Compressing images is essential in our day to day if we want to upload them to a web page or a blog but we are also concerned about storage on the mobile phone or tablet if we have excessive photographs. But imagine how important it is for platforms that have thousands or millions of photographs or images that have to be stored with quality but without being overweight. That is why HEIF or AVIF, among others, are born.
JPEG was born more than twenty years ago and it is a format that we all know and use practically every day but there are many companies or developers that seek to improve the global format and bet on other options that solve the disadvantages that it entails, such as the loss of quality . In order to become the most used and most useful, there are many photo formats and codecs that we see …

What is AVIF
To understand what AVIF is we must first understand what AV1 is. AV1 is an open source codec that means AOMedia Video 1 and whose objective is to compress videos and images so that they occupy less but the quality remains the same as always, without getting lost in the transformation. The format and content are not varied even if it is compressed using this codec supported by large companies. AVIF stands for AV1 Image File Format . That is, it is the image format of AV1.
AVIF is an image compression codec that is supported by the Alliance for Open Media , born in 2015, and aims to be the free (open source) and free alternative to HEVC. It is a codec that allows to compress images and make them ten times smaller than a normal JPEG but without losing the quality and without losing the details, being compatible with HDR. It is capable of compressing without loss but it is still a codec that is under development and is expected to improve in the coming years.
Beyond supporting HDR, it also supports color depth in 8.10 and 12 bits although it does not reach 16 as HEVC, which we will see in the next paragraphs. It supports monochrome channels and can be used for both photography and video, making it very interesting and practical. It also uses the HEIV file container. In addition, as we say, it supports compression with or without losses as we need. It has the union of all the advantages of all the formats but being open source and that is why it seems to be predestined to success although it is still early and is hardly compatible with devices, browsers or programs. For now, it begins to have support within Google Chrome and soon there will be many options.
Applications
As with AV1, which is used by large companies, AVIF is also becoming the bet of some like Netflix. For example, Netflix has thousands of covers of all the series, movies and documentaries they offer and from our mobile we have to upload all those images. That is why it is important that they are compressed but it is also important that they maintain the quality, that they are faithful to the colors or the luminosity so that the user sees them correctly without loss. For example, we can see the difference in the images on the cover of The Adventures of Puss in Boots. In JPEG we have 69,445 bytes and in AVIF we get 40,811 bytes. As can be seen in the photographs, the difference with AVIF is barely noticeable and it does with JPEG. And even then, it takes up much less.

What is HEIF
The acronym for HEIF stands for High Efficiency Image File Format (or High Efficiency Image Format) and is developed by MPEG, introduced in 2015 in its final version and uses the HEVC video format for understanding. We can find it with two different types of extension like .heif and like .heic.
It is a container photography format. That is, a photo format that can store images and their metadata so that they can be encoded in any format. It stores individual images or metadata but also image sequences that allow us to reproduce them as animations.
In addition, it has been launched as a future substitute for JPE G as it offers us the same quality in half the space. HEIF is capable, according to MPEG, to be more efficient than JPEG. In less size we have the same quality with greater bit depth. And another great advantage is that HEIF is that it would allow us to edit without destruction, as we can already do with images in RAW format, the favorite format of expert photographers. Also HEIF would allow us to apply transformations without rendering the file and it supports images with 16-bit color depth, so we could have almost the same information as the aforementioned RAW but taking up less space than these.
Applications
Apple has been betting on HEIF since 2017. The Cupertino company has been working with this format for years and has given it very interesting uses, such as the well-known Live Photos, for example. But it is not the only one because Microsoft also has support for the format to give birth to Windows 10 and we can also see this type of images on Android. Although, as we say, the most common is its use on Apple devices, but we can also edit or use it in known programs such as Adobe Lightroom or GIMP , one of the most popular Photoshop alternatives.
One of the uses of HEIF allows us to save storage on mobiles, tablets or memory cards but also helps us with image processing. And, above all, this understanding of images is beneficial for loading times on web pages that store a lot of content. Of course, it is essential that browsers include compatibility with this format to be able to see it correctly.

