In an SSD as a general rule we value certain common aspects such as its reading and writing speed, durability, temperature under stress and above all its price. But there is a much more determining and important factor of the same that is not mentioned and although it is always in the shadows, it is important that we know it to understand who is the boss in the hierarchy. What is FTL?
If the type and number of NAND Flash as well as its cells is important in any SSD, be it SATA or NVMe, FTL is the same or more important than these and instead nobody talks about it. Can you imagine not being able to format your own SSD? Well this is just an example of what this system is capable of doing for us.

Cannot understand any device with NAND Flash on desktop without FTL
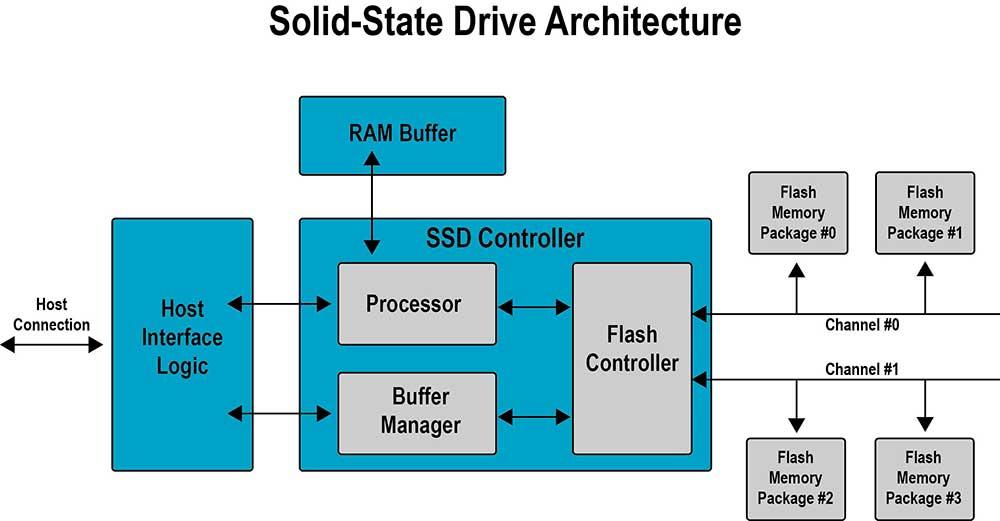
FTL is an acronym for Flash Translation Layer or translated into our language as a translation layer for Flash . This is so important because it is a layer of hardware and software that is located within the controller of each storage device that is based on NAND Flash.
This includes of course any type of SSD, flash drives, SD cards and, in short, devices based on memory cells as such. FTL is so important that many of the features added to SSDs are performed by it, where it is largely to blame for the performance of solid state drives as well as their lifespan.
It is true and it must be pointed out that there are two types of FTL as such, those that are integrated into the SSD and those that are on the host side, but the latter are as a rule very little used for a number of reasons that we will understand. continuation.
NAND Flash management and administration
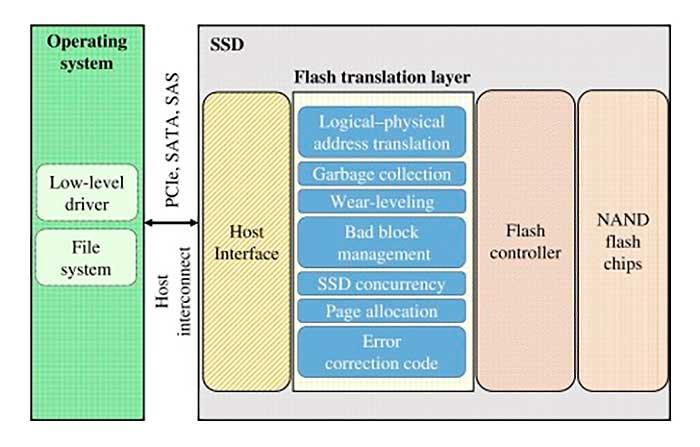
What an FTL basically does is perform the essential NAND Flash management processes of each SSD, where they do it redundantly and it is superimposed on the host’s own file system as such. Thus, they perform tasks like address translations (both logical and physical and between them), manage bad blocks, and if the SSD is over-provisioned it uses the new cells instead, takes care of the error correction code or ECC , collects the trash left by the SSD or levels the wear of it.
Although as you well know these functions we have seen separately, it is the FTL that is responsible for carrying them out. It is so important that once all these functions are performed and there is an evident decrease in performance due to all that they entail, it is the FTL that manages to return the performance to the cells so that we do not notice this drop.
In fact, the majority of SSD failures or simply breaks are due to a poorly implemented FTL by the manufacturer, which motivates us to keep a nice paperweight until the possible processing of the guarantee. Although for a normal user this will not happen in the middle of 2020, on FTL servers it is not as beloved as on the desktop, mainly because it adds a whole series of tasks that are compiled by hand and that add latency with the host.
This is why some SSD manufacturers determine not to include FTL in their business models, which makes sense for such environments if they are extremely controlled.