
One of the technical characteristics that we can see in power supplies is the 80 Plus certification, of which there are several variants that indicate their quality level, as well as their specifications. Since it is an important element in the purchase, we have decided to make a comparison between the different levels and what each one means.
The purchase of the power supply for your PC is very relevant, since you not only have to choose the one that gives you the necessary power to power your entire computer, but also that it has sufficient efficiency when transforming the energy electrical. The 80 PLUS certifications help us to know how well the PSU that we have installed in our desktop PC works.
What is the 80 PLUS certification?

The acronym 80 PLUS does not refer to a specific standard, but rather a certification that the different manufacturers of power supplies have agreed to comply with when manufacturing the different PSUs that they manufacture and that help the end user. to know both the specifications and the level of efficiency of the source when converting all the electrical energy to power the computer.
Let’s not forget that what a power supply does is convert the alternating current from the electrical outlet to direct current, but in this process a loss of energy occurs. The name of 80 PLUS comes from the fact that they are power supplies that have a minimum efficiency of 80% so the rest of the energy, 20%, that is not transformed, is converted into heat. This means that if an 80 PLUS certified power supply takes 1000 W of alternating current then, as a minimum and we emphasize this, it will give 800 W to the PC.
From what you have already deduced with the explanation, under the 80 PLUS brand the different PSU manufacturers refer to their power supplies with an efficiency of more than 80%.
History and evolution of the 80 Plus certification
In 2004 the 80 Plus certification was born, without any type of addition to the name in its most classic version of all, and offering the aforementioned 80% efficiency. This level of certification when new levels appeared was renamed 80 PLUS White when in 2008 the 80 PLUS Bronze, 80 PLUS Silver and 80 Plus Gold certifications were added. In 2009 the 80 Plus Platinum was added to finish with the 80 Plus Titanium in 2012.
Since then, no new levels have been created and manufacturers have fulfilled the certification of their power supplies.
PFC or power factor correction
One of the things to understand 80 PLUS certified power supplies is the potential factor, which is achieved by taking on the one hand the real power as delivered by the power supply to divide it by the apparent power, which would be obtained. by multiplying the volts by the amps.
Power supplies generally have a power factor of 0.7 or 0.75, but there are sources that have what is called a power factor correction that causes the figure to increase to 0.9. Well, 80 PLUS certified power supplies make use of PFC to achieve greater efficiency when converting alternating current into direct current.
It must be taken into account that a power supply is an analog electronic circuit and usually use a capacitor to operate with the voltage of continuous electricity. Said capacitor can undergo a phase change during the conversion from one type of current to another, which can lead to a decrease in the power factor. Therefore, the PFC is still an additional circuit that is responsible for correcting such losses.
The different levels of the 80 PLUS certification
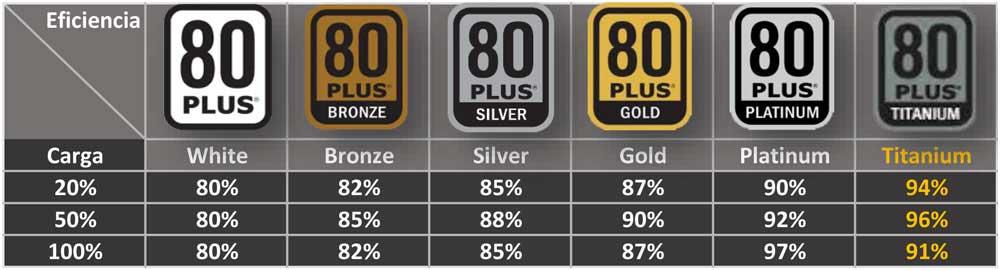
When a power supply is marked with one of the 80 PLUS certifications it means that it meets the following specifications:
- White: 80% efficient at 20% load, 85% at 0.9 PFC at 50% load, and 80% at 100%.
- Bronze: 82% efficient at 20% load, 85% at 0.9 PFC at 50% load, and 82% at 100%.
- Silver: 85% efficient at 20% load, 88% at 0.9 PFC at 50% load, and 87% at 100%.
- Gold : 87% efficient at 20% load, 90% at 0.9 PFC at 50% load, and 87% at 100%.
- Platinum : 90% efficient at 20% load, 90% at 0.95 PFC at 50% load, and 89% at 100%.
- Titanium: 90% efficient at 10% charge level, 92% at 0.95 PFC at 50% charge, and 90% at 100%.
At first glance the differences between the different certifications may seem very small, but the circuitry level of the power supply circuitry reaches higher and higher levels of complexity in order to gain a little efficiency. So the power supplies with the most advanced certifications and are consequently the most expensive.
The fact that a power supply is more efficient allows us to save on the electricity bill, since the electric company does not make us pay each month for the amount of energy we use, but rather the amount we obtain from the power outlets of our home or business, so choosing a good power supply with an advanced 80 PLUS certification becomes a money saver over time. Another advantage is the fact that sources with a higher level of efficiency make less noise, since by releasing less power in heat they make the fan turn on less times.
The shortcomings of this certification

The problem with the 80 PLUS certifications is none other than in order to comply with each one of them, low consumption levels are not taken into account. What do we mean by this? Well, while the load levels are low, such as that the PC is turned off or at rest, then the manufacturers do not have to maintain high levels of efficiency.
This means that if the necessary load level of the PC is low, we can find not only that the efficiency of the PSU does not follow what said level of the 80 PLUS certification says, but that it may also be below 80% . Of course, low-power devices use their own power supplies already designed to handle much lower power levels.