AMD‘s Vega GPU architecture brought with it numerous notable new features and features to improve gaming performance, but the one at the center of them all was the inclusion of HBCC . In this article we are going to tell you what this feature of AMD GPUs consists of, the benefits it brings and of course how it works.
When AMD launched Vega GPUs on the market, it placed special emphasis on this component, HBCC, thanks to which it promised an increase in the performance of some games of up to 50% in terms of average FPS and with a 100% increase in Minimum FPS which was a more than notable improvement and that set off all the alarms.
But before going into the matter, first let’s see what it is and what all this consists of.
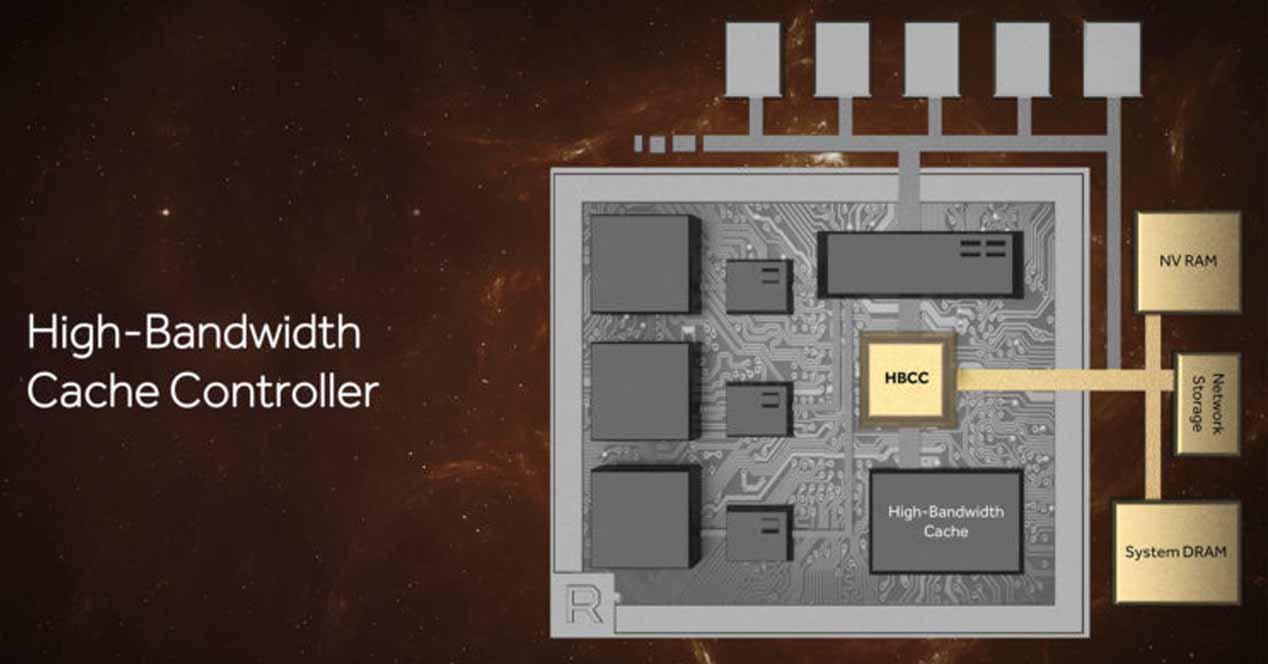
What is HBCC and how does it work?
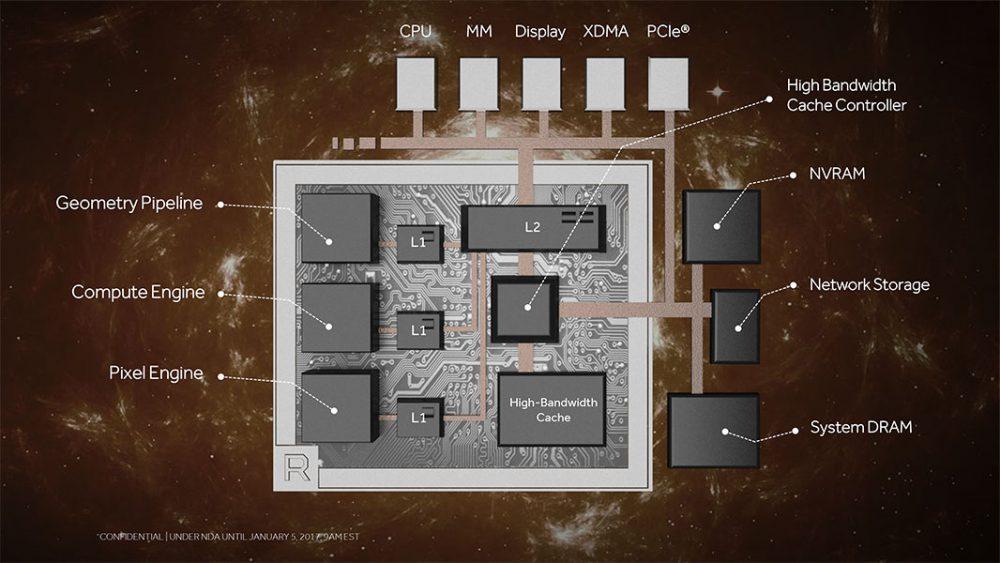
HBCC stands for “High Bandwidth cache controller,” or high-bandwidth cache controller. It is a complement to the framebuffer of AMD Vega GPU graphics cards that treats VRAM as a top-level cache, and takes some of the system’s RAM as if it were VRAM in return. Thus, when the GPU requests a resource but is not in the graphics memory at that time, the memory sections related to the request will be incorporated into the HBC (framebuffer) for faster access, while the unused data will be removed.
