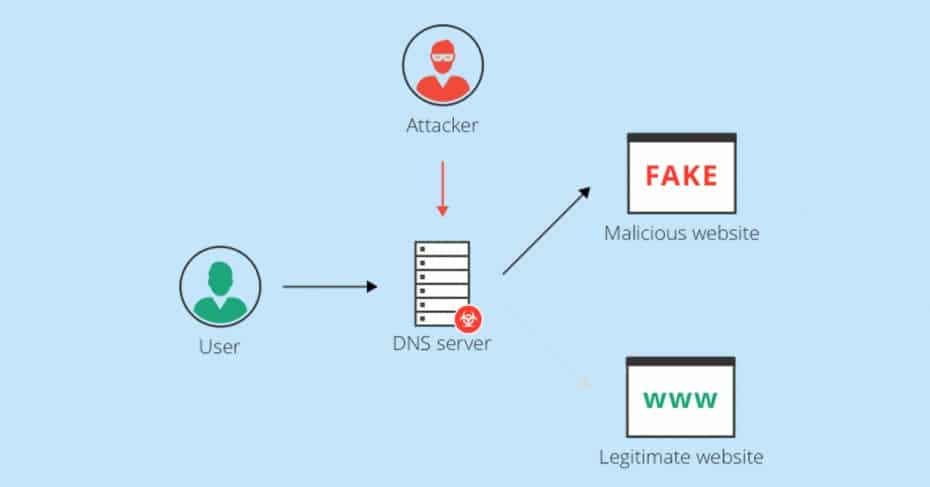
 Today, anyone knows what the Internet is and how they can browse websites. What many users do not know is that when we enter a web address, DNS servers are responsible for translating that domain name into the IP address. We have several articles on its operation very interesting, but today we want to talk about one of the most frequent attacks, known as DNS hijacking.
Today, anyone knows what the Internet is and how they can browse websites. What many users do not know is that when we enter a web address, DNS servers are responsible for translating that domain name into the IP address. We have several articles on its operation very interesting, but today we want to talk about one of the most frequent attacks, known as DNS hijacking.
As we have commented in several articles, the DNS (Domain Name System) system works by translating DNS names into IP addresses. That is, the user enters the address of the website he wants to access and the DNS server is responsible for converting it to the IP address.
When we open a web page and type in the address bar the website we want to access, we are entering a domain name in the browser. The browser, unless you have it in the cache because you have previously accessed that website, will not know what the IP address of the requested website is, and then send a request for information to the DNS servers.
This is when the hijacking DNS comes into operation, which is that the resolution of the information request of our browser is resolved by a DNS server that is controlled by cybercriminals. This attack is usually carried out in conjunction with the popular ARP Spoofing, to redirect all traffic to the attacker’s computer and “listen” and manipulate all the information that travels through it.
We have to be clear about the most critical moment, and that is when we enter a web address in the address bar of our preferred browser, since it will then request information from the DNS servers. This DNS request is not encrypted at any time, and can be intercepted and modified on the fly, to redirect our web request to the IP address they want.

For this reason, protocols have been born to provide security for DNS requests and their responses, such as DNS over TLS and also DNS over HTTPS. In RedesZone we have a complete list of the best DoT and DoH DNS servers that we can configure on our computers.
Router Hijacking
But the problem does not end here, since another method that is also used is to hijack our router. Remember that our web browser, when searching for information about the website’s request, first searches its cache, then searches the hosts file, and finally passes the query to the DNS servers indicated by the user or router in DHCP mode This, above all, can happen on routers where users leave the default access data or on ISP routers.
Once a cybercriminal has gained access to our router, it is as simple as changing the configuration of the DNS servers found in the router configuration, and that will affect all the computers that connect to the router using the DHCP protocol.
Once this is done, what will happen is that any web search of any computer in our network that uses the router’s DHCP server will be redirected to DNS servers controlled by cybercriminals.
Kidnapping of our network
If you thought that they could not fool you more with DNS servers, another very common type of attack is to hijack the user’s computer. This consists of infecting the user’s equipment by injecting specific Trojans that access the DNS configuration of the equipment and change its configuration, causing any browser request to be redirected to where the cybercriminal wishes.
The detection of this would be very simple, since it would be enough to enter the Windows network configuration (you can enter by executing the ncpa.cpl command in the start button of the start menu) and see what DNS servers we have.
