Despite the fact that RAM memory management has been greatly improved with Windows 10 , the operating system is quite “lazy” (for being benevolent) when it comes to telling users which programs or services are consuming RAM. of the system. Fortunately, there are free programs like RAMMap to be able to know in detail the consumption of the system’s RAM memory , and in this article we are going to tell you how to use it and interpret its data.
If in Windows 10 you want to know how much RAM memory the programs that you have open are consuming, it is quite likely that you are left with the doubt because the consumption shown does not correspond to the real one. For example, this is what the Processes tab of the Windows 10 Task Manager shows, sorting programs by the amount of RAM they are consuming.
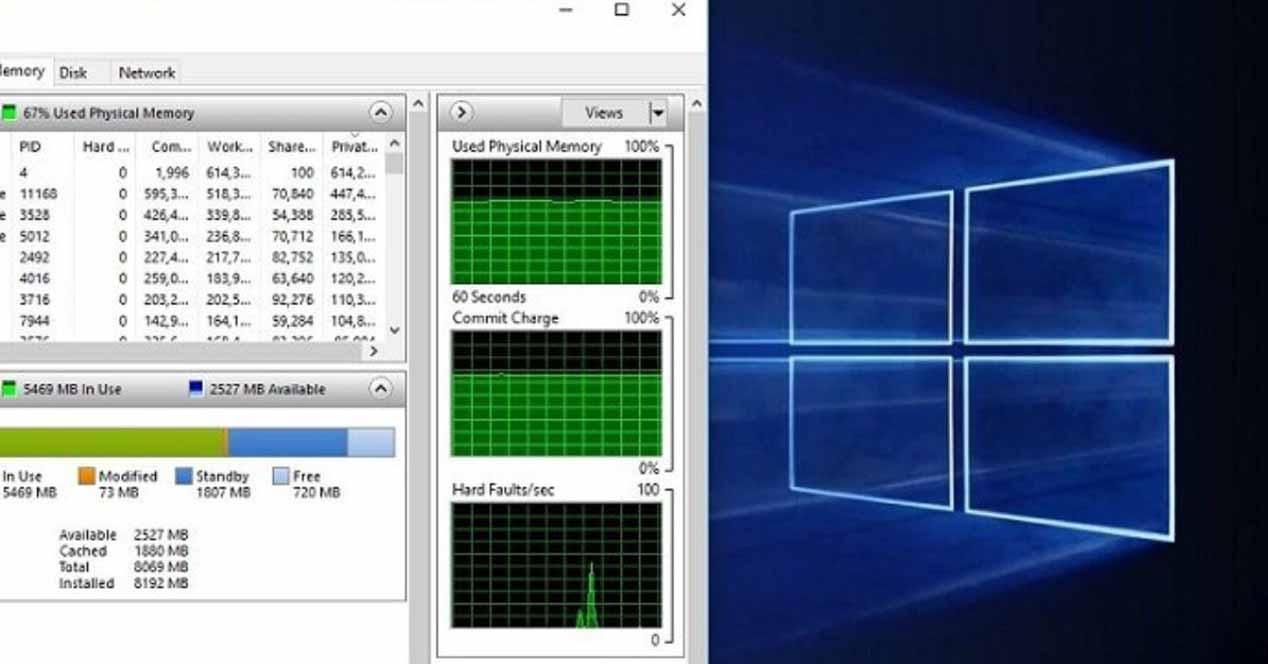
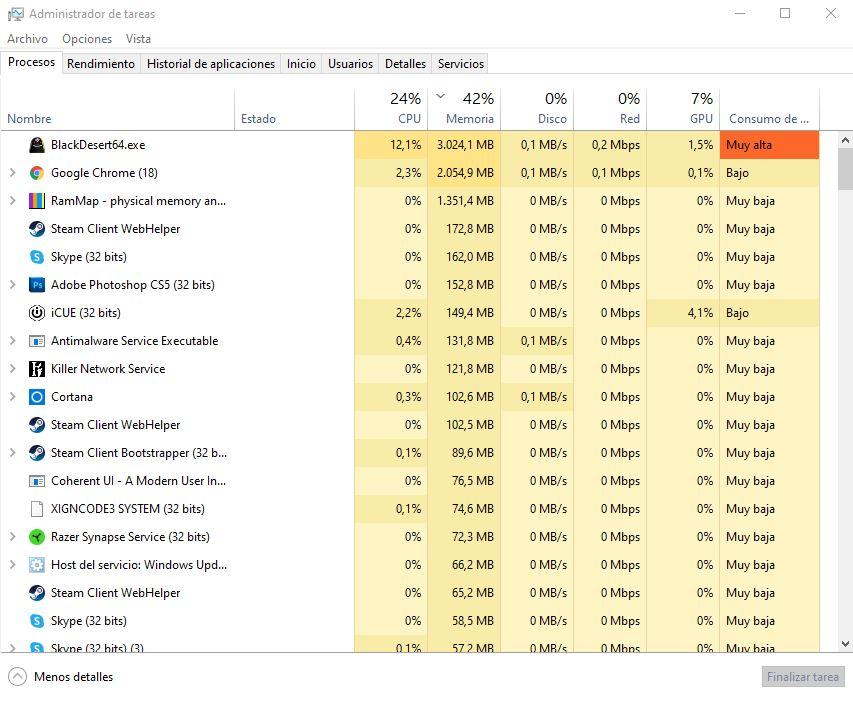
If we add the consumption that appears here with all open programs, we will have as a result that, in theory, around 9 GB of RAM are being consumed, and yet in the performance section it tells us that we are consuming about 14 GB of RAM memory right now.
