Have you ever wondered how a processor is made ? They are the most complicated and complete devices in the world, and the difficulty to improve them is increasing. Now Intel has published a post explaining how they manufacture their processors in a way that we can easily understand.
Really, processors are not limited to just PCs or servers, but actually almost all devices employ processors of some kind – from your alarm clock to your smartphone. However, and as the person who has published the video is Intel, in this case we will explain how it is manufactured, or what a brand processor consists of.

In a space not much larger than a fingernail, a processor houses billions of microscopic “switches” inside it called transistors , which are what run a processor.
Once we know that, we will look at the process of manufacturing the processors, from their design until they arrive in our homes.
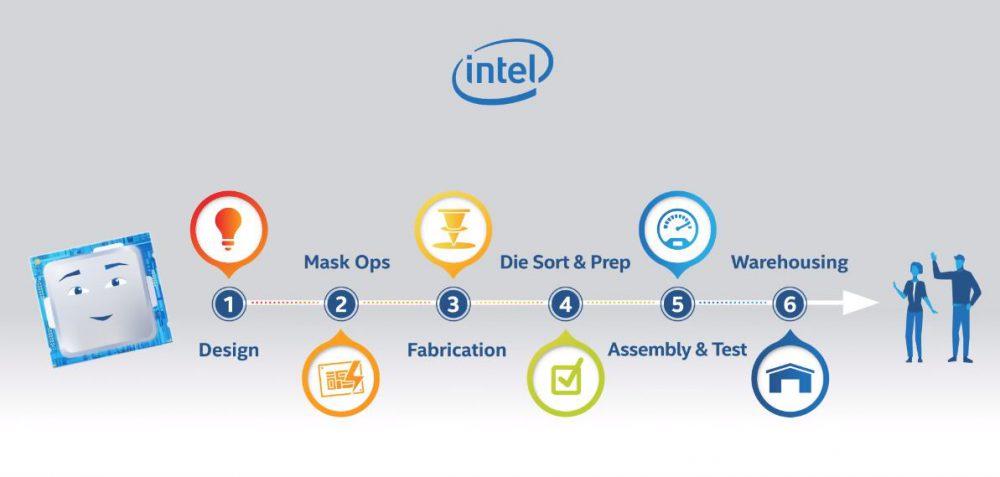
The design of the processors
Before becoming the “square” that we receive in our house when we buy a processor, it all starts with a simple idea in the head of the company’s architects. These architects work together with engineers and designers to create initial sketches of how the device should work. These sketches, when they all agree, become the final blueprints , filled with transistors, circuits, and layers.
These layers are important, and a processor can have about 30 of them. Some layers contain the transistors, others the interconnections between the different layers in specific configurations to maximize their efficiency.

