All hardware fans are aware that the power supply is one of the most important elements of the PC, and that in addition to supplying power to the rest of the components, it also incorporates a series of protections or security systems that guarantee that the hardware will be safe in the event of any electrical problem. In this article we are going to tell you what each of these protections are and what they are for.
Absolutely no one is immune to problems or breakdowns, especially when we are talking about electronic devices that we must plug into the electrical network. Electricity does not work exactly as a constant flow but it has variations that are extremely fast, and therefore any device connected to it can have problems.

Why are protections at the source important?
Surely it has happened to you or you know a case of someone who, after an electrical problem, has damaged the power supply and has taken other components, potentially the motherboard since it is the first affected and maybe even the processor, RAM or graphics card. This is what can happen if the equipment’s power supply did not have the necessary protections to safeguard the integrity of the rest of the hardware (or when the supply was of poor quality and the protection circuits did not function as it should).
The hardware components are designed to work with direct current, and obviously the power supply is in charge of transforming the alternating current that comes through the wall socket to the direct current that the components need, in addition to reducing the voltage to which need. The problem is that the components are designed to operate with a very small voltage range, but the amperage range at which they are capable of operating is even smaller, so proper regulation and protection in the power supply is crucial for its smooth operation.
In addition to this, we have already mentioned the fact that breakdowns, accidents or instabilities can occur in the electrical supply, and that is where the protections of the power supply play such an important role as if it did not have them, we could spoil literally the entire pc. Imagine, as a simile, the seat belt or the airbag of a car: normally you don’t need it, but if you have an accident, wouldn’t you rather have it on?
What the protections of the power supply do
As we have already mentioned, all the electricity that is then supplied to each component of the equipment passes through the power supply, and for this reason it is very important that it incorporates protection circuits: if when buying a power supply you see that the manufacturer it does not indicate any, the advice is that you do not buy that power supply because, following the simile that we have put a moment ago, it would be like buying a car without seat belts or airbags.

Of course, normally the manufacturer specifies the protections in the form of acronyms, so we are going to reel off all the protections and see what each one of them does.
OCP, OVP and UPV, protection for problems in the electrical network
These three protections are obviously different but we have included them in the same section because they are closely related:
- OCP stands for Over Current Protection or protection against current surges. This is probably the most important protection, since, as we have explained before, the components have a certain margin in terms of voltage variations but not in the face of current intensity variations (amperage). This protection circuit detects the increases in current intensity and corrects them at the source itself so that they do not reach the components; The bad part is that this extra current is released as heat, which is why the OTP circuit often has a dedicated heatsink.
- OVP stands for Over Voltage Protection or protection against voltage surges. Like the previous one, it is a protection system that detects voltage surges and corrects them before sending the signal to the PC components. It is also important because, for example, when there is an electrical storm, surges in the electrical network are frequent.
- UVP stands for Under Voltage Protection, or protection against voltage drops. It is extremely rare that there are dips in intensity and that is why the sources do not usually incorporate protection systems against it, but it is frequent that in the electrical network there may be voltage dips, especially if the electrical substation in your area is overloaded. This protection system is responsible for compensating for this.
SCP, short circuit protection
As you know, any electrical device has two poles: the phase and the neutral (in addition to the earth connection). It is called a short circuit to the failure or breakdown in an appliance or in the electrical line itself through which the current passes from the active conductor or phase directly to the neutral or ground. In other words, it is what would happen if you took the two cables of a power line and joined them, but it can also happen in a PC if any cable is damaged or if one is not well insulated and touches the plate of the PC case .
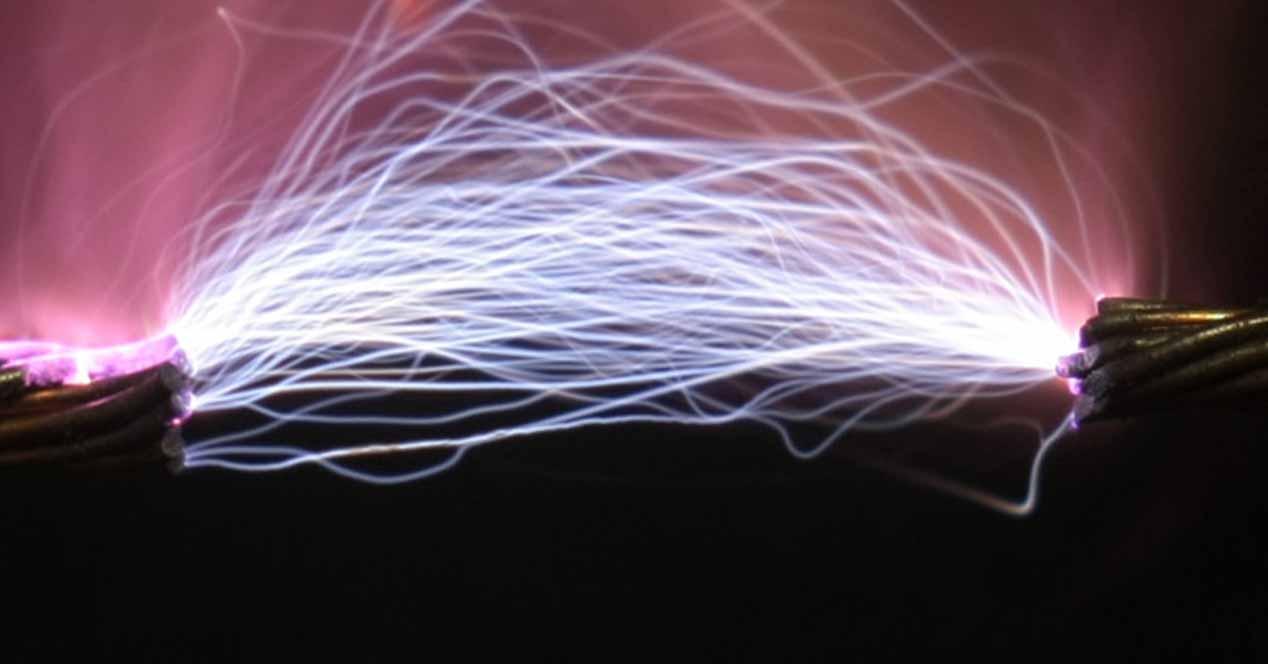

The SCP or Short Circuit Protection is a security system of the power supply that detects this fact and, in this case, instead of compensating for anything since it cannot be, what it does is cut the current and turn off to avoid breakdowns. Therefore, if a short circuit occurs in your PC, this system will cause it to turn off suddenly to avoid damage, and you will have to detect where the short circuit has occurred so that the system can turn on again, since it will not do it again while this problem is still present.
OTP and OPP, due to problems in the equipment itself
Finally we have the protection systems OTP (Over Temperature Protection) and OPP (Over Power Protection), although the latter can also be called OLP (Over Load Protection).
OTP, as its name suggests, consists of a temperature sensor that when it detects that it exceeds a certain limit established by the manufacturer, it causes the system to turn off to avoid damage. The OPP / OLP system will also turn off the PC, but in this case when it detects that the consumption of the equipment is higher than the power supply is capable of supplying.
In this second case, imagine that you have some hardware components that consume 500 watts and the power supply is 400. At the beginning the equipment will work and start because at rest the consumption will be less than that, but when starting a game or program that make the equipment draw above 400 watts, the source will shut down otherwise low voltage and low current problems will occur that could damage hardware components.