It is very difficult to see a laptop on the market that equips the Ryzen 7 6800H inside. The most conspiranoid will think of an agreement between Intel and the different suppliers to maintain their dominance in the market for high-performance laptops with an iron fist. That is why we are going to show you why Intel continues to lead in gaming laptops and why the 6000H series is not the best of AMD.
The company led by Lisa Su has been trying to get a foothold in the laptop market for some time, a world that, unlike tower units where users usually choose which components to buy, are the manufacturers who choose. Despite all the noise at this year’s CES about the Ryzen 6000, the number of models on the market with a Ryzen 6000H can be counted on the fingers of both less and we would even be long. The cause? Manufacturers do not want theirs to be revealed in comparisons made between models due to the use of a lower-performance processor.
AMD Ryzen 7 6800H versus Intel Core i7-12700H
What is surprising about the data obtained is the fact that its source is a website that is reputed to be very close to AMD, which gives much more value to the information that they have presented in their tests. For this they have used the Cinebench R23 benchmark in their tests for a single thread as well as multithreading. In passing, we will remember that the configuration of the Intel processor is 6 performance cores and 8 efficiency cores with a total of 20 execution threads, while the AMD processor has 8 performance cores symmetrical with each other with 16 execution threads .
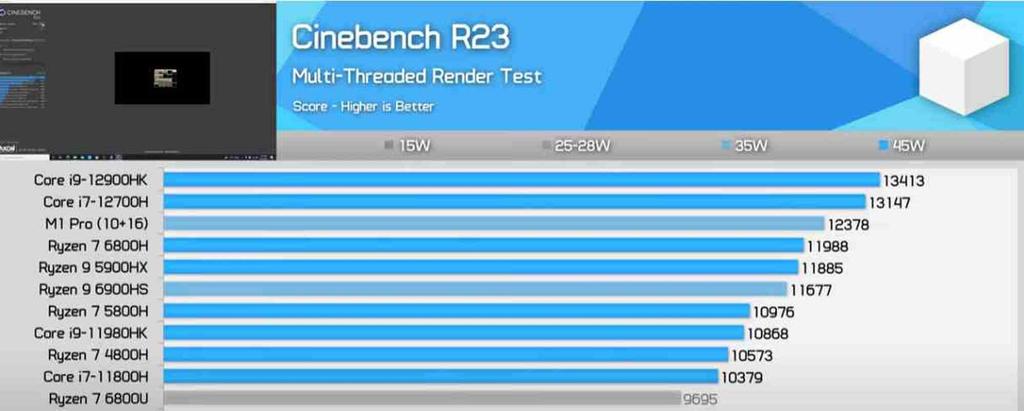
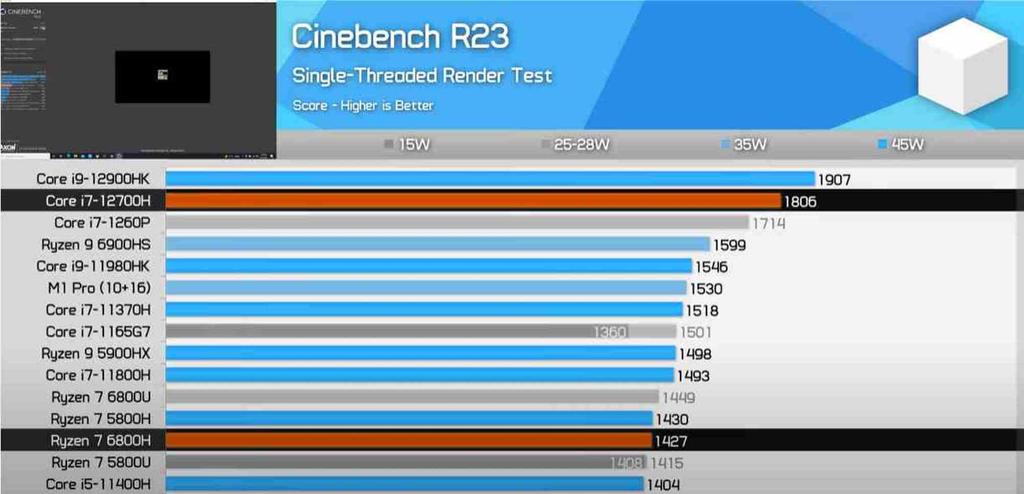
In multithread performance we can see that the i7-12700H obtains 13,147 points in the test compared to 11,988 points for the 6800H , something that should not surprise us since despite having 2 P-Cores less, they are 6 E-Cores additional that add to the total of the equation and manage to give an advantage to the Intel processor. Instead, it is in the single thread tests that we see Zen 3 compared to the Golden Cove core where we see a result of 1427 points for the former and 1806 points for the latter. Which translates to an additional 25% performance difference in favor of the Core 12 .
