In recent years we are seeing all kinds of uses for artificial intelligence , from multimedia systems that improve the resolution of images or cancel ambient noise in video conferences, through facial recognition system and even recommendation engines when we are buying online or looking for what movie to watch at night from your Smart TV. But what is the process by which AI learns to create a model to solve those problems? This is called Training and Inference and we are going to explain it to you.
What can we define as Artificial Intelligence ? For some people, it is that computers think or have their own consciousness, but in the present case it has to do with the treatment of data sets, that is, with the information that is given to the system. Today it is everywhere and it can be said that they are automated systems that generate responses based on the input data they receive from a model built from a training or learning period.

But in order to give these answers, the AI systems have to be obviously trained, in other words: they have to be educated and therefore taught. We are going to give you a small introduction on how artificial intelligence systems “learn”, what is behind this technology, which seems advanced enough to make it seem like magic at many times.
The explanation that we are going to give you about what training and inference are is completely generic and global, so it has no specific relationship with any particular hardware.
Training: Educating AI
The construction of an inference model to solve a specific problem is known as training, artificial intelligence is mainly used to solve three different types of tasks: information classification tasks, pattern search tasks and automatic driving tasks. for which three different ways of learning are used:
- Supervised learning: artificial intelligence is given a set of input data and the task is for the AI to be able to label the input data correctly. Initially the AI is given the data set with the correct labels, and this is the training data. The generated inference model is then monitored with a test data set, which can be answered true or false by the AI.
- Unsupervised learning: it is used when we want the AI not to classify the data and therefore labels associated with the learning data set are not used. What is sought with this learning method is to detect patterns, and what the AI does in this case is to search and group the data according to its similarity. It is the type of learning most used in the processing of multimedia data.
- Reinforced learning: in the specific case of this type of learning, what we do is not tell the AI, for example, what a cat is or learn to distinguish a cat, but rather what we are doing in teaching it some rules of the game. The closest simile in real life is when we are learning to drive a car and we have a good driving school teacher, and it is precisely the AI that is used to train cars with automatic driving. In this model, the training data set is provided in real time and the conclusions drawn by the AI are evaluated by a supervisory agent who feeds it. Said agent can be a human, a complex database, and even another AI.
Another type of artificial intelligences are generative ones, which are based on generating data in a random way; These data are actually nothing more than noise and require an external element to discard and / or classify them. In this case, the generative AI does not know what it is looking for from the outset and only ends up learning it from a second AI, which can perform the evaluation by classification or by searching for patterns.

Depending on the type of problem for which you want to create a model-solution, the training process may require more or less power and time. For example, there are cases where it is necessary to use data centers made up of dozens or even hundreds of computers while other problems can be solved by a low-power home PC.
Inference: AI puts what it has learned into practice in training
Once the AI has learned the model, it creates an inference model that it will use to solve and / or classify the problem. For this we use a type of hardware in which each unit is connected to others in a network and the data is passed in turns; We call this hardware neural or neural networks and they are units whose operation is inspired by the way in which the brain processes visual information through the eyes. This structure is what allows artificial intelligence processors to learn complex structures without requiring massive amounts of data.
Neural networks
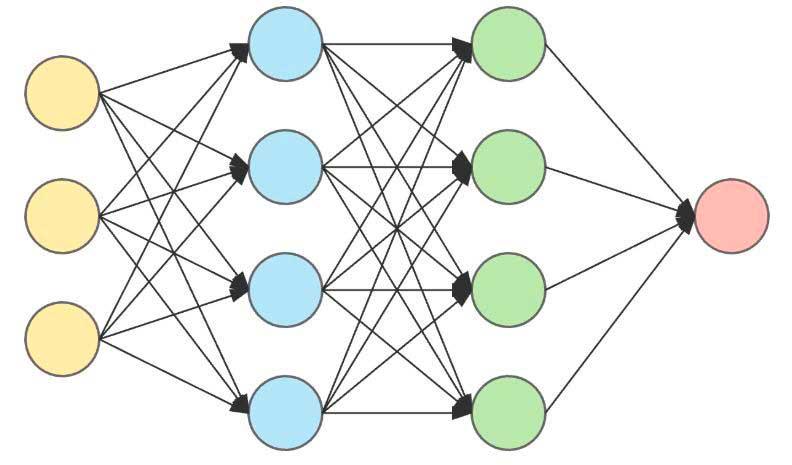
A neural network, regardless of whether it is artificial or natural, consists of a large number of simple units (neurons) and information is transmitted between them. In the computer world, a neuron can be a simple ALU or a complete processor. At the hardware level, all the units are interconnected, but when an inference model is generated, what it does is deactivate the connections that are not used.
In this type of network, the cable or data path used to provide the input data are called dendrites and the cables that communicate between neurons are called axons . For more information, we recommend reading this website entitled ” Dedicated processors for AI, what are they and how do they work? ”