AMD FreeSync is AMD’s answer to NVIDIA‘s G-SYNC, we explain the reasons for the existence of this technology, what it is based on, what advantages it brings us and the requirements to be able to use it in our AMD Radeon.
For some time now we have seen how AMD talks from time to time about a technology called FreeSync. But what does it consist of? What is its usefulness? Can i use it with my screen?

What is the usefulness of AMD FreeSync?

To understand the need for technologies such as AMD’s FreeSync or NVIDIA’s G-SYNC, we have to note that there is a lack of coordination between what is the generation of the frame by the GPU and its display on the screen. What is the reason for this lack of coordination?
The screens change the image that they show a certain number of times per second, this is called the refresh rate, well, this marks when the front buffer is replaced with the rear one and therefore there is an image change . What is the problem? Well, there are frames in a game that take a different amount of time to render with respect to the screen refresh, which causes a series of associated image problems that are not pleasant to the eye.
This is due to the fact that the information sent to the screen does not correspond to the current frame in that part of it, which causes annoying image artifacts such as Tearing.

To solve this, what is done is that the screen refresh is no longer controlled by the monitor, letting it be controlled by the GPU itself and achieving direct coordination between the screen and the generation of the image buffer, thus avoiding artifacts produced from incoordination.
How are images sent to the screen?
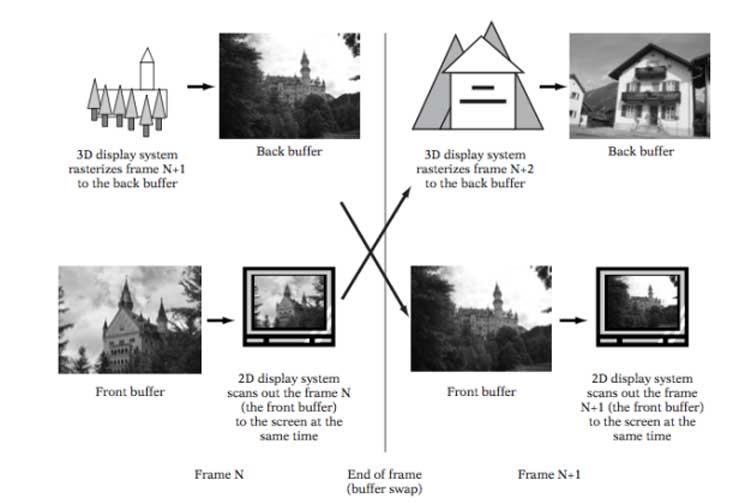
In simple terms, when a GPU is generating a frame, what it does is draw it in an area of memory that we call the image buffer, which is divided into two different memory buffers:
- The first of them houses the frame previously generated by the GPU, which we call Front Buffer or front buffer, already finished by the GPU that remains in memory for the display driver to read and send it to the HDMI or DisplayPort interface.
- In the second one, what we have is the frame that the GPU is drawing, which is currently what we call Back Buffer or rear buffer, the screen controller does not interact with it.
When the monitor has generated the image from the front buffer, then its values are completely cleared and a swap is made, what was previously the front buffer becomes the rear buffer and vice versa.
But what really is AMD FreeSync?
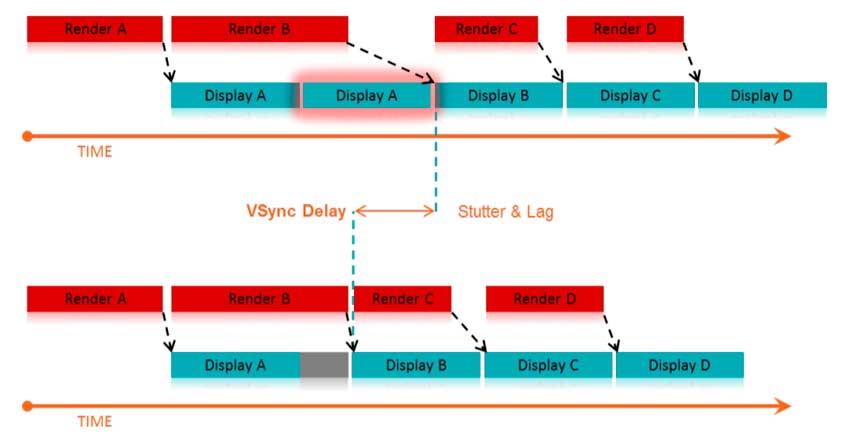
The FreeSync is nothing more than the commercial name of the adaptation to the AMD GPUs of the VESADISPLAYPORT ADAPTIVE-SYNC. It is the VESA standards that mark how an image has to be sent to a screen in each and every one of the monitors that come out on the market.
To control when you start sending an image to the screen, what you do is control the start and end of the vertical synchronization (V-SYNC) of that frame. The idea with the DISPLAYPORT ADAPTIVE-SYNC, or FreeSync if we talk about AMD, is none other than to give the GPU full control of when the vertical synchronization begins.
The advantage of AMD to take the VESA standard is very simple, all the screens compatible with the VESA Adaptative Sync are compatible and, unlike the G-SYNC, we can also use it if our monitor supports HDMI 2.0 onwards.