Every day, millions and millions of people turn on their computers at work or at home to work, surf the Internet or perform all kinds of tasks. In this case, most users only worry about whether the computer is going faster or slower, if they run out of disk space, they can buy a higher quality monitor or expand the RAM so that everything runs smoother. However, there is a key element for the operation of our team, and that is the operating system . Now, what exactly is an operating system, what is it for and what types are there.
Specifically, without an operating system, the vast majority of components of a computer do not provide us anything, since it is in charge of making the equipment work and that any software can make use of the hardware necessary for its operation. For this reason, when buying a computer, we must always check whether it includes the system or it must be purchased separately for its later installation, since in this way, the equipment will not even be able to turn on until it has a system.

A little history…
Although we have just said that the operating system is necessary to be able to start the computer and run other programs, the truth is that on the first computers, this was not the case. Originally, computers did not have an operating system, therefore, each program that was run on the computer had to include all the necessary code to be able to run individually, connect to hardware, etc.
This was a big problem when developing any application or program, hence the need to develop system software that would facilitate the execution of programs, giving rise to the first operating systems.
Although there was some attempt in the 1950s , it was really in 1960 when IBM got down to business and the first version of the Unix operating system was born. A system programmed in C language and that little by little was adapting and gaining wide acceptance.

Later, it was Microsoft who set about developing a system at the request of IBM itself to install it on its range of personal computers. This union of two great computing companies led to the emergence of MS-DOS in the early 1980s, a system developed by Microsoft for IBM computers but which they continued to develop in their own way since Redmond. In the 90s the system was when operating systems that offered a graphical user interface began to emerge and where the first generations of Microsoft Windows began. Little by little we have seen how Windows has evolved until today, with Windows 10 being the latest version of the system.
For its part, in the mid-80s Apple also developed its own system on the technology developed by NeXT, until those from Cupertino bought the company in the late 90s, which was when the version of macOS for servers was released. Later, new versions were released for the desktop version until reaching the current version.
The history of Linux is written from the 1990s , after the Free Software Foundation was formed in the previous years and the GNU General Public License was developed. The large amount of software stored at the beginning of the 90’s made it possible to develop a complete operating system from the hand of Linus Torvalds, who was the one who started the project and who made Linux come later.
Much more modern are the operating systems for mobile devices, iOS, Android or Windows Phone. In the case of Android, it is a mobile operating system developed by Google and based on Linux Kernel and other open source software and designed for touchscreen mobile devices such as mobiles and tablets. It was launched in 2007 in conjunction with the founding of the Open Handset Alliance.
That was also when the initial launch of iOS, Apple’s mobile operating system and originally developed for the iPhone (iPhone OS), also took place, although we have later seen how it has been used in other brand devices such as the iPad or iPod touch.
What is an operating system and what is it for?
That said, we could say that an operating system, OS or also OS ( Operating System ), is the software in charge of managing hardware resources and providing services to the rest of programs that run on it, being the system that always runs on privileged mode with respect to the rest.
It is an intermediary between the user and the hardware . That is, every time a program is run on the computer, the system is the one that allows it to open, access the hardware and peripheral resources that it needs for its correct operation, and assign the amount of memory that it will use depending on its needs. and the number of programs we have open on the computer.
In addition, it is responsible for providing services to facilitate the efficient execution and management of resources of any application that runs on the system.
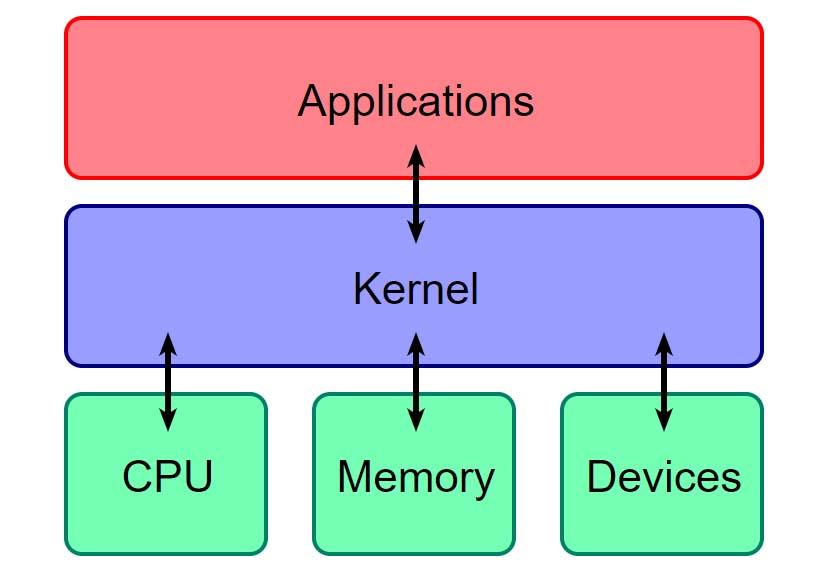
Today, it is generally found operating systems with a graphical interface, in this way, they allow interaction with users to be much simpler and more intuitive. Its main function is to provide all the necessary tools to be able to control our PC and to be able to use it in the most comfortable and easy way.
But also, it is in charge of controlling and managing access to computer resources, coordinating hardware, organizing files, controlling access to data and processing tasks, etc.
Parts of an operating system
An operating system is made up of many parts, components, or features that can change depending on the type of system. However, the three parts of the system most defined and used by the vast majority of systems are:
- Kernel or nucleus : A software that constitutes a fundamental part of the system. We could say that it is the heart of the system itself, and hence its name. It is defined as the part that runs in privileged mode or kernel mode and that is the main responsible when starting the system itself, providing basic level control over all the hardware components of the computer and whose main functions are to read and write. data in memory, process orders, interpret data, decide what to program can make use of a certain resource and for how long, etc. The Kernel runs in an isolated area to prevent any malicious software from manipulating it.
- User interface : it is the part that allows the user to interact with the computer. This interface can be graphic, providing a desktop, windows and graphic components for a more intuitive interaction, or it can be through a command line.
- Device driver or driver : Software in charge of allowing the system to interact with any peripheral. Although it is not always necessary for the use of new hardware, its use is recommended to avoid problems, improve security and the user experience.
- File system : It is the component of the operating system in charge of allocating space to files, managing free space and accessing protected data. It structures the information stored in the storage unit and most systems manage their own file system.
In addition, we could highlight other components of the operating system such as the protection system, responsible for forcing the use of protection mechanisms, determining the security controls to be carried out or establishing differences between authorized and unauthorized use. The resource manager, responsible for managing input and output devices, programs or processes running, secondary memory or disks and system resources in general. Communications system to control the sending and receiving of data through network interfaces, the main memory manager, which chooses the processes to load into memory when space is available, or the process manager, which is in charge of stop, continue, create or delete processes,
Types of operating systems
It is possible to make different classifications of operating systems, such as, depending on the computer or device where they are running or their processing capabilities. In this sense, we can talk about operating systems that run on:
- Computers : systems like Windows itself, macOS or Linux, specially designed to manage and control our computers.
- Mobile devices : are those specially developed for mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets (iOS and Android).
- Integrated : Integrated systems are those that are embedded in certain devices and that favor their function, printers, household appliances, etc.
Now, we could also make a classification based on their abilities when processing tasks or supporting different users:
- Single user and single task : those who are only capable of processing a single task by a single user at the same time.
- Single user multitasking : operating systems capable of multitasking from a single user.
- Multitasking and multiuser : systems that have the ability to execute multiple tasks at the same time from different users.