
The presentation of Valve’s PC in the form of a portable console, dubbed the Steam Deck, caught many of us by surprise. Not only because of the fact that it was not expected, but also because of what it supposes. Being able to play PC games anywhere. But how capable is it? That is why we have decided to analyze architecture.
Who wouldn’t want to be able to play their favorite PC games on the go? It is true that the Nintendo Switch exists for high definition games on a laptop. But it must be borne in mind that not all games are on the Nintendo console and there are PC games that we would like to be able to take anywhere, be it a hotel room, our apartment or during a long car trip where we don’t. we are driving.
That is why we have decided to do an analysis of the Steam Deck hardware, specifically taking into account its usefulness. PC games anywhere or anywhere. So we have also taken it into account and we have pointed out the parts where we believe that in terms of portability both Valve and AMD could have done better.
Van Gogh, next gen console technology at scale
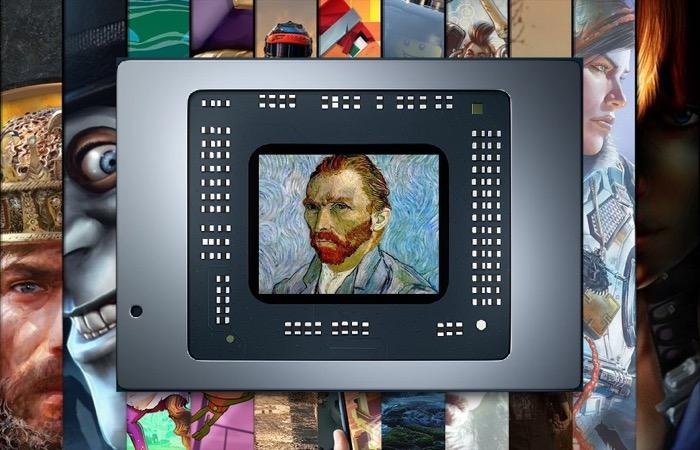

If we look at the two main premises of the main Steam Deck APU, then we will find that it has a CPU with Zen 2 architecture and a GPU with RDNA 2 architecture , two points in common with all new generation consoles, but on a smaller scale. .
Starting with the CPU, Steam Deck uses a Zen 2 4-core CCX , instead of using 2 of them as in consoles, so this is a 4-core and 8-thread design . It is surprising to us that a device that works under a battery opts for multithreading, but at the same time it must be taken into account that the energy cost of placing 8 cores is much higher. Your clock speed? It is between 2.4 GHz and 3.5 GHz . Again we find another surprising element if we consider that we are talking about a system that is designed not to be connected to the power outlet.

