
The first time anyone uses any Android device, the most normal thing is that they start installing dozens of applications for their day to day life and accept all the necessary permissions to use it (camera, contacts, microphone, etc.). Even, on many other occasions, there are people who leave several apps installed which they stopped using a while ago.
The main problem with this is that all kinds of permits are granted to which, in most cases, not much attention is paid. But, in the case of having given certain permissions, or simply having certain suspicions about all those privileges that have been granted, there is always the option of being able to remove the permissions .
The importance of controlling permissions
Always have control of the permissions that are granted to the various apps that end up being installed on the mobile. A fact that should be fundamental because it could affect our own privacy and security . And although at first glance it is simple, not everyone wastes time on it.
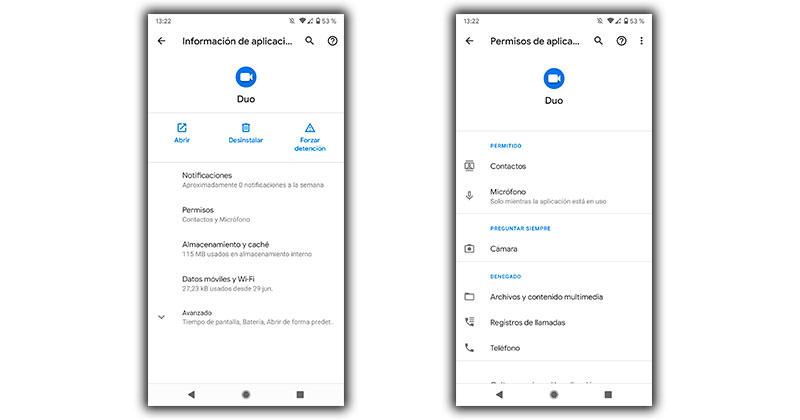
Many security experts alert to this problem. And for that reason, Google itself has launched different automatic tools to control this aspect. So, today, when you download any application found on Google Play, you will be able to see all the information or functions that said application will have access to . That is, we will see the permissions that we are going to grant to said app that we will install on our smartphone
In addition, each permission that is granted is different, but all of them should be in line with the use that is going to be given to the application. What does this mean? Well, it will not make any sense and it will even be suspicious by the app that, for example, an image editor requires access to our microphone if at no time it is going to have to be used to edit a simple photograph. However, here we will show you the permissions that applications usually require on mobile devices:
- Body sensors
- Calendar
- Camera
- Contacts:
- Location
- Microphone
- Telephone
- Text messages
- Storage
The big change in management
In the old versions of Android, the user could review these permissions and decide whether or not to install the application, everything will depend on what each one considers appropriate. But, as of Android 6.0 Marshwallow, any user could choose which permissions to accept when starting the application for the first time on their mobile.
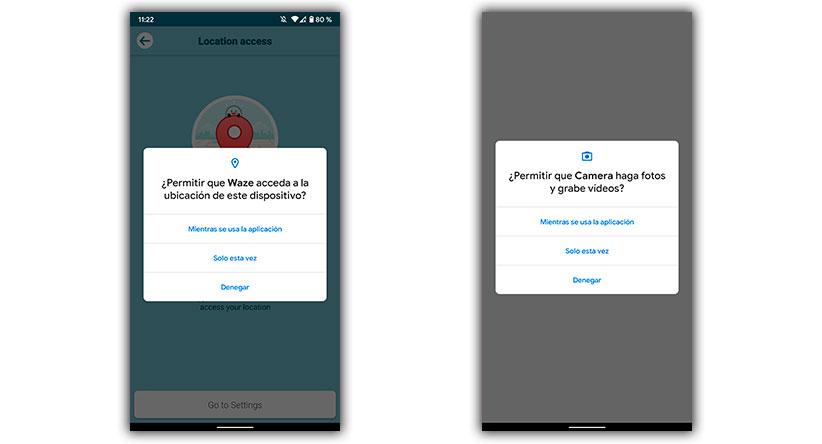
However, one of the events that changed the landscape of permissions was with the arrival of Android 10. From that moment, the permissions to remove appeared. And it is that, instead of giving permission to an application to access your location or the microphone while the app is installed, you can grant a momentary permission while the application is used.
And that’s not all, since from the version of Android 11 , the permissions for the location in the foreground or background are given. Although, Google continues with its policy of restricting access to special permissions in Android 11. So, for example, users cannot give you permission to access the location in the background in the normal way, but will have to do it from the settings of the system itself.
How to disable permissions
The easiest way to see what permissions have been granted is as follows. We will have to directly open the list of all the permissions that the Android device has , such as body sensors, location, microphone … After this, we will discover how many applications installed on our mobile have access to that specific permission. And it is that this method is the fastest to know what are the permissions that the applications have.