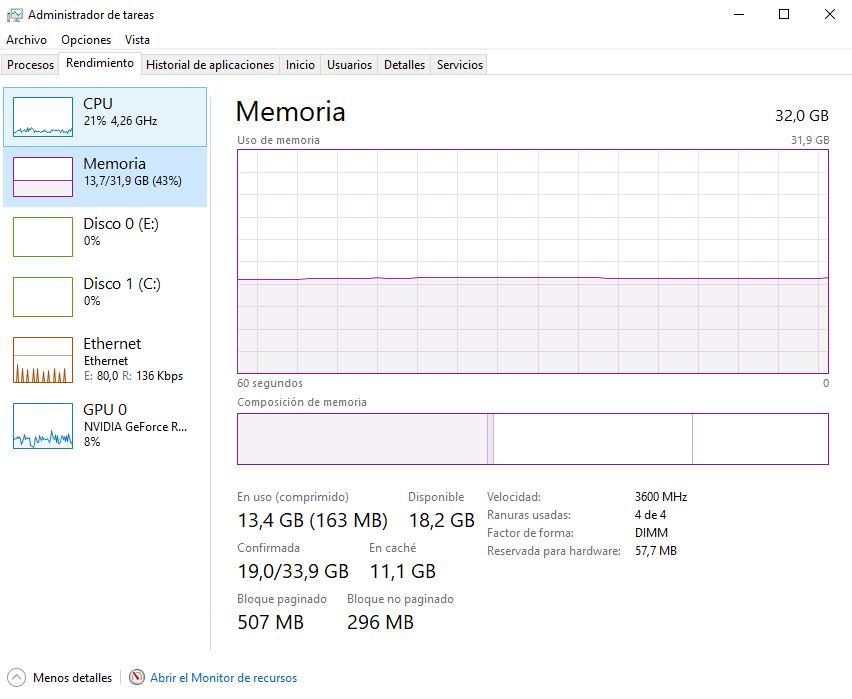
Why is there such a large discrepancy? How can you know the actual consumption of RAM memory of the system? For that there is RAMMap, and then we are going to show you how to use it.
Know the real consumption of RAM memory with RAMMap
RAMMap is a tool belonging to Microsoft‘s Sysinternals suite, and its download and use is free for all users. To download it, you simply have to access this web page and click on “Download RAMMap”.
You will download a compressed file, which obviously you will have to unzip in a directory on your hard drive, and execute the file RAMMap.exe. This will be what you will see initially.
This software is actually intended for developers and engineers so that they can develop their applications and programs, but it can also give us very useful information for users. To do this, the first thing you should do is go to the “Processes” tab, where all the processes that we have currently loaded in memory will be detailed, including services. We recommend sorting by the “Total” column, simply by clicking on its name, so that we will see at the top the processes that are consuming the most memory.
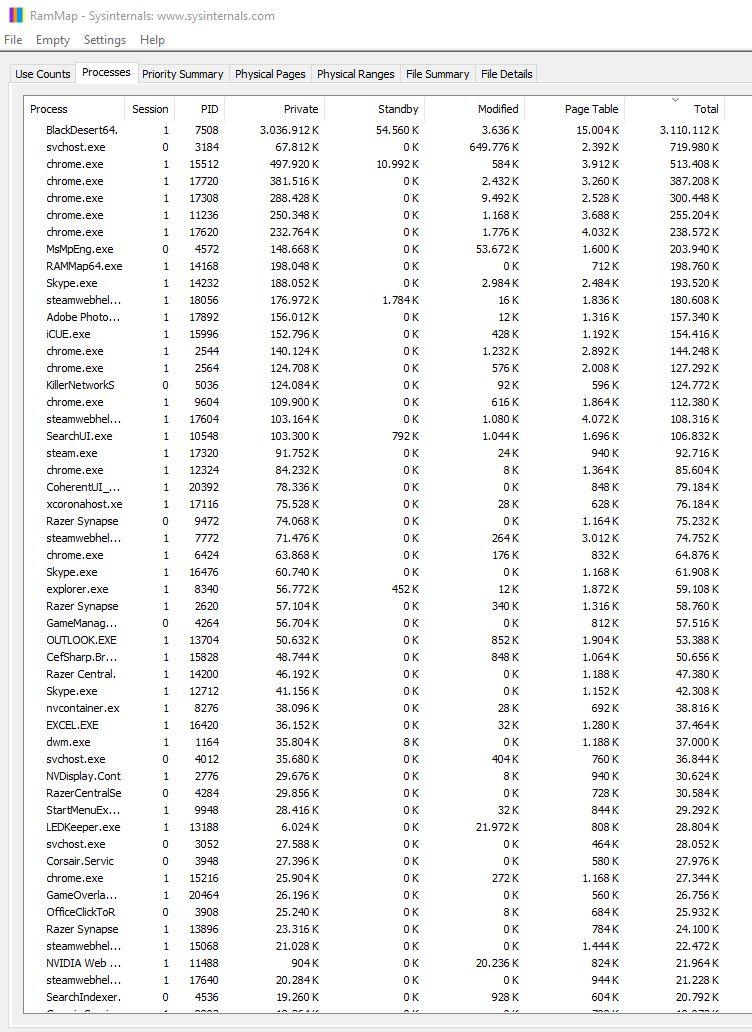
Here we have the detail of EVERYTHING that is loaded in the RAM memory of the equipment, and in fact here if you add the entire column Total it will give you the real consumption of RAM memory of the system, since it is adding both the assigned memory and the reserved one, as well as the busy one in the system paging file.