Rogue DNS Hijack
Another more complicated type of attack is the Rogue Hijack DNS. In this case, this attack never attacks the user directly, but the hacker attacks and hijacks the DNS server directly. This really is very dangerous, since, any user who uses the infected DNS server will be in danger, and the most serious of all is that he will not be able to know it in any way.
Luckily when this happens, the cyber criminal is looking for very specific requests that reach the DNS server. We also have to keep in mind that it is very complicated for an attack and hijacking of a DNS server, such as Google or Cloudflare, to be successful, since these meet very high security standards and protocols.
In the worst case, if a cybercriminal managed to gain control of a DNS server, millions of users would then be in danger.
The dangers of infected DNS
After seeing all the many ways to infect a DNS system, talk about the dangers that this can bring. A very simple example would be that the IP address to which the cybercriminal redirects us, takes us to a website that infects our computer with a virus, or a malicious code or a Trojan.
But in reality, and so that you are much calmer, nowadays these types of attacks are no longer used, but instead use phishing or pharming. But this does not mean that it is not very important that you know how they work and how they can affect you in case one day this type of attacks is back in fashion among hackers.
- Phishing : we have to know that phishing is an exact replica of the website we want to access, and, normally, they are websites such as banks, that what interests criminals is that we enter the access credentials, in order to steal it . This happens with any website that asks us for credentials. We have to know that, once the credentials have been entered, the offender will automatically obtain them and the website will then redirect us to the authentic website where we will be asked for the credentials, and the user will think that it is a failure of the website, and will return to enter the credentials and will access well without the user suspecting that he has been the victim of a phishing attack.
We have to know that a phishing attack can occur without the need to have infected DNS. This usually happens, especially by clicking on fake email links. A simple way to detect it is to look at which website we are really looking at the address bar. However, if they have really hijacked the domain we want to access, it will be almost impossible to detect it.
- Pharming : we have to know that pharming is to redirect the user’s request to a website full of ads. This directly does not affect the user much, but it can be very annoying. On the other hand, for the offender, it is ideal, because thanks to these ads for each visit he is making money, and it is a very simple way to earn a lot of money thanks to redirecting DNS requests to the website full of ads.
As we can see, this last method would be the least dangerous for the user, since the only thing that will affect him will be that he will see many ads, but, luckily, they will not steal any data.
Another type of DNS hacking that could be considered, would be the one that certain governments of certain countries make to their citizens, blocking access to websites that the government itself does not consider fit to be visited by its citizens. In this case, when a citizen tries to access a censored website, he is usually notified of the block, so there are users who do not consider this a “DNS hijacking”.
ISP
Another type of DNS hijacking is the one that occurs when a user tries to access a website and does not load, showing an error message. This usually occurs in countries where pircy is pursued, especially, and these types of websites are usually blocked by court orders.
The notice that comes out normally is the same as when we try to access a website and we make a mistake in the web address and the web does not load us. To avoid this there are methods to skip DNS locks, such as using a VPN or simply changing the DNS addresses we use. In this article we explain the best DNS with no records policy that you can use.
How can we protect ourselves
Surely at this point, you will be wondering how to protect yourself from this type of DNS hijacking attacks. Since the ways of handling DNS requests are so different, we have to take a series of precautions that we will see next, to mitigate as much as possible the different attacks
- Change the access data to the router: the first thing we must do is change both the user and the access password to our router, if the router does not allow us to change the user and it must be “admin”, then only change the password. Above all, we must use strong passwords.
- Update the router firmware: it is useless to change the access data to the router, if it turns out that we have the router without updating, and, therefore, without solving different security problems that are solved with the router firmware update.
- Having a good antivirus: as for our computer equipment, it is very important to be protected, and therefore it is very important to have a good antivirus installed on our computer, which analyzes the files and our activity on the internet and on our network.
- Having a firewall: another very important point is to have a firewall installed and activated on our computer that monitors the incoming and outgoing connections of our computer.
- Use secure DNS protocols such as DNS over TLS or DNS over HTTPS, where all requests and responses will be sent encrypted point to point.
- Use a VPN: if we want more security, we recommend that you use a VPN for your connections, so that all traffic is encrypted from the source (us) to the VPN server where we have connected. This is especially important if you connect to the Internet from public places, such as airports, coffee shops, restaurants etc. Thanks to this system, we will mainly avoid Man in the Middle attacks.
After having seen the different ways that exist to hijack the DNS, and see possible solutions to protect us, we can only advise that the best way to protect yourself is not to click on strange links, and, above all, to know what websites we enter. Finally, always try to browse websites that use the HTTPS protocol, since all connections will be encrypted point to point.