The boot process of any computer can be compromised if there are no security measures to protect it. AMD‘s Platform Secure Boot or PSB is one of the mechanisms that guarantee integrity in this regard, but it can also be abused by manufacturers to tie you to specific hardware.
It is much more profitable for computer manufacturers to sell an entire computer than to update it with parts from different brands, that is an undeniable fact and that is why most pre-built computers carry artificial limitations so that you are tied to a specific brand.

If we add to this that AMD for many years has been the ugly duckling for the different computer manufacturers and has had to fight very hard to get certain major brands to use their CPUs and those of Intel. So, it is clear that they have had to make some assignment in order to benefit the interests of their partners. One of the most controversial is the Platform Secure Boot or PSB , which has served manufacturers such as Dell or Lenovo to tie the Ryzen, Threadripper and EPYC CPUs of the company led by Lisa Su to their hardware exclusively.
How does the manufacturers’ interest in tying you to their platform relate to AMD’s boot protection system? Well, let us explain it to you.
What is the AMD PSB?
Within BIOS UEFI is stored in flash memory on the motherboard, which since it is non-volatile RAM is addressed as if it were part of main memory. There are times when even with all protection measures, malicious software can still inject code into the firmware and perform an unauthorized update. Let’s not forget that the boot process establishes the location of certain public and private keys, used only by the security processor.
This means that if we do not use a TPM module in our PC with an AMD processor, then our confidential information such as that related to the validation certificates that we use to interact with our bank are stored via fTPM that is found in the boot firmware, therefore, additional security measures must be added in order to protect it.
The AMD Platform Secure Boot or PSB is one of the security measures built into the security processor inside AMD CPUs. Its usefulness is none other than to prevent the execution of a firmware related to the boot process that has been modified for malicious purposes. To do this, it creates a chain of trust that is responsible for authenticating all the firmware that the CPU accesses when we start the computer, including the BIOS and the startup of the operating system.
How does it work?
The PSB adds a higher level of security than the UEFI BIOS itself can provide, because it validates the contents of the memory that contains everything in the boot program. It does this through a chain of trust executed purely through hardware and without any external programs before the entire startup process is executed.
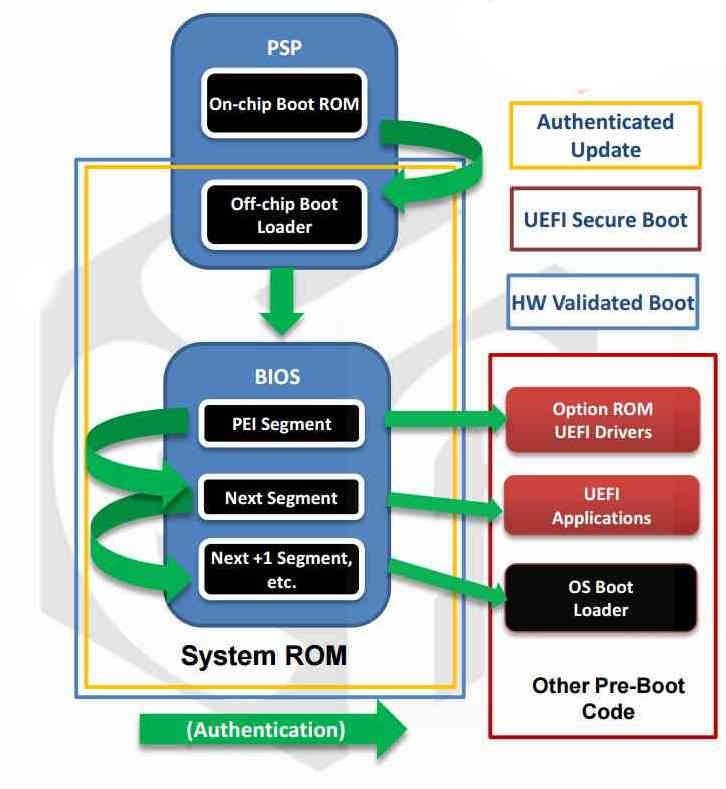
- It performs the validation of the first block of the BIOS/UEFI, while doing this it sends a signal to the HOLD pin of the CPU so that it does not start up while it performs the verification.
- It is responsible for verifying the content of the system ROM, this memory contains a backup copy of the basic functions of the BIOS and contains the entire boot process in an immutable way. Note that new BIOS feature updates are not related to system boot.
- The security processor performs the comparison between the contents of the ROM and the firmware stored by the UEFI to check for any unauthorized changes. After doing this, it frees up the CPU so that the PC can be booted without problems.