Regarding the GPU we have an RDNA 2 with 8 Compute Units , which moves in speed between 1 GHz and 1.6 GH z, Valve has not talked about the use of AMD’s SmartShift technology, implemented in the RX 5000 and RX 6000 Gaming and in the PlayStation 5 APU. But we have to take into account the problem of thermal throttling that leads to cut the clock speed of the CPU, the GPU or both at the same time and more in low-power devices.
The way in which for example Nintendo does this with Nintendo Switch is by leaving the CPU at 1 GHz and allowing variations in the speed of the GPU. Only at times when there is a screen transition, in the form of a black fade, or playing a video that cannot be skipped. That the Nintendo Switch CPU is put to maximum speed to perform the task of copying data from the NAND flash memory of the console to the RAM. where the next level data is located. But, in general, it is rare that the design of a portable system that is designed to give hours of gaming away from home ends up throwing Boost speeds in CPU and GPU.
Lack of Infinity Cache is crucial
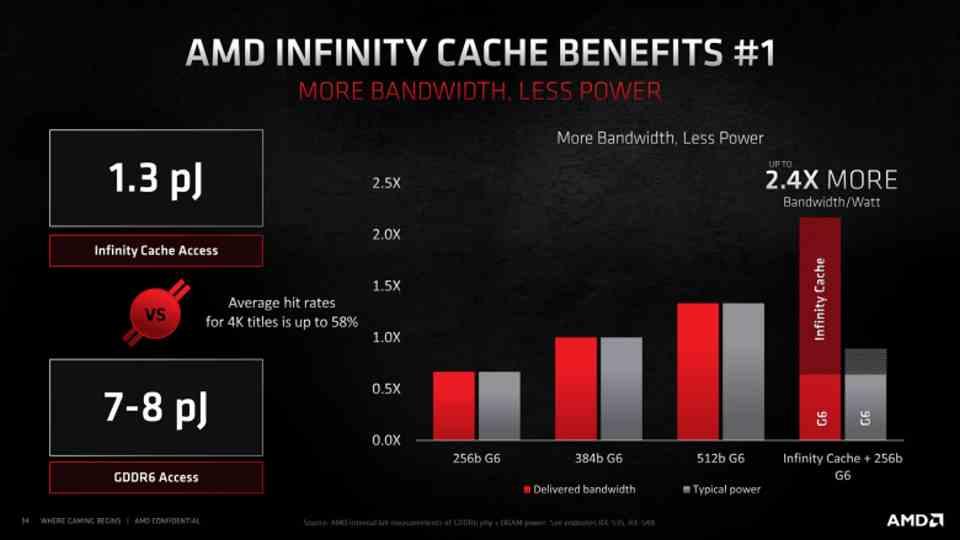 We do not know if the Steam Deck carries Infinity Cache or not , but we think not because it is not confirmed for the rest of AMD APUs at the moment and it seems to be a unique feature of the dedicated GPUs and not the integrated ones. but we do know how important the Infinity Cache is when it comes to performance. Especially due to the fact that current GPUs behave by rasterizing for tiles. We are not talking about tile rendering. Tile raster is found on all NVIDIA GPUs since Maxwell under the name Tiled Caching and on all AMD GPUs since Vega under the name DSBR.
We do not know if the Steam Deck carries Infinity Cache or not , but we think not because it is not confirmed for the rest of AMD APUs at the moment and it seems to be a unique feature of the dedicated GPUs and not the integrated ones. but we do know how important the Infinity Cache is when it comes to performance. Especially due to the fact that current GPUs behave by rasterizing for tiles. We are not talking about tile rendering. Tile raster is found on all NVIDIA GPUs since Maxwell under the name Tiled Caching and on all AMD GPUs since Vega under the name DSBR.
The idea is that the part of the 3D pipeline that goes from the raster of the triangle to the one drawn in the image buffer is done as in the rendering by tiles, but with a difference. The tiles are stored in the L2 cache. Which is not RAM and therefore does not work as such. This means that any data that falls from the L2 cache lines will end up in RAM directly. Since the L2 cache is directly related to the bandwidth of the memory controller, which is much smaller with an integrated GPU and a 128-bit LPDDR5 bus. So the chances of data falling into RAM are much higher.
In RDNA 2 for PC and only in the Radeon RX 6000, AMD added the Infinity Cache, it is an additional cache level that acts as Victim Cache, collecting the discarded data from the L2 cache and adopting it inside. The importance of this is that accessing the data that is in the Infinity Cache increases energy efficiency by requiring less pJ / bit to access. It is true that the LPDDR5 has a lower consumption than the GDDR6, since it is close to 4 pJ / bit on average, but the addition of the Infinity Cache in the APU would have made the Steam Deck more efficient.
Ray Tracing is not necessary, VRS is

Because the integrated GPU is RDNA 2, it contains support for Ray Tracing, given the inclusion of Ray Intersection Units. But Ray Tracing is not only the intersection calculation, but also the BVH tree traversal. Which is done in RDNA 2 through computing and believe us that the power in that aspect in the case of the Steam Deck is not enough.
Another topic is the Variable Rate Shading, which groups the pixels to which the Pixel or Fragment Shader that have both a color value and a shader program in common, to process them as one and then copy the data. This gives a performance depending on the game between 10% and 30% additional compared to not using it, apart from cutting the damn accesses to the VRAM, deadly as we have said before in the face of energy consumption.
Most Steam Deck users will use their existing Steam library, where 99% of the games do not require Ray Tracing they will not have to worry about the ray tracing capabilities of the Steam Deck GPU.
RAM, speed, size and access on Steam Deck
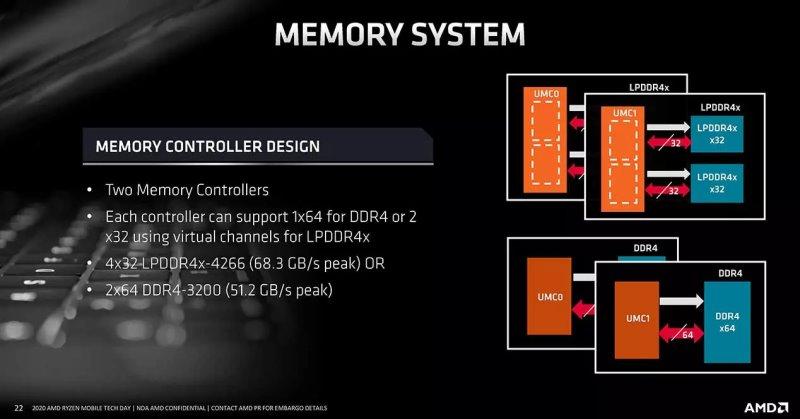
In all AMD APU / SoC whose CPU is from one of the generations of the Zen architecture there is one element in common: the way it accesses. In all cases, its unified memory controller, UMC, communicates with the RAM with a 256-bit bus at the memclk speed, which in DDR and LPDDR memories is half its transfer rate, in this case 2750 MHz, which is half that of 5500 MT / s. The total bandwidth? 88 GB / s, which is more than triple the 25.6 GB / s of the Nintendo Switch SoC.
The UMC has therefore been updated with respect to the one used in the Ryzen 4000 and Ryzen 5000 APUs for PC, since it has gone from supporting 4 LPDDR4 channels to exceeding the same number of LPDDR5 channels. It must be taken into account that with each new generation of any type of memory, the voltage is lowered to reach a clock speed, this allows to increase the clock speed and have a faster RAM and therefore with a greater bandwidth. The problem comes with energy efficiency, which is measured in pJ / bit, and it can be said that the evolution in that aspect is going backwards.
Since watts are Joules per second, we can easily extrapolate the bandwidth of RAM into what it consumes in each second. The answer? In the Switch Deck we have a much higher figure than what the RAM of the Nintendo Switch consumes, so from the outset we already have the first problem in terms of design, the energy consumption of the memory is much higher than that of its direct competition, being one of the problems regarding its energy consumption and therefore battery life.
Arithmetic and Texturing Intensity in Steam Deck
In computing there is the concept of Bytes per FLOP or Bytes per floating point operation. We use it to measure the arithmetic intensity of the different algorithms when executing them on the GPU. Another issue to measure is what we have baptized as texturing intensity, where it helps us to check if there is a bottleneck in relation to the capture of textures with respect to GPUs with RDNA 2 PC architecture.
For this we have decided to take the AMD RX 6700 XT, in order to make a comparison within the same graphics architecture. AMD’s RX 6700 XT, to compare it with another RDNA 2, has a width of 412.8 GB / s and a power of 13.21 TFLOPS, which gives us about 0.032 Bytes per FLOP. The maximum GPU power of the Steam Deck is 1.6 TFLOPS with a bandwidth of 88 GB / s as we have deduced before. The figure we get? 0.055 Bytes per FLOP , so memory is not a bottleneck compared to the desktop AMD RX 6000 for computing shaders and the rest of graphics shaders except Pixel or Fragment Shaders.

