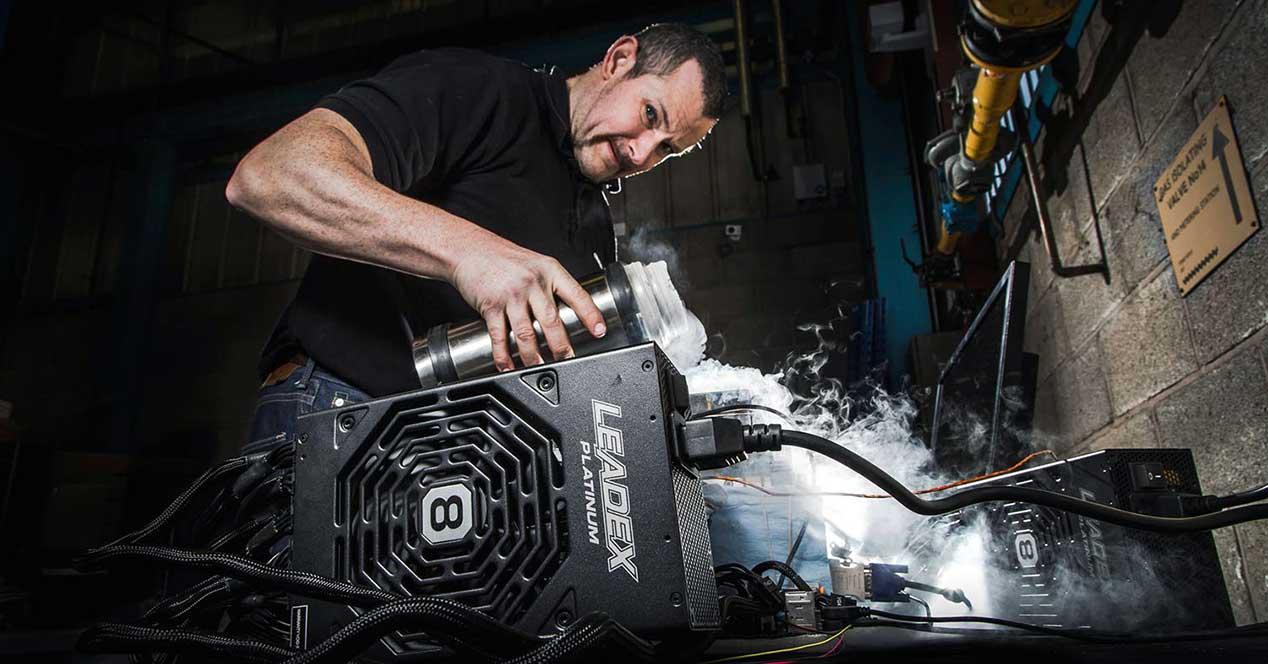
From the user’s point of view everything revolves around overclocking. An overclocker or any ordinary user who is going to overclock is always going to want the best chips for it. The overclock fever reaches the point where batches of processors are compared, online lists are made between users and it is concluded that in X factory, in week Y of batch Z, these CPUs are ” black-footed “.
Today there are websites that are dedicated to doing this and charge for it, so that they test each processor under overclock in the same conditions and ensure maximum speed, after which they set a higher price than the stores and with that they make deal. The user saves time and is trying or searching in exchange for an amount that is not usually very high, except in those buses that go beyond the norm of how good they are, the so-called Binning GOLD .