Transistors, like “switches”, can be turned on and off to represent the ones and zeros of the binary system used in computing up to 5 billion times per second.
Creation of the template and mold
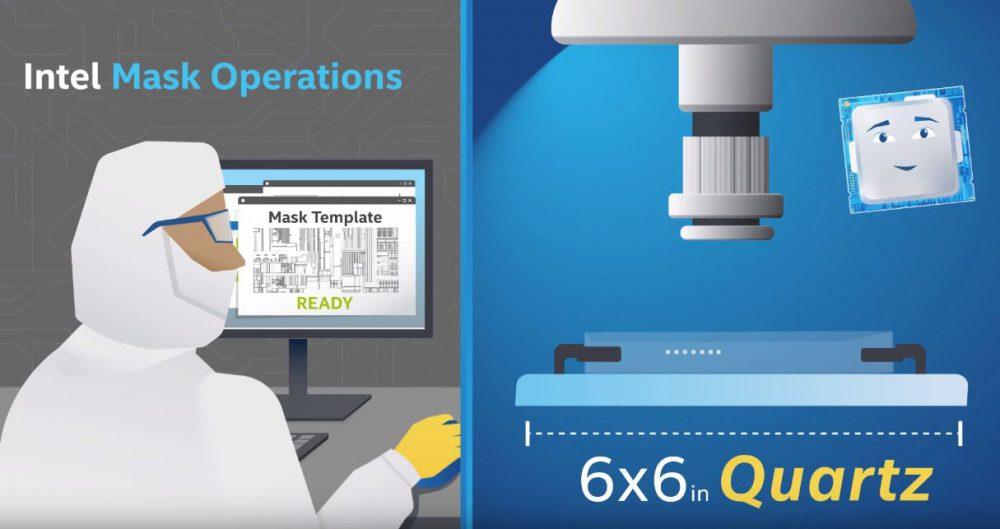
Once designers, engineers and architects are happy with the design that they have shown in the plan, this design is sent to the “Mask Ops”, engineers who are responsible for translating the design into a template that can then be used to manufacture the processor.
To do this, an electron pulse machine (Electron Bean Machine) replicates this design in 6 × 6-inch pieces of quartz , 1/4 inch thick. These pieces are called masks (Mask), and are the ones that are later used to capture the internal circuitry of the processor in a silicon wafer . A kind of mold, and it takes more than 50 Mask to make all the layers of the processor.
The manufacturing process
Once all the masks necessary to make a processor have been created, it goes to the manufacturing phase and these Masks are shipped to factories, known as Fabs. This is where these molds will be used to capture the circuits in the wafers, which you have surely seen many times before. Obviously, these wafers do not exist in that state, and before they have to go through chemical processes to convert the sand (silicon) into the wafers that we know.
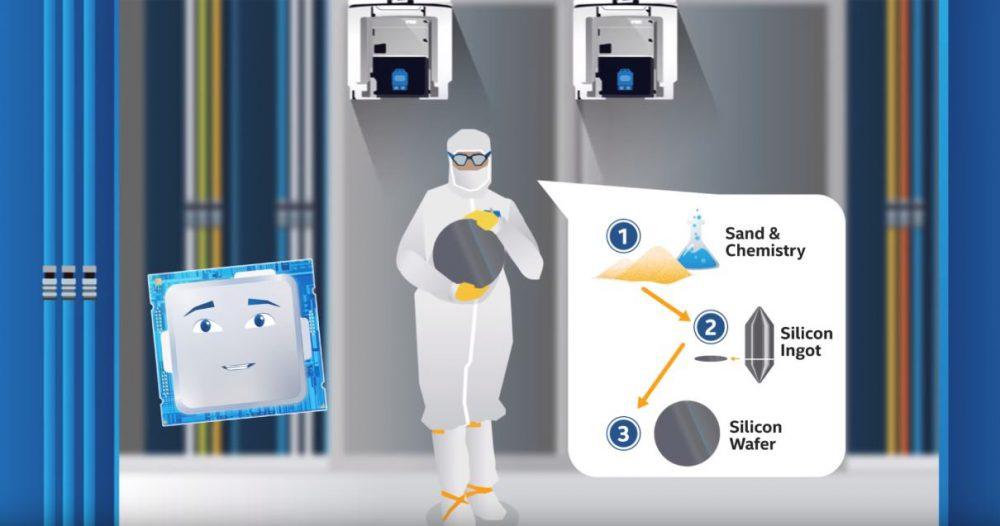
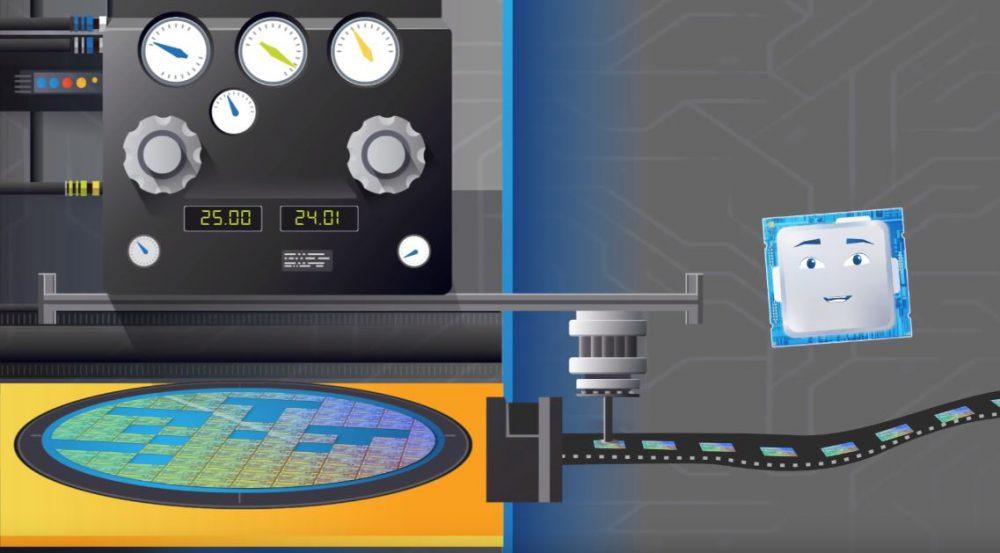
To “print” the masks on the wafers, a process called photolithography is used, through which an electron gun reflects the light on these masks, which passing through different lenses to reduce the process to the necessary size, are primed in the wafers.