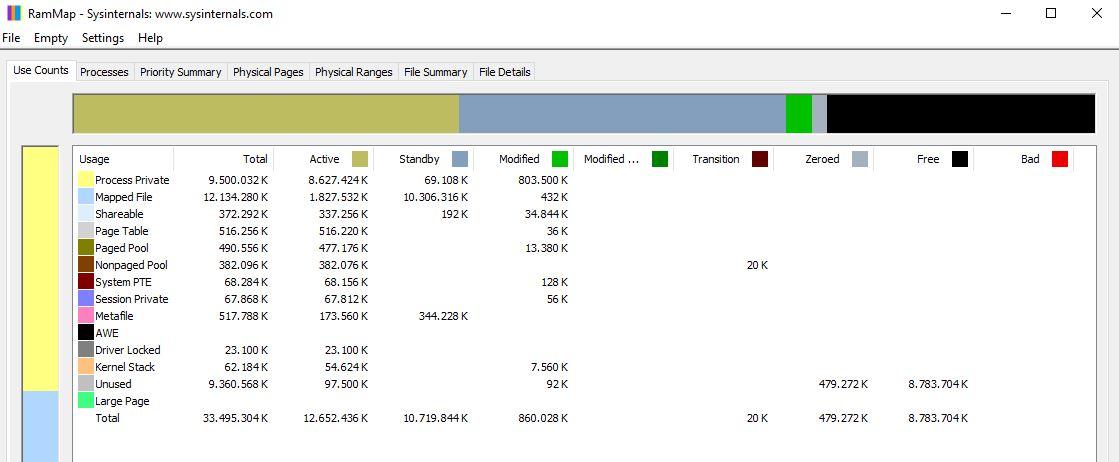
We can see the same thing in the first tab, the one called Use Counts that we had at the beginning, where the total memory is shown. Here we are essentially interested in three columns:
- In the Total, we can see the total memory available in the system and how Windows is allocating it.
- In Active, we see the memory that is currently being consumed by all applications and services.
- In the Standby we can see the system memory that is allocated but waiting, and this Windows does not count it as “consumed”.
If you look, here we do have the 13.7 GB that was shown before in the Performance tab of the Task Manager.
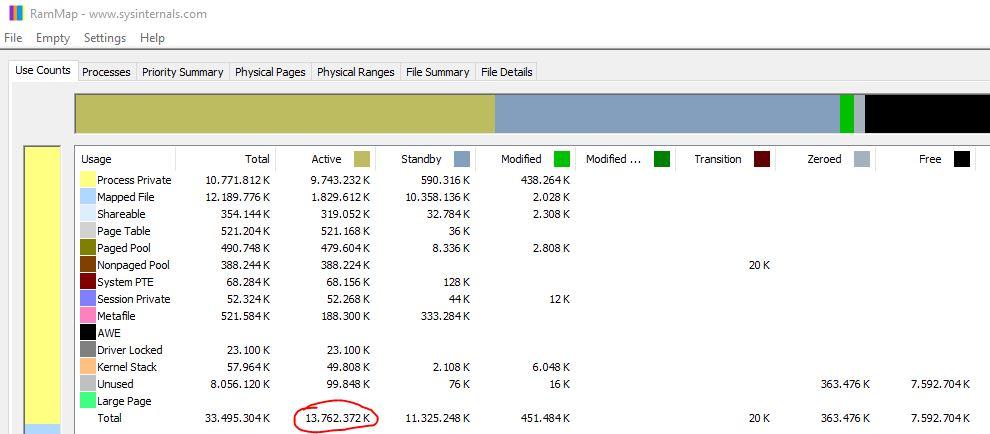
Here you can also acquire a much deeper knowledge of how Windows 10 manages RAM memory. In this example we have 32 GB of memory installed, and there is 13.7 GB in consumption (Active) but Windows has assigned another 11.3 GB (Standby ), so in reality there is about 25 GB of memory occupied, and only 7 GB available (this is reflected in the Free column).
As you can see, RAMMap will provide you with much more detailed information about what is consuming the RAM memory of your computer, and it can be especially useful if at any given moment you run out of RAM available in the system and you don’t know why.