Real-time resolution autoscaling technologies are continually improving. Not only because they are programs that run on the graphics card, but also because there is high competition between AMD, NVIDIA and Intel. Well, the last one has decided to show again the benefits of its algorithm, giving us new details of XeSS, stating that it is comparable with DLSS 2.0 and FSR 2.0. Let’s see the details.
If we are to compare the strategy of the three great graphics card designers, we will see that there is a subject on which Intel and NVIDIA bet very heavily: artificial intelligence. The reason? The inclusion of units of the systolic array type for the calculation of matrices given their massive use in deep learning algorithms. So NVIDIA bets on its Tensor Cores to accelerate its DLSS and Intel on its XMX to do the same with its XeSS. Reality? They are the same type of unit intended for similar tasks. The difference? It lies in the way the algorithm is programmed.
New details of Intel XeSS, the counterpart of DLSS for ARC
Yes, with the near launch of the most powerful ARC Alchemist and, therefore, suitable for gaming in terms of performance, Intel has shown new details about its XeSS algorithm and has talked about the different existing quality levels, which is analogous to what we have already seen in NVIDIA and AMD solutions. The idea of these algorithms is to generate the image at a lower resolution than the one that will be emitted on our screen, for this a process of reconstruction of the final image is carried out to generate the one that had originally been generated with more pixels.
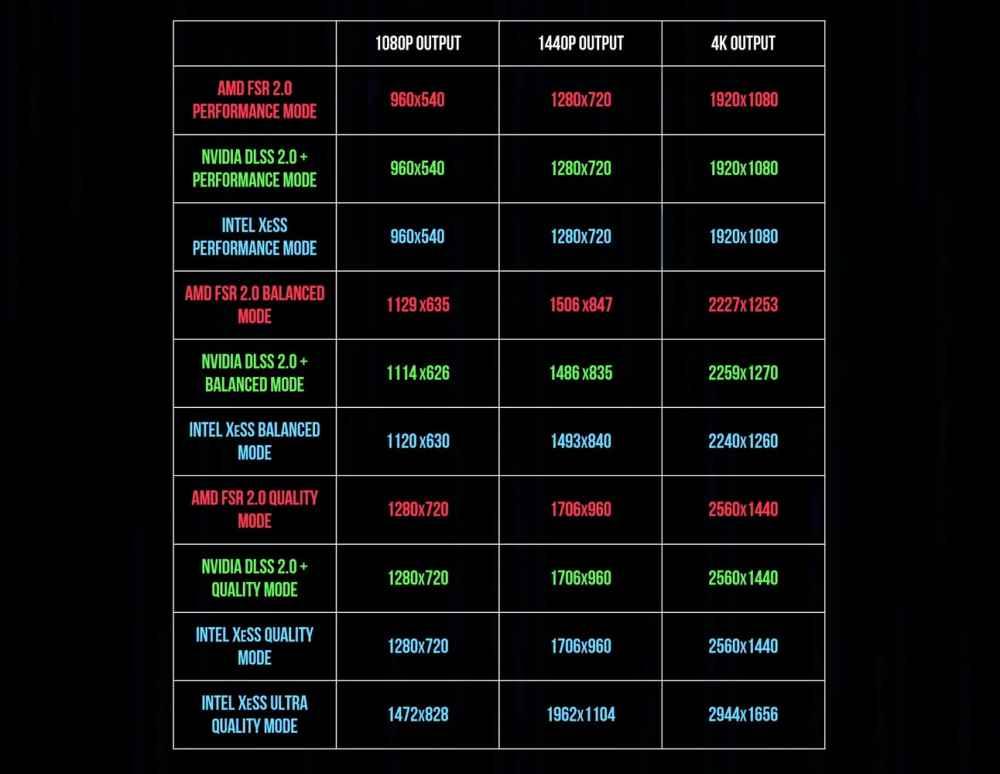
The trick is that with this you get an image at the new resolution in less time than using it as a base. That is, an image is generated at 1080p to scale it to 4K. However, this has a problem and it depends on the level of information of the source. The lower the resolution of the input image, the less accurate the output image will be. Hence, there are different quality levels of these algorithms that require that the input image generated by the GPU in real time have a certain resolution.
As you can see in the table, the resolution requirements for the different quality levels of Intel XeSS differ from those of NVIDIA DLSS and AMD FSR. In addition to that four modes are confirmed: performance, balanced, high quality and ultra quality. Which go respectively from lower to higher image quality.
How many frames do we gain using XeSS in games?
In another order of things, the people of Digital Foundry have shown in a comparison the performance that is achieved by activating the XeSS in its different modes to achieve a higher frame rate. It has been done using the Shadow of the Tomb Raider game and at both 1080p and 4K resolutions, achieving results of up to an additional 88% in frame rate. Which once again demonstrates the potential of these solutions in modest equipment.


So in conclusion, the Intel algorithm is competitive against its rivals from NVIDIA and AMD. In any case, and as a final note, at the moment we have not seen anything about the XeSS D4P , designed for old graphics cards and other brands. Although it makes sense, at the moment the goal is to introduce the ARC Alchemist to the market with all the artillery possible.