Surely you have heard, read and even spoken many times about the term SATA , especially related to hard drives and other storage devices . But do you really know what SATA means? In this article we are going to tell you what this term means , what it is used for and what its characteristics are.
Quite possibly you use the word SATA in your day to day to talk about storage devices, and surely you know that there are different types (SATA2, SATA3 …) and with different types of connectors (eSATA, mSATA …) but, what is this term ?

The meaning of SATA, what is it and what is it used for?
SATA comes from the English term Serial Advanced Technology Attachment, and is a bus interface on computers for data transfer between the motherboard and some of the devices that make up a PC, such as the hard drive or the optical disc drive and writer. . SATA replaces the previous interface, PATA (Parallel-ATA), also known as IDE, providing better speed and stability .

This interface became standard on PC motherboards since the group responsible for its development, the SATA-IO, presented its design. It provides higher speeds, better utilization when multiple simultaneous units are connected, longer data transmission cable length and the ability to connect devices instantly (hot-swap) without having to turn off the equipment to do so.
Speeds
When referring to data transmission speeds, units of measurement are sometimes confused because SATA 1.5 Gbps, 3 Gbps and 6 Gbps are used to refer to SATA, SATA2 and SATA3 standards, but the reality is that the speed actual transfer is different. It should be noted, by the way, that the units that support speeds of 3 Gbps are not compatible with the interface at 1.5 Gbps, but those of 6 are 3.
| SATA | SATA 2 | SATA 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency | 1500 MHz | 3000 MHz | 6000 MHz |
| Bits / clock | one | one | one |
| Coding 8b10b | 80% | 80% | 80% |
| bits / byte | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| Real speed | 150 MB / s | 300 MB / s | 600 MB / s |
Topology
This standard uses a “point to point” architecture, which means that the connection between the device and the port is direct; each device is connected to a controller, not as it happened in the old PATA, whose interfaces were segmented into “Master” and “Slave”.
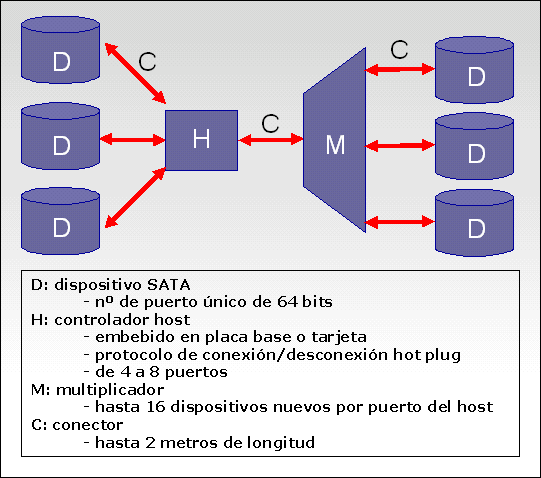
Connectors and ports
Connectors and cables are the biggest difference between SATA and ATA drives, since the former use the same connector in equipment or server (3.5-inch) and portable (2.5-inch) storage units, as well as for SSDs, DVD drives etc.
The standard defines the data connection cable with seven conductors (3 ground and four for data in two pairs of differential type), making use of an 8mm wide “wafer” type connector.

Data cables support lengths of up to one meter, and unlike PATA cables, each cable and each connector can only service a single unit.
As for the power connectors , which also appear in the image above, a different color code is used than the MOLEX used by the PATA. They are much wider since they have 15 pins instead of 4, and they have a notch so that we can only connect them one way.