One of the most unknown elements that exist within our PCs: they are processors that are integrated within the CPUs of our PCs, and whose job is supposedly to provide a reliable environment, or “trusted” in English. But what does this mean and what consequences does it entail? We explain what this processor is and its relationship with the negative execution rings.
From the point of view of IT companies, the fact that a platform is reliable has nothing to do with what we traditionally understand as IT security, but with control methodologies based on making sure that the environments are legal. In other words, that the user is running an operating system and the applications they have purchased are not pirted.

The running rings and their function
When the implementation of multitasking operating systems became necessary, CPUs evolved to include MMU units that were responsible for controlling access to RAM for both the operating system and the applications.
In order to isolate the sensitive parts of the memory, from 80386 onwards the execution rings were added, which delimit four privilege levels for the software, which go from level 0 to level 3 and from higher to lower rank of privilege.
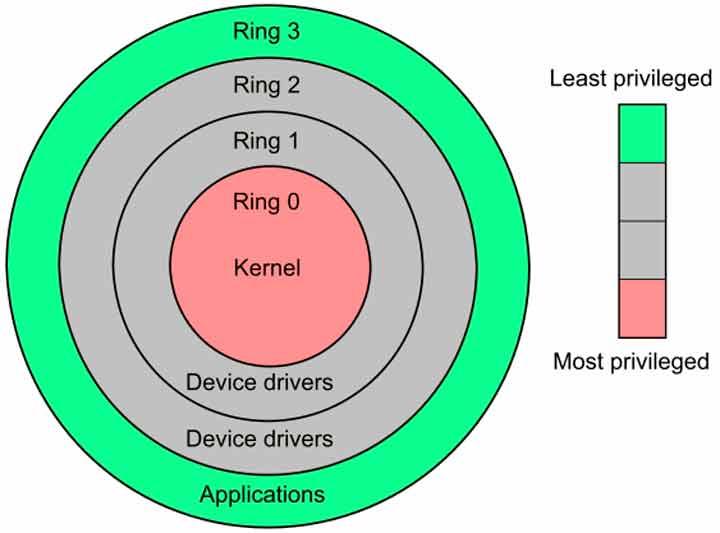
Each process executed by the CPU has an associated privilege level, in such a way that if the CPU is executing a process with a privilege level 3 then it will not be able to access the memory addresses associated with rings 2, 1 and 0. But On the other hand, a process that executes in ring 0 will be able to access rings 0, 1, 2 and 3 due to its greater range of privileges.
As a curiosity rings 1 and 2 are not usually used in Windows and Linux, these operating systems only use 0 and 3, and certain virtualization programs such as VirtualBox, VMWare and the like usually take rings 1 and 2 for themselves.
Negative Run Rings

Actually, there are no negative rings, in the case of the execution ring -1 it is a nickname given to the virtualization function of the CPU that allows you to run a hypervisor capable of running several operating systems at the same time.
As for the execution ring -2, it refers to the system management mode, which is an operation mode that exists from 80396 onwards, it is executed when a special type of interruption called SMI occurs, then when this is being executed. break all related code runs in the highest privilege mode of all.
Because this can be exploited for the execution of malicious software, since it is only necessary to activate such an interrupt and execute said software in the middle of that interruption. Actually, it is not an easy thing to do, but the possibility exists and this is what forced both Intel and AMD to find a solution to the problem.
A computer inside your computer’s CPU: The AMD PSP and the Intel ME
The solution they came up with? Create an additional element of control, a separate processor in charge of verifying that all the software that, between this signed, something that results in a huge nonsense in the PC world where the development and distribution of programs is completely free and open but that It “prevents” the remote control of our computers by malicious elements, but which in turn results in another back door.
These processors are found in all PCs in the world with x86 architecture, they have privileges that correspond to ring -3 within the system and therefore are the ones with the highest hierarchy of privileges, in the case of AMD, this processor is called PSP (Platform Secure Processor) and in the case of Intel it is the ME (Intel Management Engine).
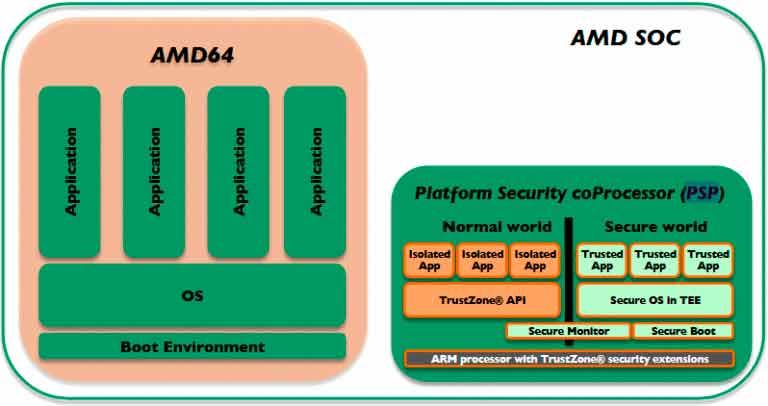
The privileges and functions of both the PSP and the ME are basically the following:
- They have full access to the system RAM independently of the main CPU
- They have direct access to the TCP / IP stack and network interfaces.
- You can send / receive packets over the network, even with the OS having this banned.
- It is active when the computer is hibernating and when the rest of the system is off.
- You can take control of your computer remotely via the internet if you get control over them.
However, although they both perform a similar function, they are both two distinct hardware implementations. While the AMD PSP is a Cortex A5 CPU, the ME is a classic Intel Pentium, that is, we are talking about an x86 inside your x86.
Actually, they work as spies inside our computers, which are not directly accessed in a normal way due to the fact that both the PSP and the ME completely block access from the other execution rings of the system to their area. privileged. There are supposed to be ways to deactivate them, and we say it is supposed because we cannot check when these units are active.