Artificial photosynthesis with solar panels seeks to overcome the limitations of biological photosynthesis, including low efficiency of solar energy capture and poor carbon dioxide reduction, and could provide an alternative route for food production.
Food production is ultimately limited by the energy conversion efficiency of photosynthesis, so a new study uses solar panels to provide a first solution to this problem.

Goodbye to photosynthesis
The process of photosynthesis is key in our life . Plants use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to grow, and then humans eat those plants directly or after they’ve become part of an animal, fungus, or whatever else we like to eat. All the energy that ends up in our bodies starts with sunlight captured by plants through photosynthesis.

Solar panels
However, according to scientific calculations, plants are quite poor at converting sunlight to growth , converting sunlight and carbon dioxide into biomass with only 1% efficiency .
Robert Jinkerson, a professor at the University of California, Riverside, noted this low efficiency of photosynthesis and tried to engineer it out. If we can squeeze more energy out of every square inch of sunlight, then we can reduce the total amount of land we need to grow food.
“Our ultimate goal is to transform the way we think about how to produce crops and agriculture. If we can be more efficient with the area needed to produce the food needed for humanity, then we can convert agricultural land to natural land.”
Electrolysis: solar panels to feed crops
One way to do this could be to grow crops in the dark using electricity provided by solar panels, which are many times more efficient than plants at converting sunlight into energy .
Through this process called electrolysis, solar panels are used to power a machine that converts carbon dioxide, electricity and water into acetate , a molecule that can be diluted in water and used to feed plants. They then fed this mixture to algae, yeast, fungi, and a selection of commonly grown plants.
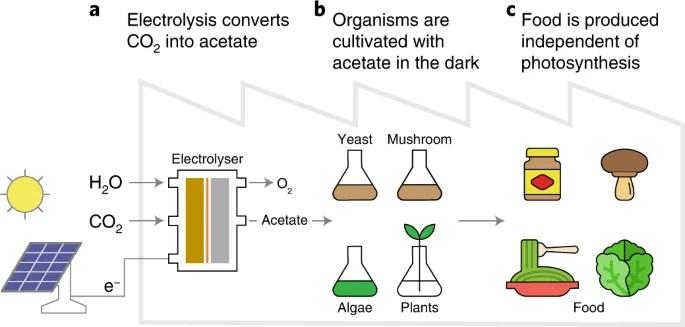
Electrolysis Scheme
What was most surprising was that the crop plants also consumed the acetate and grew, although they grew in complete darkness, although there was a catch: giving the plants enough acetate for them to grow ended up being toxic to them, so although the plants they can technically grow on acetate, they don’t exactly thrive on it.
Jinkerson believes that if researchers can find a way to grow plants that actually thrive on acetate, it could be a much more energy-efficient way for vertical farms to divert electricity to acetate production rather than lighting.
Growing plants in the dark can be useful in places where power and space are scarce, such as on a space flight to Mars, but it is not suitable for most crops on Earth. Jinkerson’s project was one of the winners of the first phase of NASA’s Deep Space Food Challenge . For the next phase, the team will build a prototype food-growing device to share with the space agency, in what may be a step forward for our future life on another planet.