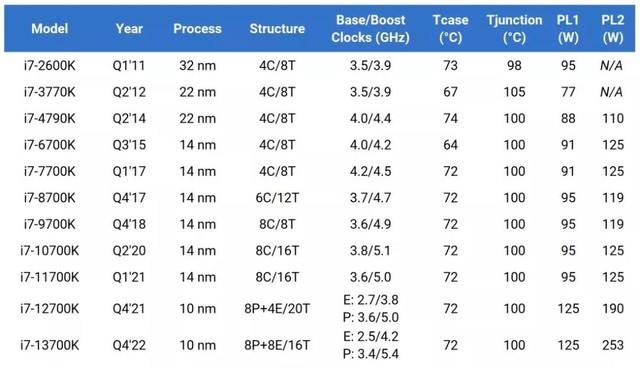
During the hot summer months, you may have experienced sudden drops in FPS or computer freezes. The root of these issues is likely related to your processor’s temperature, which can result from inadequate maintenance. More specifically, the culprit could be the “Tjunction” parameter of your CPU, which is crucial to understand.
Firstly, it’s important to know that processors have optimal temperature ranges for operation. When playing, the ideal temperature range is between 50-70 ºC. However, there are certain temperatures that are considered “limits” and programmed to protect both the processor and the system.

If the temperature exceeds the limit set by the manufacturer, your system will automatically slow down or even shut down to prevent damage to the processor. It is essential to take care of your computer’s maintenance and ensure proper cooling to prevent your processor from overheating. This includes cleaning the fans and heatsinks regularly and ensuring proper ventilation.
In summary, understanding the “Tjunction” parameter of your CPU is crucial to maintaining optimal performance and preventing damage. Take the necessary steps to maintain your computer’s cooling system, and monitor the temperature regularly to ensure it stays within the optimal range.
Decrypting the Tjunction parameter of the processor
All processors have an internal “thermometer” in the form of a small element integrated into the encapsulation, which is a resistance that varies according to the temperature. This element is crucial to protect the CPU and the system in case it reaches certain temperatures.
Processors have optimal operating temperature ranges, usually between 50-70 ºC during gameplay. However, there are certain temperatures programmed as “limit” to protect the processor and the system. This limiting temperature of any processor is called “Tjunction”. It is worth noting that this parameter does not indicate the maximum temperature that silicon can withstand before suffering damage, as is commonly believed. Instead, this parameter serves to protect the welds of the DIE with the PCB of the processor.
If the processor temperature rises above the Tjunction parameter, the system will start to limit the performance of the processor, causing sudden drops in FPS or computer freezes. These problems are especially noticeable during summer when the temperature is higher. To prevent these issues, it is important to maintain the temperature of the processor and avoid letting it get too hot. Proper cooling, such as using fans or liquid cooling systems, can help maintain optimal operating temperatures and prevent damage to the processor.
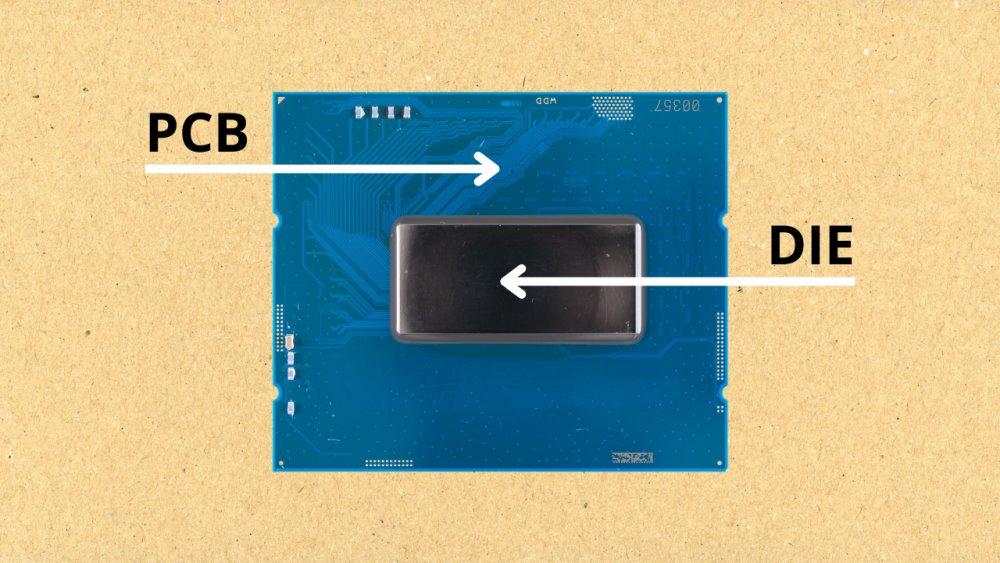
It might seem insignificant, but understanding the Tjunction parameter is crucial in protecting your processor from overheating. All processors have an integrated thermometer – a small resistance element that varies according to temperature. This element is designed to protect the CPU in case it reaches certain temperatures. The limiting temperature of any processor is called Tjunction, which protects the solder connections between the DIE and the PCB of the processor.
These solder connections are made of tin, a delicate material that becomes “liquid” after reaching 200ºC. However, processors, graphics cards, and even RAM memory are often damaged by these solder connections. This is why the Tjunction parameter of the processor is set to 100 ºC – a significant difference from the melting point of tin.
This difference is because other effects, such as expansion with heat and contraction of the material, occur before the melting point of tin. These effects can generate microcracks that, over time, can lead to the breakdown or degradation of the solder connections, which occurs at temperatures above 100 ºC. In other words, Tjunction serves as a protection mechanism for the processor’s weakest part. Understanding this concept can help prevent sudden drops in FPS or computer freezes, especially during summer, due to overheating caused by lack of maintenance.
How they protect themselves from excessive temperature
It’s not uncommon to experience sudden FPS drops or computer freezes, especially during the summer months. These issues are likely due to the processor overheating from a lack of maintenance. To prevent this from happening, it’s important to understand the “Tjunction” parameter of the CPU.
All processors have an internal “thermometer” integrated into their encapsulation, which is a resistance that varies according to the temperature. The limiting temperature of any processor is referred to as Tjunction. Contrary to popular belief, this parameter doesn’t indicate the maximum temperature silicon can withstand before suffering damage. Rather, it protects the welds of the DIE with the PCB of the processor.
It’s important to note that processors, graphics cards, and even RAM memory often break due to these welds. The solders are made of tin, a delicate material that becomes “liquid” after 200 ºC. However, the Tjunction of the processor is set to 100 ºC because the expansion and contraction of this material due to heat can cause microcracks that lead to the degradation of the material at temperatures above 100 ºC. In other words, Tjunction is a protection mechanism of the processor from its weakest part.
While the processor has an additional protection that makes it never reach Tjunction, there is a limitation of 10% of the Tjunction that causes the processor to protect itself. When it exceeds 90 ºC, the processor reduces the frequencies to reduce the temperature, causing noticeable drops in performance, such as sudden FPS drops, game freezes, and even crashes.
To prevent these thermal problems, it’s essential to periodically clean the desktop computer and change the thermal paste every year. By doing so, we can protect our computer from damage and ensure it performs optimally. Remember that Tjunction doesn’t protect the silicon so much as it does the solders that are present in all processors.