The AMD Security Processor or Platform Security Processor is a small microcontroller with the highest privilege level for access to RAM and system peripherals. It is rated on an ARM Cortex-A5 and due to its low power consumption it can work with the computer in sleep or standby mode. So it will be the first processor to be put on the mark when we turn on our PC or take it out of one of the low consumption modes.
How do manufacturers abuse the AMD PSB?
In recent times we are seeing not only how there are movements towards integration, but also that in the midst of this process one of the bases that has defined the PC since its inception is being attacked: the capacity for expansion and configuration by the user. Most manufacturers have come to the dangerous conclusion that the fact that we can expand the capabilities of our PC affects the purchase of future products. Hence, the controversy of the right to repair has appeared in the face of the practices of different assemblers and hardware manufacturers.

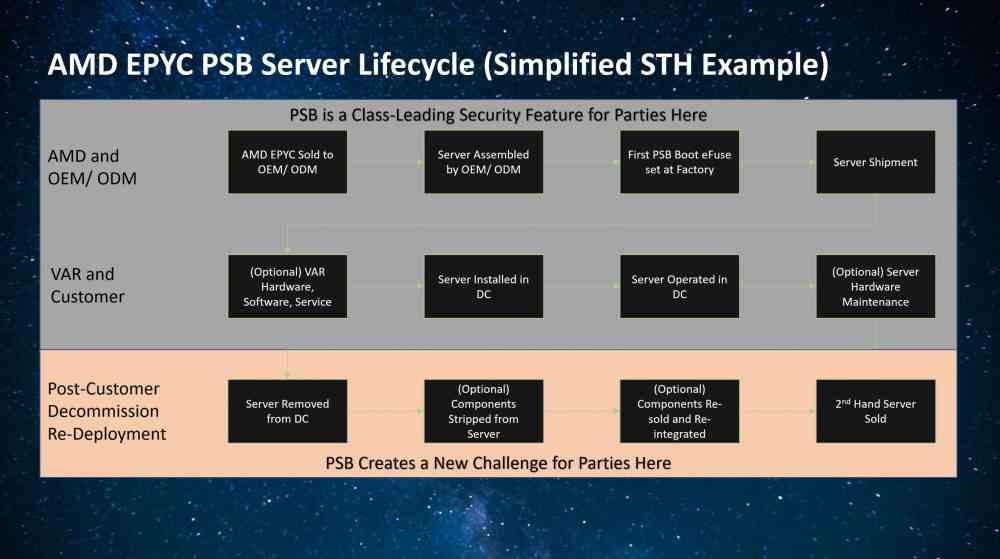
Logically, one would expect this to affect only the consumer market. So the servers and data centers used by both the different public bodies and large companies that in theory should not be affected by it. However, AMD decided to create a program called PSB so that manufacturers and assemblers could sell their entire servers and not parts. The reason behind it? There is a second-hand market where EPYC processors already stripped from their servers are used for second-hand servers and data centers.
In other words, when a company discards its old server or data center, it does not throw it away, but sells its parts to recover part of the investment. This creates additional competition for server manufacturers. Since they may find it more attractive for their customers to build a server themselves and maintain it themselves, this abuses one of AMD’s EPYC security features to lock customers into a particular brand.
How do they make the lock?
In order to make an AMD EPYC server CPU only work with a specific model of motherboard and the second-hand server market, manufacturers abuse the boot certification process provided by the PSB to tie processors to their specific servers, which means we can’t pair certain processors except with certain server boards.
To understand the whole process, we must start from the fact that when the manufacturer has finished creating the PC, whatever type it may be, a process is executed in which the boot image stored in the ROM is created and which will include two keys associated, both with a size of 4096 bits and SHA-384 encoding . The first one will be stored in the system ROM and will be reflected in the Boot Firmware. The second, on the other hand, will do so within the HSM, a hardware in charge of generating cryptographically encrypted keys and also decoding them.
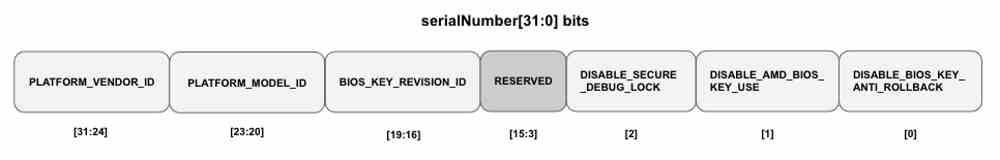
Both keys are part of the Public Key Infrastructure and are used to sign the content of a certificate found in the boot ROM on the motherboard and which includes the identification code of the processor and the rest of the hardware elements. If one of these items is missing from the system, then the PSB will simply not allow the system to boot.