The other issue to measure with the arithmetic intensity in the Steam Deck has to do with the texturing units that operate in conjunction with the Pixel Shaders. On the RX 6700 XT we have a texturing rate of 413 GTexeles / s. In the case of the Steam Deck we have 8 Compute Units, which make 32 texture units each and a maximum clock speed of 1.6 GHz, which transforms into 51.2 Gtexels / s. rate. Applying the same rule of Bytes per FLOP we can measure the performance with regard to texturing.
And what do we get? On the RX 6700 XT it is 0.99, not to say a 1: 1 correlation, obviously the bandwidth will not be used for texturing. It is just a way to measure memory intensity for this task. And what about the case of the Steam Deck? Again the memory intensity is better, being 1.71. So again the balance between the integrated GPU and the bandwidth is one of the strengths. This ensures that memory is not a bottleneck for console graphics performance.
The dark part, the Steam Deck storage
The base version of the console comes with 64 GB eMMC , a figure that seems ridiculous and where it will be impossible to install anything at all, so it is essential to purchase an M.2 2230 module to install it inside the console . Maneuver that could void the warranty since Valve does not recommend fiddling with the console for it. And this is where our first slap on the wrist to Valve comes from. Since at the time of writing this article, we can find M.2 2230 modules for a much lower price than the difference between the different models. So for us it would have been much better to give easy access through a cover to the M.2 interface.
But what if we run out of space and don’t have the M.2 SSD installed? Don’t worry, Valve has placed a microSD card slot. At first glance this seems very good, but the performance of a microSD when transmitting data is very, very low and you are going to see how the loads of the games become eternal. That is why we recommend that you go head first to an M.2 2230 PCIe and install it or, failing that, go for the two most advanced modules.

It is not only because of the storage, it is that we are talking about multiplying the bandwidth several tens of times and this means that the device becomes directly another in terms of performance. However, without forgetting that the Steam Deck is designed to be a laptop we are surprised by the choice of this type of storage. An NVMe SSD is the best memory access speed you can put in a system, that’s true.
Is it the best in a portable system? Not really, since eUFS 3.x memory would have made more sense, since it makes no sense to use an NVMe PCIe if the games that the machine from within the PC catalog will be able to run without performance problems of any kind they are those who do not take advantage of the advantages well. From here to the release of games that take advantage of the NVMe SSDs on PC, then the Steam Deck will potentially have been out of date to run them at a decent speed.
And now to finish the screen

For many, the inclusion of a screen at 800p and with a 16:10 aspect ratio will seem like a step backwards, but it is not if we take into account the associated costs in terms of bandwidth and computing needs that have higher resolutions. .
A negative point is that the screen is not OLED, since this type of screens consume less and the problem of burning the pixels should not be a problem in a video game system. Taking into account that Nintendo has adopted it in the new Switch model and those in Kyoto take years to adopt a technology and when they do it is at a bargain price. The inclusion of an OLED screen by Valve for its Steam Deck would have been a better option and no, we are not saying that the screen is bad, but we are talking under the concept of energy consumption that is important for a portable system.
In any case, it has enough resolution to give good image quality and performance, since Valve ensures that all the games in its catalog work with a minimum frame rate of 30, which is not ideal for all games.