Historically, monitors have been plagued by so-called screen artifacts, better known as tearing , a visual problem characterized by two (or more) frames being displayed at the same time. This annoying flaw not only reduces overall fluidity and immersion when playing our favorite titles, but also puts us at a distinct disadvantage when competing at higher levels.
Fortunately, GPU makers realized this long ago and introduced variable refresh rate technology that allows the GPU and monitor to talk to each other and reduce such artifacts. AMD FreeSync and Nvidia G-Sync have come to solve this problem.

What is FreeSync
FreeSync is AMD’s entry-level variable refresh rate technology. It was released in 2014 to help reduce screen tearing that would occur when the monitor’s refresh rate was out of sync with the GPU’s frame rate output.
The refresh rate of a monitor is measured in hertz and allows us to know how many times the screen can be refreshed every second . A GPU, on the other hand, is a graphics processor that generates frames and outputs them to the monitor. The goal is for the GPU to represent the exact number of frames (FPS) that the monitor can update every second. Therefore, a monitor that refreshes 75 times per second (75 Hz), will run most efficiently when the GPU feeds it at 75 frames per second. And when this synchronization does not occur, the tear occurs.
Many PC setups will struggle to maintain a fixed number of frames when playing more demanding modern titles. We often see huge variations in FPS depending on the game we’re playing, its graphics demands, and what screen resolution we’re using. In these scenarios, whether it’s two frames being displayed at once or just choppy gameplay , we’ll often see some form of screen tearing.
And that’s where FreeSync steps in. AMD Variable Refresh Rate technology allows the GPU to control how often the monitor refreshes per second, synchronizing the monitor’s refresh rate with the amount of FPS you’re getting at any given time.
This obviously comes with its limitations, as a monitor with a 60Hz refresh rate will only be able to support a variable refresh rate of up to 60 frames per second. In this case, we will have to limit the FPS to 60 for best results. That said, if your PC is having trouble reaching over 60 FPS, FreeSync will reduce your monitor’s refresh rate (down to 9 frames per second) to match your frame rate, creating a much smoother, stutter-free experience.

What components and features do I need for FreeSync
To use FreeSync, we will first need a compatible AMD graphics card or APU (AMD all-in-one processor that offers integrated graphics). Fortunately, almost every new GPU coming to market from AMD will offer FreeSync support , no matter the price. However, if we are not sure, it is best to check the product specifications first.
Second, we’ll need a compatible monitor or TV that supports VESA Adaptive Sync, a technology used in almost all modern panels. Adaptive sync is powered by a built-in scaler board that also powers the OSD, overdrive settings, backlight controls, and everything else a monitor has to offer. Without it, the monitor and the GPU would not be able to communicate with each other.
In addition to a compatible monitor and GPU, we will also need to use the correct input cable. DisplayPort 1.2a was added to the variable refresh rate support list in 2014, followed by HDMI 2.1 in early 2017. These are also essential requirements when using FreeSync technology.
According to AMD, every panel that offers FreeSync support goes through a custom certification process that ensures only the smoothest, most seamless, and low-latency gaming experience possible.
What is G Sync
V-Sync was the first sync technology to hit the monitor market, helping with screen tearing by limiting the monitor’s frame rate to match your GPU’s output. While this was good news for gamers who could produce FPS that dwarfed the refresh rate , it had the opposite effect when frame rates dropped well below that figure, resulting in minor stuttering and large framerate lag times. entry.

G-Sync was originally designed to be used with V-Sync, however Nvidia soon allowed users to disable this option. The G-Sync module enables a dynamic refresh rate that matches your GPU output, much like V-Sync only without the choppy dropouts and high input lag times.
G-Sync updates the screen exactly when the frame is finished and wants the GPU to output it. The refresh rate is the maximum frame rate used by the G-Sync module and with this you shouldn’t have any noticeable lag or tearing . This works in the same way as V-Sync, synchronizing the refresh rate with the GPU’s frame rate output, resulting in a seamless gaming experience that is much more immersive.
What components and features do I need for G-Sync
G-Sync monitors also support Variable Refresh Rate from 1 to 240Hz (or whatever the monitor’s maximum refresh rate is), Low Input Lag, Ultra-Low Motion Blur (ULMB), Factory Color Calibration and G-Sync support in windowed and full-screen mode. This is why we often only find G-Sync on high-end monitors , as it’s simply not cost-effective to include on cheaper ones.
That said, since G-Sync is a fixed standard, we also need to know exactly what we’re getting every time we buy a G-Sync-enabled display: effectiveness won’t be slightly different between monitors, as is the case with FreeSync.

