When you’re in the market for a new computer, whether it’s a desktop or a laptop, one of the primary features you likely seek is a Solid-State Drive (SSD) as the primary storage unit. The advantages of SSDs over traditional Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) are well-documented, but while many users focus on factors like capacity, interface type, and sequential speeds, the 4K random speed of SSDs often goes overlooked. In this article, we’ll delve into the significance of 4K random speed and why it’s a crucial consideration when selecting an SSD.
Overcoming HDD Limitations
HDDs are inherently limited by their mechanical components. The rotation of their platters and the movement of their read/write heads result in relatively slow speeds. SSDs, on the other hand, have no moving parts, which allows them to deliver dramatically faster performance.
One concept shared by both HDDs and SSDs is the use of cache memory. Cache acts as a temporary data storage area that enhances performance. Data first enters this cache before being written to the drive. Interestingly, the same principle applies to both types of storage devices.
Sequential Speeds: A Deceptive Metric

When you’re shopping for SSDs, you’ll often find manufacturers prominently displaying sequential read and write speeds, typically measured in megabytes per second (MB/s). For instance, M.2 PCIe 4.0 SSDs can boast impressive sequential speeds of 6,000-7,000 MB/s. However, there’s a catch to these speeds that manufacturers don’t always explicitly clarify.
SSDs, like HDDs, utilize cache memory. This cache serves as a high-speed buffer where data is initially written before being transferred to the NAND Flash memory, ultimately contributing to the sequential speed that’s widely advertised.
Understanding the Significance of 4K Random Speed
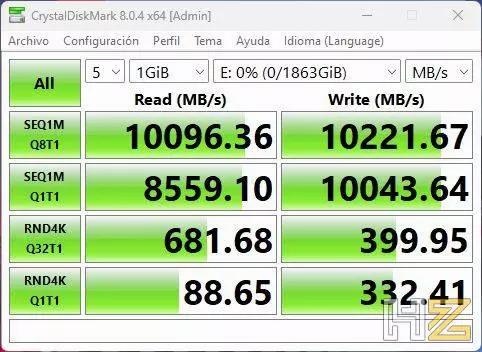
The critical factor often overshadowed by sequential speeds is the 4K random reading and writing speed, which has more profound implications for everyday tasks. To grasp this metric’s importance, it’s essential to understand how data is stored within an SSD.
Inside an SSD, data is randomly distributed in small file fragments across the drive. When you access a file, the operating system must repeatedly query the file table to locate these fragments. This process creates a significant reduction in reading and writing speeds.
This fragmentation strategy is employed to prevent excessive wear and tear on individual memory cells, ultimately extending the lifespan of the storage unit.
Why Random Speed Matters
The nature of everyday files, such as games or web browsers, involves the non-contiguous placement of data within the SSD. Frequent addressing and querying the file table become necessary, leading to a drop in read and write speeds.
But why is the performance difference between SSDs and HDDs so vast? HDDs suffer from slower 4K random speeds due to their mechanical parts. In contrast, SSDs, free from moving components, experience significantly higher 4K random speeds. However, it’s essential to note that the performance leap between different generations of SSDs is not as substantial, such as when comparing M.2 PCIe 3.0 and PCIe 4.0 drives.
In practical terms, while sequential speed matters for installing large files like games, the 4K random speed plays a more pivotal role in day-to-day tasks, such as game loading times and system responsiveness.
So, the next time you’re shopping for an SSD, don’t focus solely on sequential speeds; pay close attention to the 4K random speed, as it’s a more accurate indicator of everyday performance and responsiveness.