Of course, for this to work you need a controller, which is precisely HBCC built into AMD Vega graphics cards.
The bad part is that this is a mechanic that doesn’t work if the game developers don’t implement it in the games. Certainly, the efficiency of the GPU is maximized when the workloads are very high, but the second bad part is that it requires a large amount of memory (in fact 32 GB of RAM is optimal to use it in conditions, since in the Radeon Software configuration this section requires between 11 and 24 GB of RAM).
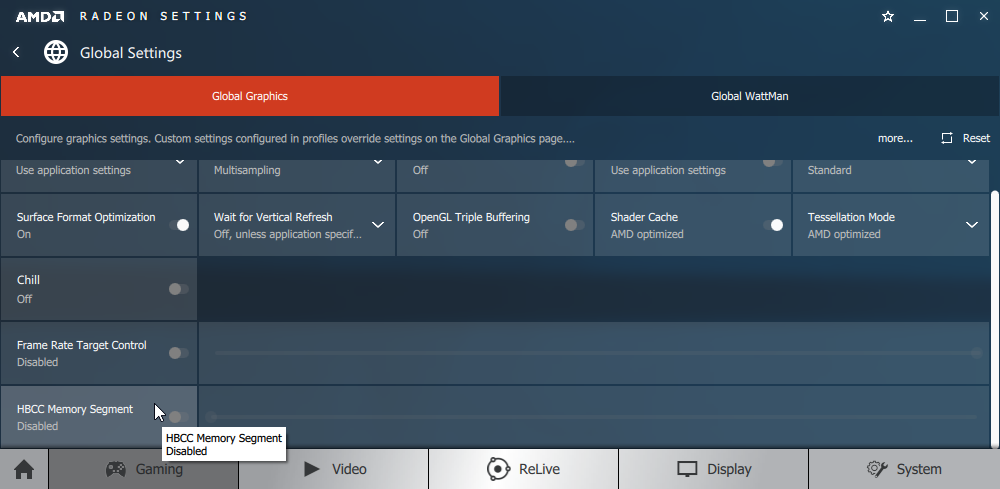
For this reason, in addition, HBCC is disabled by default in the Radeon Software options.
It is assumed that in the future this technology will reduce the graphic memory needs of the most demanding games, since as we have explained it uses part of the computer’s RAM.
How is performance improved?
As we’ve discussed before, one of the bad parts of this technology is that developers need to implement their compatibility in games, and certainly not too many are compatible. Yes there is a good handful, such as Deus Ex: Mankind Divided, Ghost Recon Wildlands, Rise of the Tomb Raider or Metro: Last Light Redux (basically those optimized for AMD), but the performance result is, as you will be able to appreciate then sometimes contradictory:
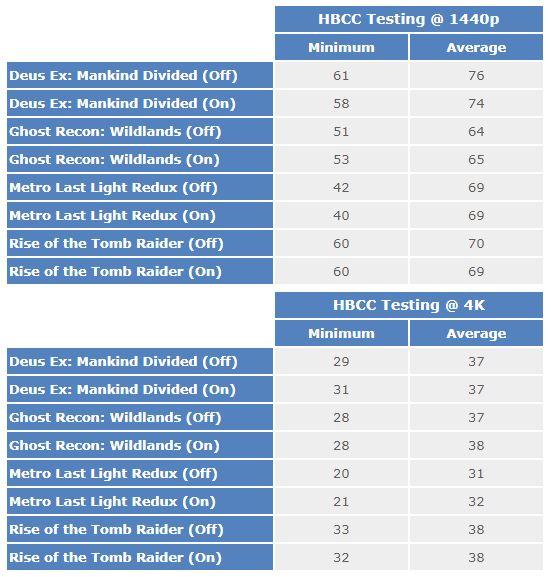
A clear example can be seen in Deus Ex at 1440p, where having HBCC enabled is even counterproductive since both minimum and average FPS are reduced. In other games like Ghost Recon: Wildlands, the FPS are somewhat improved, but the difference is certainly not too noticeable, and falls far short of AMD’s promise to improve the minimum FPS by up to 100% and even a 50% the average FPS.