G Sync Ultimate
G-Sync Ultimate adds HDR support and we can still get everything described above, but every G-Sync Ultimate display also gets specs like 4K resolution, at least 1000 cd/m2 brightness, 384 dynamic backlight zones, compatibility with DCI-P3 colors and ultra-low latency.
The Ultimate version covers both regular desktop monitors, such as Asus ROG Swift PG27UQ and Acer Predator X27, as well as Nvidia. BFGD (or Big Format Gaming Display) screens like the HP Omen X Emperium.
How to activate them
Both G-Sync and FreeSync are only supported by Nvidia and AMD GPUs respectively. The two systems have been improving and adapting their characteristics to the market rival and G-Sync already adapts to AMD.
How to activate FreeSync
Activating FreeSync when using a compatible monitor is an extremely easy task. First of all, we start by entering the monitor’s OSD. Nine times out of ten, this will have a variable refresh rate option that will allow us to enable/disable FreeSync. The first thing we need to do is make sure FreeSync is enabled.
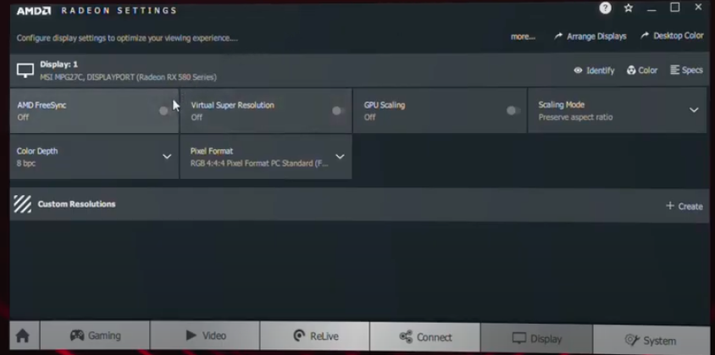
Second, we must have all the latest drivers for the AMD GPU. To do this, the latest drivers can be downloaded from the AMD website. The installer will fetch the latest drivers needed to enable FreeSync support. We can also manually enter the GPU or APU in AMD’s “Manually select your driver” tool; we just have to select the correct version of Windows .
When the latest drivers have been installed and the computer restarts, open the AMD Radeon software package. We can do this by right-clicking on the desktop and selecting “ AMD Radeon Software ” from the available options. Once inside, we go to the “Display” tab in the top navigation bar and to the “ Display Options ” part of the tab. Within this section, we will look at the toggle settings for AMD FreeSync. We simply click on the toggle bar on “Activate”.
How to activate G-Sync
Once we have connected the computer’s graphics card to its port, it is time to start G-Sync. First, we’ll need to open the monitor’s menu, usually using the buttons on the side or back of the screen, and make sure the G-Sync, FreeSync, or Adaptive Sync setting is turned on. This will be in a different location depending on the model, but it shouldn’t be hard to find.
Make sure your Nvidia drivers are up to date , then right-click the Nvidia icon in the system tray to open the Nvidia Control Panel . Let’s go to the Change resolution page on the left sidebar and set the refresh rate as high as possible. Many people don’t realize that you need to enable high refresh rates before you can take advantage of them.
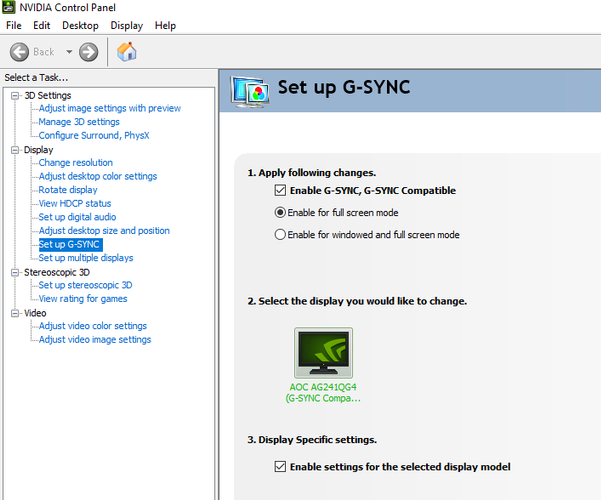
We go to the Configure G-Sync option in the sidebar and if we are using an official G-Sync monitor, it should be on by default, but if it is not, we may have to do it ourselves. Checking the Enable G-Sync box, we choose whether we want to enable it for full screen or windowed mode, and select (if we have multiple monitors).
Finally, we check Enable settings for the selected display model at the bottom. This checkbox doesn’t exist for all monitors, but it’s easy to miss even when it’s present. Click the Apply button and G-Sync should be enabled and ready to go.
To make sure it works properly, we can download Nvidia’s Pendulum demo and play around with the settings. Switching between “No Vsync” and “G-Sync” at the top, you should see the screen tearing disappear when turning on G-Sync. If checking the G-Sync box does not work, a previous step may have been skipped or the monitor does not support G-Sync. We can also try enabling the FPS sliders and playing around with them to see how the monitor is doing and its reaction to different portions of the refresh rate.
Differences between FreeSync and G-Sync. Conclusions
G-Sync and FreeSync are essentially the same thing, as they both sync the monitor to the graphics card and allow that component to control the refresh rate in a continuously variable manner. But a monitor can also go beyond the requirements and for example a FreeSync monitor is not required to have HDR and some of these achieve motion blur through an associated proprietary technology such as Asus ELMB Sync .
Getting into more technical specifications, FreeSync is an open standard , which means that any company can use its technology to develop products. Rather, Nvidia’s permission is needed to use G-Sync. The maximum supported refresh rate of FreeSync Premium Pro is 120Hz or higher, and with G-Sync Ultimate 144Hz or higher.
Monitors with FreeSync require no proprietary hardware components to run the technology, and G-Sync does to support it. FreeSync certification does not guarantee HDR high dynamic range color support and G-Sync monitors must have HDR to be certified . FreeSync’s minimum refresh rate is 60Hz so Nvidia’s trademark 30Hz.
According to various experts, there is no visual difference between FreeSync and G-Sync when the frame rates are the same. They acknowledge that G-Sync is technically superior , because it offers some extra features on top of adaptive sync. But on the other hand, FreeSync is usually much more affordable , making it the best option for gamers who are on a budget.