The FPGA market is extremely complex, but to learn Verilog or VHDL it is not necessary to make use of a complex FPGA with hundreds of thousands of logic gates and with a really high price it is worth it with a very simple one. That is why if you are newbies we are going to give you a series of tips when choosing your first FPGA
One way to learn something is to develop that something, something that FPGAs allow us thanks to the use of hardware description languages, which allow a C-like syntax to describe each and every one of the logical parts of it. FPGAs, unlike microcontrollers, do not run software but behave like hardware itself.

The advantages of FPGAs

One of the advantages that FPGAs have compared to microcontrollers is their enormous power and versatility compared to microcontrollers. With an FPGA we can have a piece of hardware that we completely need from its specification, since we make the FPGA behave literally like that piece, we can even make it behave like several different pieces at the same time.
But to program them it is necessary to know a hardware description language such as Verilog and / or VHDL, which cannot be learned if we do not have a support platform and an FPGA that allows us to test the code as we learn to handle these hardware description languages.
FPGAs are tied to their manufacturer

You have decided to learn VHDL or Verilog, for this you have a book with lots of examples to learn. In which they recommend a specific model and our recommendation is that you pay attention to the letter.
The reason for this is that those teaching books have tested the code with a specific model and do not guarantee that it will work with a FPGA from another brand and in some exercises they make use of exclusive elements of that board.
This means that if, for example, you choose a model from Altera, Xilinx or any other brand, you will be trapped for life in their development tools and policies, since part of their business model comes from the sale of development tools. .
Where does the problem lie? When code is written in a hardware description language, it is “compiled” into a specific format, which is different for each manufacturer. What causes the tools to end up associated with a manufacturer of FPGAs in
SoC FPGA or FPGA just plain?
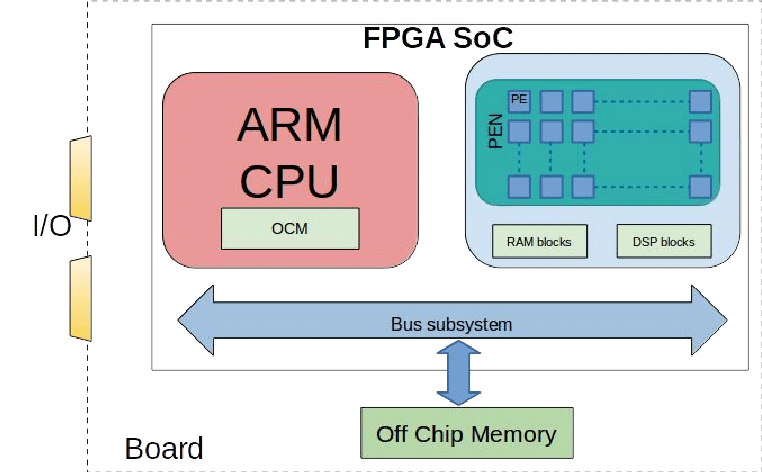
No, we are not going to compare them, but we must bear in mind that there are many FPGAs that do not come alone but incorporate a SoC, the same type as those we have in smartphones, which interacts with the FPGA.
The other and cheaper option is to opt for a board that only carries the FPGA and not the SoC. In the first case it is ideal to learn the possibilities between the components of a SoC and the FPGA in combination. But if you are looking to learn to program an FPGA without other frills then you may be interested in a board that is just an FPGA.
Our recommendation is that you go for the second type, especially since this will allow you to interact with the I / O interfaces that the SoC already has integrated, instead of having to buy them separately and even program them.
Best choice for newbies: Raspbery Pi + FPGA
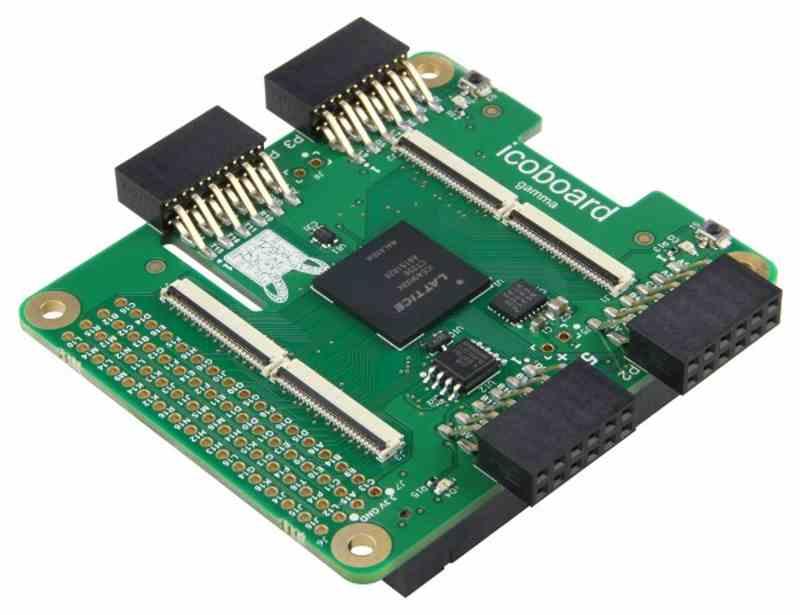

The safest thing is that many of you have a Raspberry Pi to do certain projects, well the IcoBoard is compatible with the pins of the different models of Raspberry Pi 2B onwards, so it will be very easy to install it on your Raspberry Pi to add new functionalities to it and use it to learn Verilog.
The FPGA used by the icoBoard is a 7680 LUTS 8 Megabit SRAM Lattice iCE40-HX8K. The fact that it is designed to be used together with a Rasperry Pi means that you can save the SoC, but there are a number of reasons why we recommend this model and not others.
Also given that many of you will have carried out projects with a Raspberry Pi for different projects, the use of an FPGA will add new functions to your projects with your Raspberry Pi, which greatly expands its functionality, while you are learning how the hardware really works.
Why are we making this recommendation for FPGA newbies?

The reason why we recommend the use of the icoBoard if you are newbies is due to the fact that its FPGA, the Lattice iCE40-HX8K, has been reverse engineered in order to be able to use totally free and open tools for development in this license plate. The downside to it all? You are going to need to have a Linux distribution installed to be able to do it, but from the moment you may have one running on your Raspberry Pi.
The reverse engineering project on the Lattice ICE40-HX8K is called IceStorm, you can find a link at the end of this article, specifically in the sources that we attach at the end of it.