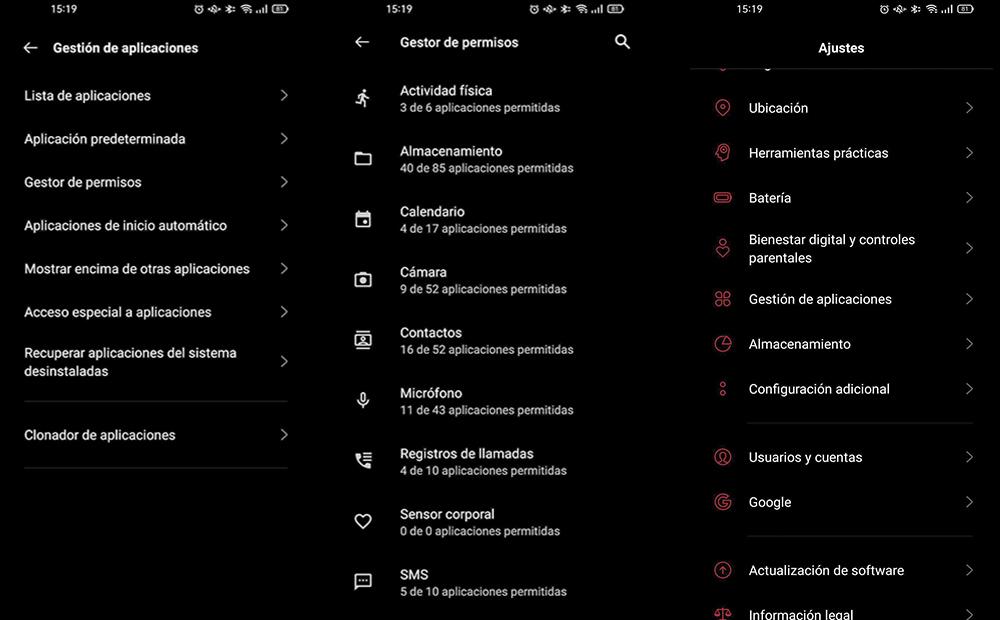
However, there is another slightly longer way in which we will see application by application what permissions we have given. And it is the following:
- Open the “Settings” application.
- Tap “Applications” or “Application Manager” (although this option may vary depending on the smartphone).
- Once inside, touch “Settings”> “Application permissions” (if you cannot find this option, you may have to touch “Privacy and security”> “Application permissions”.
- Finally, you can now touch any permission. And you will only have to activate or deactivate said permission. In the case of appearing in color, it will mean that it is activated. But if it is grayed out, it means that it is disabled.
Change permission settings
As we have mentioned before, the permissions can be changed at any time and set the required permission. Therefore, beyond giving all the permissions that any application requests, the permission that each user requires for an exact moment can be granted. What is positive about this? Well, we will avoid giving permissions to an app of dubious origin that always requests access to the camera, location or the multimedia content of our terminal.
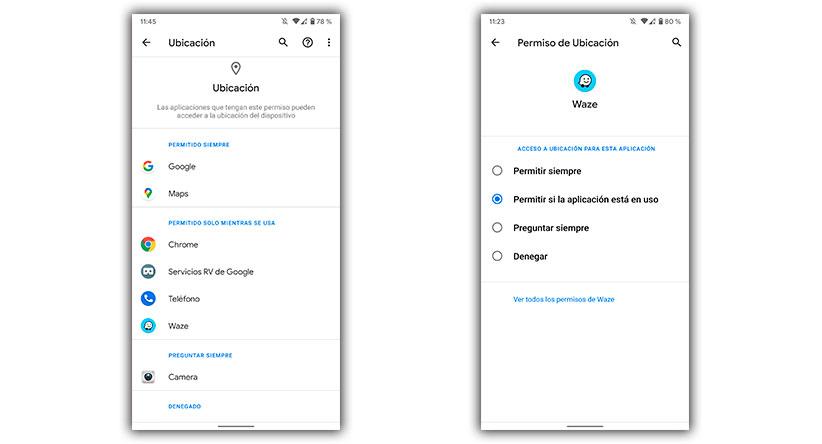
And in the case of doing so, you will have to ask us before. To configure this measure we will have to enter “Settings” / “Applications” / ” Permissions manager “. Inside, we will see all the requested permissions. Also, within each app we will see the following:
- Always allowed.
- Allowed while wearing.
- Always ask.
- Deny.
Permissions can change on installed apps
Something that many users are unaware of is that the permissions of the apps that are installed can vary over time. This will depend on whether or not you have automatic application updates activated.
In the event that you have an Android superior to Marshmallow, which will be the most common, you will not have to review or accept the permission changes for the application to be updated. This means that the first time you are going to use an app function that uses a new permission, it will give you the option to allow or deny the use of that data or those functions .
Although sometimes it is better to review each update manually, to be able to guarantee that they cannot invade our privacy. Therefore, it is important that you have a regular control of these updates and permissions.