When choosing a processor , many people may be overwhelmed by its specifications and do not know which one has the greatest impact on its performance . So, in this article we are going to explain what are the factors that have a greater impact on the performance of a processor, so that when choosing it and seeing its specifications, you are aware of the values in which it will move.
Normally, the more expensive a processor is when buying it, the better performance it will have. However, there are many times that in reality you are paying double for a CPU that really only has a performance 5 or 10% higher than its previous alternative, in which case you could have saved a lot of money if you had correctly identified its characteristics.
Next we are going to tell you how each of the main characteristics of a processor influences its performance.

How a processor works
As you know, the processor or CPU (Central Processing Unit) is one of the most important components when determining the performance of a PC. It is as if it were the brain of the system, the one that controls everything, and works (roughly) in the following way:
- When you run a game or application, the raw instructions are loaded from the hard disk into memory, and from memory to the processor for processing.
- When the processor receives the instruction, it executes its internal logic and computes the result.
- Once it finishes processing, it sends the result to the corresponding device.
It may seem very simple because we have explained it in a crude way, but really this occurs millions of times in a very short time, since a simple movement of the mouse implies that the processor has to process it, so a slower CPU will take time more to perform any action on the PC.
Features that affect processor performance the most
When we look at the characteristics of the processor, we can always look at the number of cores and process threads and their speed as the two main characteristics, but a processor has many more that we should also take into account. Let’s see what affects the performance of a processor the most.
Operating frequency
Also called “Clock Speed” or “clock speed”, since each processor is equipped with an internal clock that provides a functional “rhythm”. Clock speed refers to the number of operations that the CPU can perform in a single second.
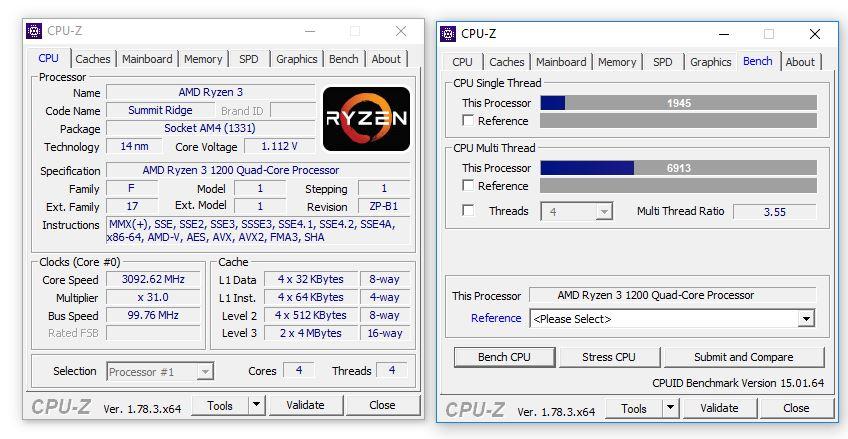
This is the number in Hertz (Hz), usually expressed in MHz or GHz that you will see next to the name of the CPU. So how does operating speed affect the performance of a processor? It generally affects single-threaded applications, and at the current time almost all programs are designed to take advantage of multi-core processors. In other words, a processor with more cores is worth more than one with less but faster.
Number of cores and process threads
Currently, both Intel and AMD have long had difficulties reaching or exceeding the 5 GHz barrier in their processors, and when they have succeeded, there have been few occasions and many of them in a single core and not all. Given these difficulties in increasing the operating frequency, processors increasingly have more cores and simultaneous processing threads (with HyperThreading and SMT) to be able to perform a greater number of tasks at the same time.
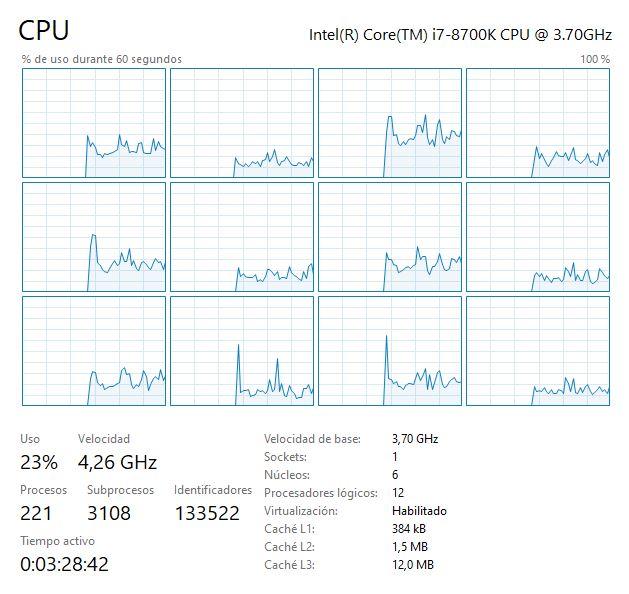
With manufacturers increasing the number of cores instead of focusing their efforts on improving speed, software and operating system developers followed suit, and most programs are optimized for multi-core processors. In this way, the number of cores and process threads is something that has become much more important now than before and, surely, today will be the most important factor in determining the performance of a processor.
Cache memory and architecture
By coexisting on the same die, the individual cores of a processor often share some resources, such as cache memory or interconnects to other elements, both to reduce manufacturing costs and improve performance.
In the 8-bit days, a PC’s RAM was fast enough to provide the processor with everything it needed, but as CPUs got faster and more cores, a new type of memory, called cache memory, so that it could measure up.
The cache of a processor is important because (and without going into detail regarding its types or speed ) it is where the instantaneous information of the calculations made by the processor is stored so that you can immediately get hold of them without having to recalculate them. again. In other words, the cache is not that it improves the performance of a processor, but rather it serves to alleviate the load on the processor (which ultimately affects its performance because it can be used for other things).
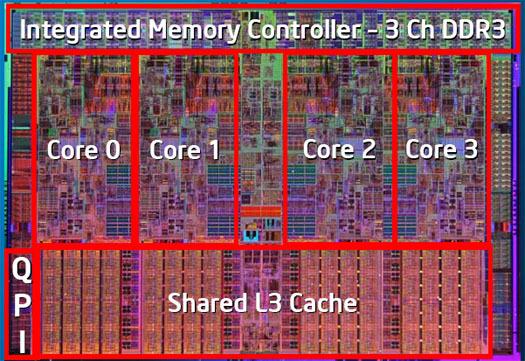
Of the factors we have mentioned so far, it is perhaps the least important, but it is also something that must be taken into account.
The same is true of processor architecture and lithography. With a better and more modern architecture, instruction sets are introduced to make the calculations more precise and require less work on the processor, and with a smaller lithography, efficiency is improved.
In other words, and to give an example, a ninth-generation Intel processor with two 3 GHz cores has a much better performance than another Intel 2-core 3 GHz but fourth-generation processor.