In the market there are a large number of LCD monitors, with all types of screens, different form factors and resolutions, which are a real dizziness for the novice user with acronyms such as WQHD, 4K, Full HD, HD, UHD , etc. In this article we will clarify what these acronyms mean, as each screen resolution corresponds to, as well as the types of monitors on the market that support these resolutions.
That is why we have made a small resolution guide for all the monitors that you can find at the moment in the market, and for this we have divided it into three different sections according to the form factor of the screen, either panoramic or ultra panoramic and without leaving aside those that are less used but also available on the market with a 4: 3 aspect ratio, based on the VGA screen resolution standards and derivatives.
Monitors with widescreen resolution

Widescreen monitors are those whose horizontal to vertical ratio is sixteen ninth or colloquially known as 16: 9. It is the type of screen most used today because television screens use this format, and here is a table with the standard resolutions of this type.
| Names | Vertical Resolution | Resolution | rec. 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|
| qHD or Quarter HD | 540p | 960×540 | Not |
| HD | 720p | 1280×720 | Yes |
| HD + | 900p | 1600×900 | Not |
| Full HD or FHD | 1080p | 1920×1080 | Yes |
| Wide Quad HD (WQHD) or QHD. | 1440p | 2560×1440 | Not |
| Quad HD +, QHD + | 1800p | 3200×1800 | Not |
| 4K, UHD, Ultra HD | 2160p | 3840×2160 | Yes |
True 16: 9 resolutions are considered those whose division by 8 in both height and width gives exact, and this is due to the fact that all screen drivers work in groups of 8 * nx 8 * n pixels when converting the image buffer and transfer the information to the screen through the HDMI or DisplayPort port.
As for the standard rec. 2020 refers to the resolutions that a screen must support to reproduce television content, so if you buy a television and plan to use it as a screen, it is very possible that it does not support the resolutions not supported by said standard or simply a few, being the more common of these the 1440p.
Finally, there are monitors with 2K resolution, which is 2048 × 1080; this resolution is not supported by the rec standard. 2020 but they have the particularity of being able to reproduce content in Full HD without problems.
Monitors with ultra-wide screen resolution

Ultra-wide screens are those with a ratio of horizontal to vertical resolution of twenty-one or 21: 9 , although there are screens with a 32: 9 aspect ratio that are called super ultra-wide screens .
This type of screen is not used for audiovisual content so none of them follow the rec standard. 2020, but they have the advantage of granting a larger work area and allow us not to be constantly minimizing and maximizing applications or making quick jumps between them with the tab.
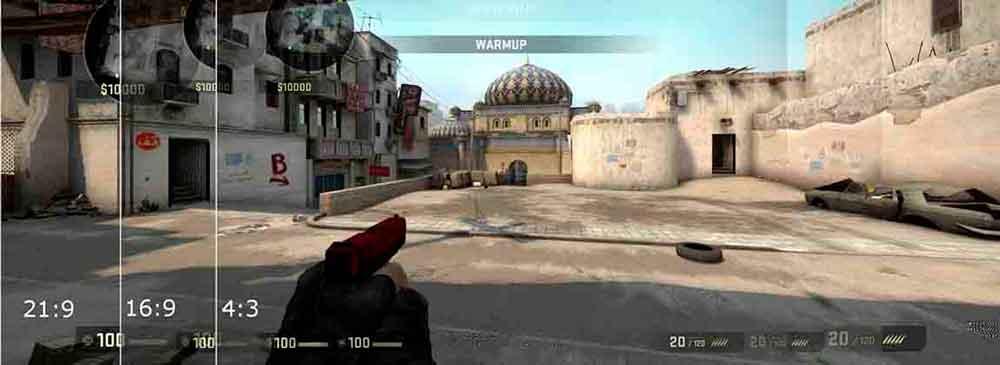
There are also games that support resolutions at 21: 9 and 32: 9, and although compatibility is not complete in all games with respect to these resolutions, it is one of the differentiating elements between the PC and the consoles, so if you have a ultra wide monitor you may find that your favorite game shows more of the stage in front of your eyes.
When building the 21: 9 and 32: 9 screens, what manufacturers usually do is take the panels for resolutions within the rec standard. 2020 and make them wider without varying the height, making the most common resolutions are the following:
| Vertical Resolution | 21: 9 | 32: 9 |
|---|---|---|
| 1080p | 2520×1080 | 3840×1080 |
| 1440p | 3360×1440 | 5120×1080 |
| 2160p | 5040×2160 | 7680×2160 |
Although we really find that the monitors on the market do not exactly support a 21: 9 ratio but rather 21.33: 9 or 21.5: 9.
| Vertical Resolution | 21: 9 |
|---|---|
| 1080p | 2560×1080 |
| 1440p | 34400×1440 |
| 2160p | 5040×2160 |
This is because a binary counter is used to control the sending of the pixels to the screen, much more difficult to implement with pure 21: 9 resolutions.
Monitors with VGA resolutions


Before the advent of LCD monitors, the quintessential standard for cathode ray tube ( CRT) monitors were VGA resolutions, which became the absolute standard for 4: 3 resolutions, although there are also VGA resolutions with Different ratios that have been adopted by different devices outside the PC, especially by handheld devices, in the PC world have always been associated with resolutions of four thirds.

The VGA output is an analog output, unlike those used today with HDMI and Display Port outputs, and this means that graphics cards had to carry a digital-to-analog converter, DAC, which in the process causes quality loss , which is not the case with the newer video outputs which are entirely digital. Another consequence of this is color, so it is possible that games and applications designed to be viewed on a VGA screen have slight changes in the color representation when displayed on a current screen.
What’s more, currently graphic cards do not have VGA output, but if you need to use a VGA monitor so that at a certain moment it can get you out of a trouble or you simply want to play one of those games of yesteryear designed for 4: 3 screens, you can choose one of those Display Port to VGA converters.

As for the list of VGA resolutions on the market, they are the following, but let’s not forget that most monitors have a 4: 3 aspect ratio, since resolutions with a different ratio were used in other types of devices.
| Name | Resolution | Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| QVGA | 320×240 | 4: 3 |
| Vga | 640×480 | 4: 3 |
| SVGA | 800×600 | 4: 3 |
| WVGA | 800×480 | 5: 3 |
| XGA | 1024×768 | 4: 3 |
| WXGA | 1280×768 | 5: 3 |
| WXGA | 1280×800 | 8: 5 |
| SXGA. | 1280×1024 | 4: 3 |
| WXSGA + | 1680×1050 | 8: 5 |
| HD VGA | 1368×768 | 16: 9 |
| UXGA | 1600×1200 | 4: 3 |
| WUXGA | 1920×1200 | 8: 5 |
| QXGA | 2048×1536 | 4: 3 |
| QSXGA | 2560×2048 | 5: 4 |
| WQXGA | 2560×1600 | 8: 5 |
| SXGA + | 3200×1800 | 4: 3 |
As a historical curiosity, the first HDTV panels to hit the market were actually converted VGA LCD panels with a native resolution of 1366 x 768 pixels in total, which used to incorporate a VGA input in addition to the RCS ports for the signal. from TV. With the standardization of HDMI first and DisplayPort later, the VGA port disappeared from most screens and became part of the past, but we must bear in mind that it was one of the longest-lived ports in history and lasted almost on PCs. Two decades.