What about the AMD Ryzen 7 6800H?
If we take a close look at the specs of the different Ryzen 6000 series processors and compare the 6800U to the 6800H and be insightful, then we will realize that it is the same chip but at different clock rates.
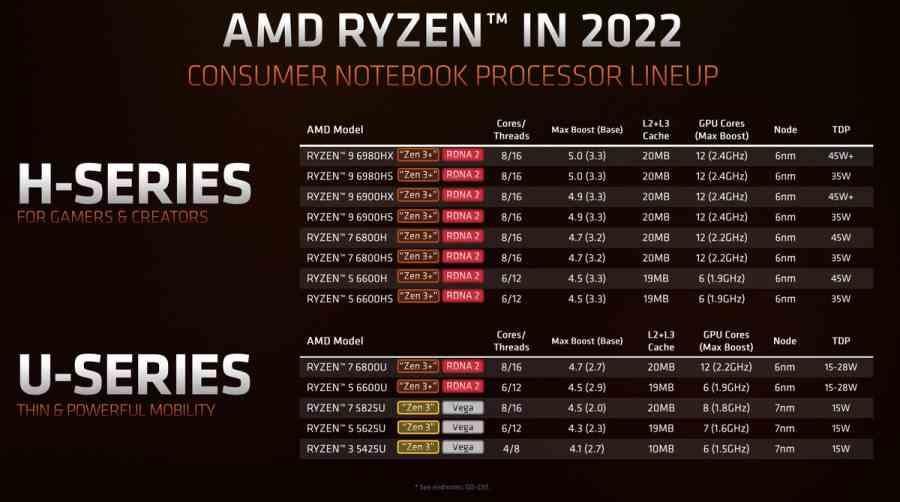
The only difference is that the 6800U starts from a base clock speed of 2.7 GHz, while the 6800H starts at 3.2 GHz. A jump of only 0.5 GHz that takes it to increase its TDP from 15 W to 45 W So the performance per watt is in the ultralight notebook model and not in the performance model. Well, this point is what the people at Hardware Unboxed have based on to compare the 6800H against Intel’s i7-12700H based on the Alder Lake architecture.
Conclusions and explanation of the phenomenon
One of the biggest challenges when designing a processor architecture has to do with power consumption. Things get complicated when you have to design one that works from an ultralight laptop to a server. Since we are talking about 15 W per processor at tens of times the power. This is what has happened to AMD for years when it comes to scaling down its processors. The consequences? The need to develop a variant of its Zen 3 architecture which they named Zen 3+ . Higher performing? No, but optimized in its design for use in laptops thanks to the redesign of everything we call the Power Delivery Network . Which is the equivalent in a chip to the electrical installation of a house.
One thing is the architecture where we define the parts and the way in which they are organized and interact with each other and another thing is the part of the design responsible for making a chip have a specific performance per watt at a given consumption. So it is important to know that since frequency goes up with voltage and TDP is calculated as the equivalent of capacitance times frequency and voltage squared, then it is clear that a design does not have performance per watt. constant throughout all your consumption.
To conclude, there is something in which the AMD chip wins The great advantage of the Ryzen 6000 is its integrated GPU with RDNA 2 architecture, but in high-performance computers, where these are usually accompanied by a dedicated graphics card for gaming or creation of content, that advantage is dissipated. Which gives the AMD 6800U more value.