In the times we live in, privacy is one of the factors that is most highly considered in the digital world. Being able to keep our information secure and encrypted is a crucial factor, and on this subject you have probably heard of PGP as one of the most widely used privacy systems in the world. In this article we are going to tell you what PGP is, how it works and why it is so important to maintain a good level of privacy .
When we talk about hardware devices, in many cases – and especially when we talk about storage systems – we are talking about compatibility with encryption systems, the aim of which is none other than to keep the data safe, making access to outsiders impossible. Likewise, the management of this data encryption and decryption is the responsibility of the processor , since the power of this will depend on the performance when managing this data.

What is PGP and what is it for?
It must be recognized: in this digital age, most users are entering our email on one and another website to “register”, we accept the use of cookies without reading or configuring their options and, in general, we are leaving an endless trail easily locatable by professionals. All of this is a trap for our privacy, and it is unavoidable because most websites require us to accept these small transfers of data in order to use their services.

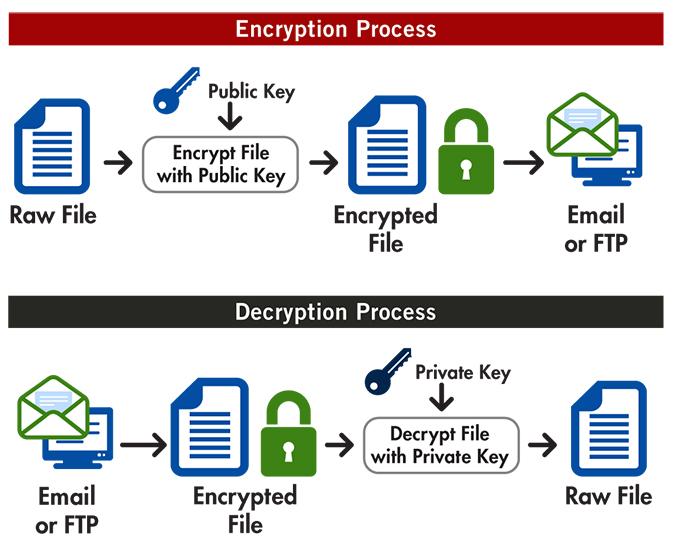
PGP is short for ” Pretty Good Privacy “, or “Pretty Good Privacy”, a system developed by Phil Zimmermann in 1991 and is currently the most widely used quality crypto system in the world. It is a system to encrypt and decrypt data in such a way that only by using a public key can they be accessed. This offers a protection mechanism for communications and improves their privacy.
PGP combines several processes to encrypt data: hashing, data compression, symmetric key encryption, and public key encryption. A public key is associated with a username or email address (which we enter when registering on a website, for example) and thus available to anyone, but the key to this is that PGP compresses the data and generates a unique random private key , used later to decrypt the information in a reverse process on the receiver side, thus guaranteeing the security of the information.

In addition, PGP also supports digital signatures , allowing you to verify the integrity of the data, its authenticity, and whether the person who originally sent it is really who they say they are. Likewise, this process serves to guarantee that the message has not been altered during the communication, thus guaranteeing the inviolability and security of the transferred data.
Where is this encryption system used and how does it affect you?
Actually PGP can be used in absolutely any communication system, even if it is not point-to-point (sender to receiver), and in fact it is especially useful in this case. It can be used to digitally sign a message and can be verified by the sender as authentic, to generate security certificates on websites (https), or even to verify the authenticity of an official document (digital signatures in a PDF, for example).
There is an open source variant of PGP called GPG or GNUPG (GNU Privacy Guard), which is already integrated into email clients such as Evolution (very popular in UNIX distributions). There are extensions for web browsers like Chrome or Firefox that allow you to encrypt your email data with PGP, as well as plugins to integrate this security mechanism into email clients like Thunderbird for the same purpose.
How does hardware affect encryption with PGP?
As we have mentioned before, all data encryption and decryption processes take place in the processor, or rather we should say that the processor is in charge of using the private key as if it were a dictionary, encrypting or decrypting the information.
Generally we do not know about it and it does not have a great impact on performance because normally there is not a lot of data it contains and the operation is performed quickly, but if instead of dealing with an encrypted email, for example, we would deal with a file several GB in size, then we would run into a huge performance impact, which as we say will depend on the processor and, to a lesser extent, on the RAM (since the data is temporarily stored there for the encryption process and decoded).