Where they come from
As we explained at the beginning, the image compression codecs are born from the AV1 and HEVC video codecs. Two video codecs that are intended to compress and decompress multimedia files without altering the quality, thus achieving a balance between quality and weight, that we have a good quality but without taking up too much. This is especially useful and that is why some streaming platforms such as Netflix already bet on these systems.
The main differences between the two lie in understanding, compatibility and free. AV1 and HEVC differ in reducing their size , the first being more interesting if we want to compress more. For example, with the AV1 format we would have a video of about 10 GB with the same quality that we would get with a video in HEVC format but it would occupy 12.5 GB. It may seem like a minimal comparison but it influences the case of platforms that host thousands and thousands of videos because the size will constantly multiply.
The other two differences are its compatibility and gratuitousness. AV1 is an open source codec so it is free. HEVC does not and requires royalty payment . In terms of compatibility, HEVC has been available for a longer time and that makes it more widespread that AV1 will be gaining ground thanks to the massive support of many of the big technology companies around the world.
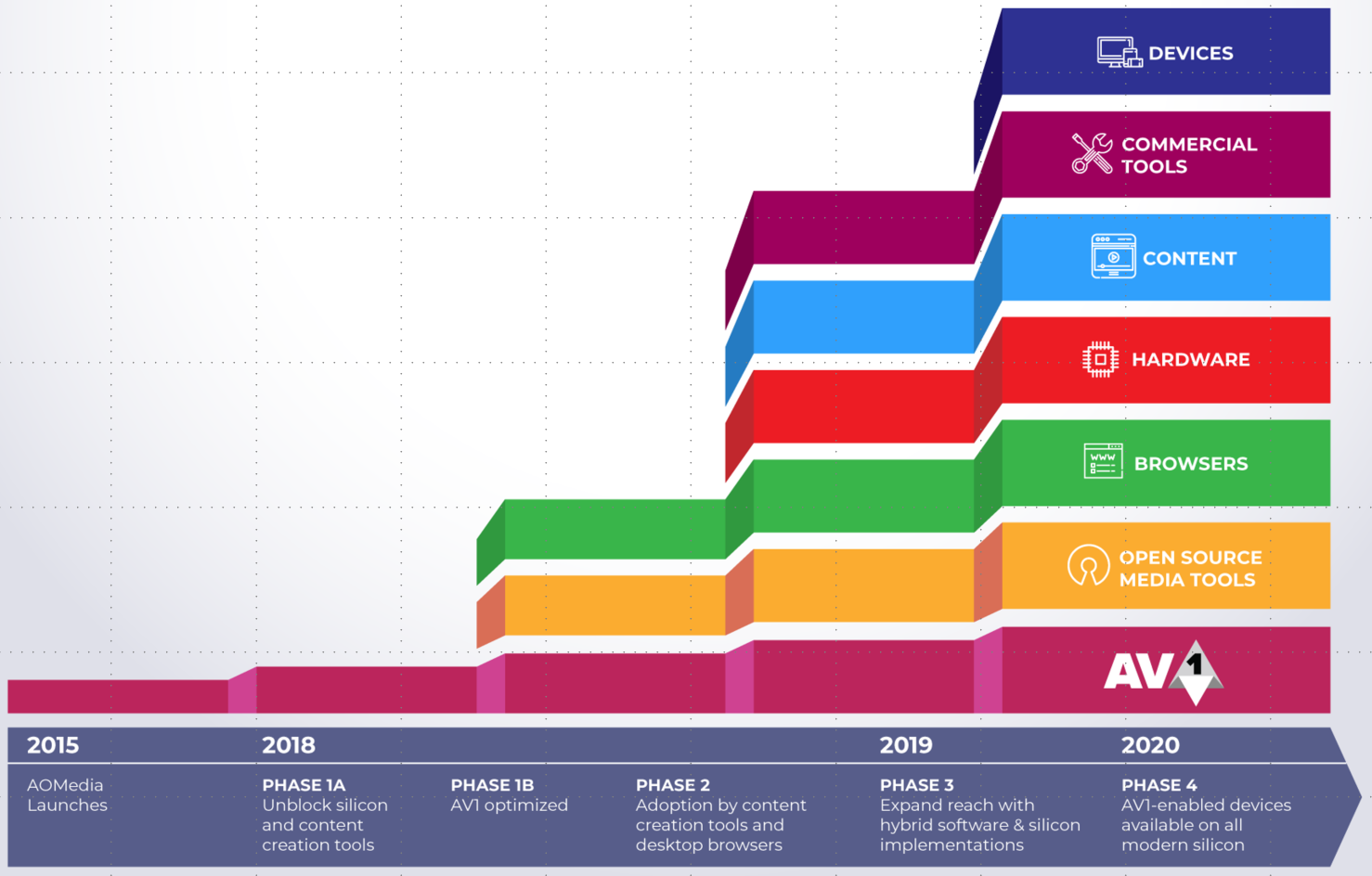
What do we expect from them?
Although currently HEIF can be considered to be more widespread, AVIF seems destined for success and everything indicates that it will be a format that has come to change everything. Its compatibility is expected to be global in a few thanks to the fact that, like AV1, it has the support of companies such as Google, Amazon or Microsoft. But, in addition, it is an open source format and does not require paying for it. Of course, at the moment it is under development but everything indicates that it will be compatible with browsers and companies are already working to make it become the future. We will have to wait to see how it evolves.
The future points to a change in standard, since JPEG, with more than 20 years, seems exhausted and surpassed by other new formats. New technologies, which increasingly demand more quality and less weight, demand a new standard, a position for which JPEG cannot be presented as competition. It remains to be seen who will be the winner of this battle, but AVIF and HEIF will have a lot to say in the coming years.
Other photography formats
HEIF or AVIF are here to be the future but they are not yet the present and JPEG is still king. Many people want to replace JPEG with improved codecs, container formats, etc. But it is still the most widely used and widespread format. JPEG is a format that makes automatic adjustments to photos you take with your mobile phone or camera.
These settings allow the image to be compressed and take up less, but you can also delete or modify details and they cannot be recovered later. At a professional photography level, the image does not come out stored as you have done, but parameters such as saturation or white balance are adjusted and you cannot recover the original format. Another small drawback is that editing is destructive: every time you edit a JPEG image and save it, the file loses information and the quality decreases.
Beyond this drawback, the JPEG format is very widespread and allows access from any program, browser or device. In addition, they are photographs that occupy little compared to others such as RAW , for example. It is expected that it will be replaced in the future because AVIF promises to give us images that do not lose information and that occupy less, but compatibility will gradually increase.
WEBP, PNG, BPG …
WEBP is an alternative to JPEG that has had more development in recent times than the others and is already used by web browsers. It is developed by Google and uses the VP8 video codec. Save 30% space if we convert an image from PNG or JPEG and allow lossless compression. It is, at the moment, the most evolved alternative to JPEG, although it still has to solve many problems, such as the possibility of opening your files with traditional image editors.
Another of the formats that seemed to come to end the JPEG was the BPG, which however has remained stagnant and has been overtaken by new appearances, especially by HEIF, with whom it has many similarities but is already clearly inferior.