This must be done with all the masks to create the layers of each chip. Thus, hundreds and even thousands of small chips can enter a single wafer. And, once done, we move on to the next step in the process of how to make a processor.
The preparation process
Once we have the wafers, we move on to the preparation and sorting step. Basically, a wafer contains hundreds or thousands of chips, and you have to cut them precisely to be able to separate all these chips from each other so that we can then use them in the processors. For this, extremely precise laser cutting machines are used.
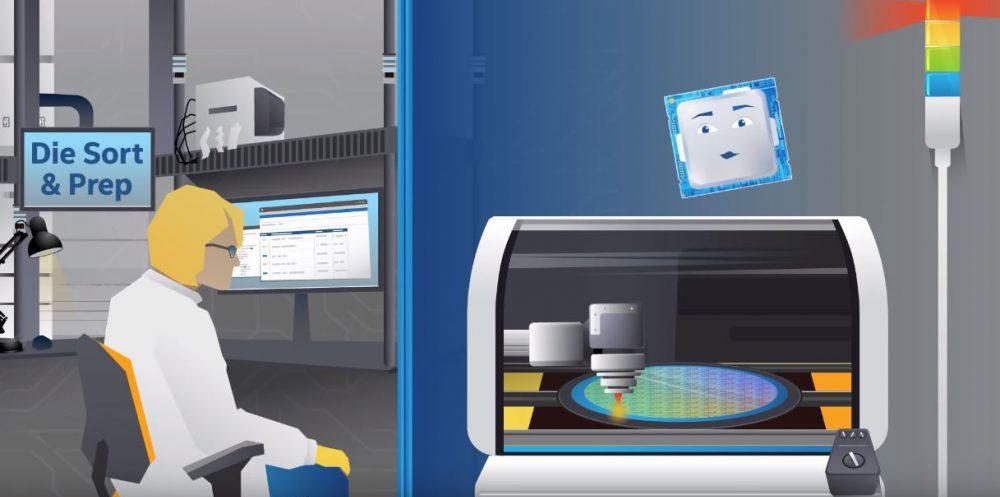

The result of this process is the die that we all know, which is the brain of processors. Once the chips are cut, another machine transports them to the next phase of the preparation chain.

In this next phase, the chips are put on a kind of rolled tape so that they can travel by plane, since they have to be sent to other Intel Fabs: those for assembly and testing.
Assembly and testing
In this phase, engineers test all chips individually and rule out chips that do not function properly or those that do not meet manufacturer quality standards. If they pass the test, the chips are mounted on a substrate and the heat sink (IHS) is placed on top of them , creating what we all know as a processor. This process is called assembly.

This outer packaging protects the chip from almost all damage, including shock, splash or heat. This substrate has in its lower area all the necessary contacts for the processor to work in conjunction with the motherboard where we install it, of course.

Once the assembly process is finished, the processor goes to the last step before it reaches us, the stored one.
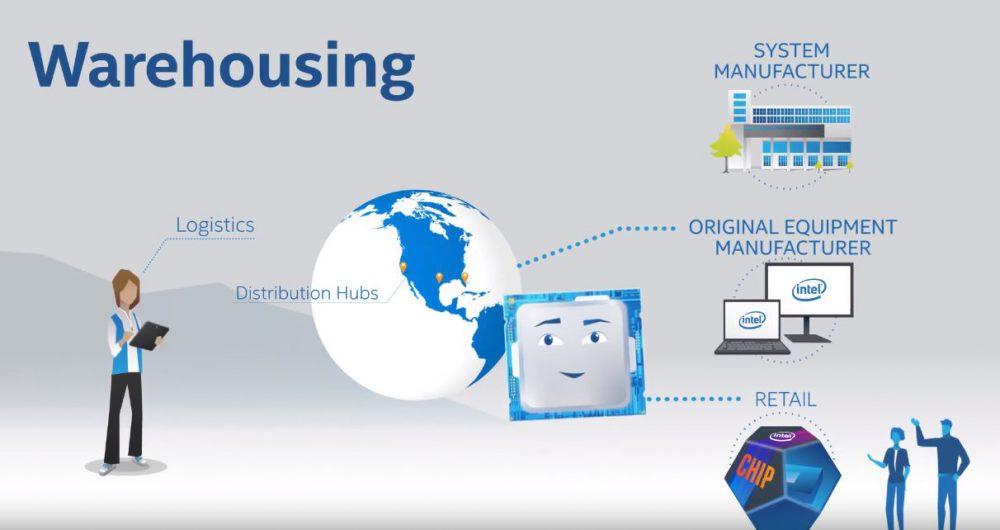
Inventory and warehouse
In this last step, the processors are put in their boxes, along with the heatsinks, instruction manual and more, and they are all packaged together. This is the product that we will buy in the end.

From here, Intel sends its processors to OEM manufacturers, distributors and all the sales network that it has around the world, who will either sell the PCs with an already installed processor, or they will serve the material to the stores that is where we we can buy a processor.
You have already seen it. From the time the processor is designed until it reaches our homes, it goes through a complex process that takes place around almost everyone, and involving hundreds of people.