Lately you have heard or read that a graphics card has a certain number of power phases. What does this expression refer to? What are the GPU phases ? Why is it important when adjusting the clock speed of these? Is it something exclusive to graphics cards or is it a common element with other types of electronic products? We are going to explain everything to you.
VRM (Voltage Regulator Module) and its relationship with the phases of a GPU
What a voltage regulator module does is take the voltage from the power supply and redistribute it to the proper voltage of each of the parts that make up the motherboard or card. It is not an exclusive piece of computer products, but we can find them in other equipment with electronic components inside.
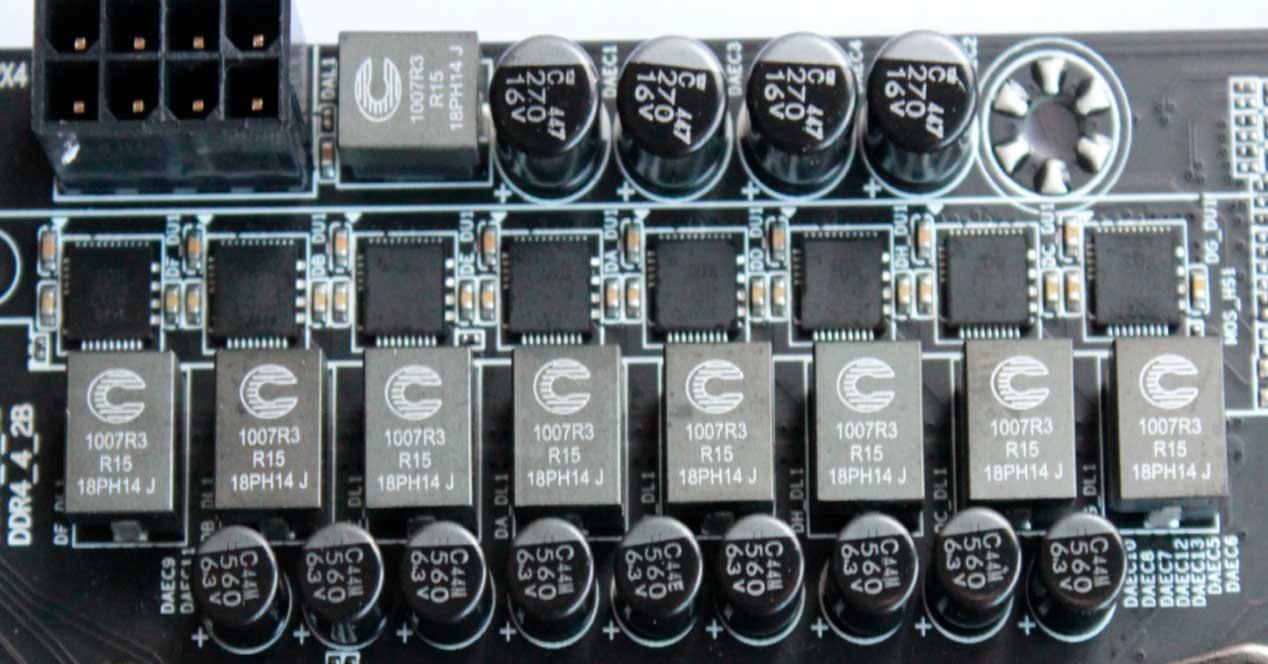

VRMs are not a single piece of hardware but are normally made up of three different elements: MOSFETs together with their integrated circuit, a series of capacitors and a series of choke coils.
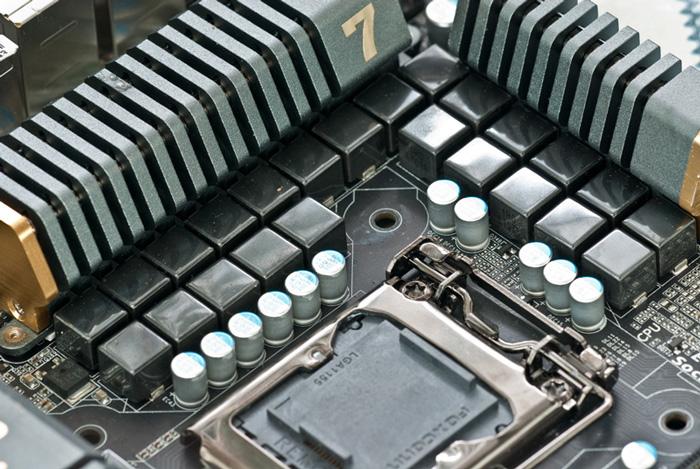

MOSFETs (Metal-Oxide Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors) communicate with the CPU. The CPU sends them through a data channel the voltage that it requires to function properly at all times. Through a series of logic gates and voltage reduction and amplification circuits, it adjusts the voltage that goes from the power supply to the GPU in a dynamic way, adjusting in real time to each moment. In this way, the GPUs can vary in clock speed according to the workload, which helps to increase the useful life of the graphics card.
In the process of lowering the voltage from the source to the processor, the electrical current is passed through the phases which helps to clean the supply reducing the possibility of a vDroop (voltage drop below that specified in the vCore value).
Voltage drop issues can cause GPU malfunctions causing the graphics card to stop working.
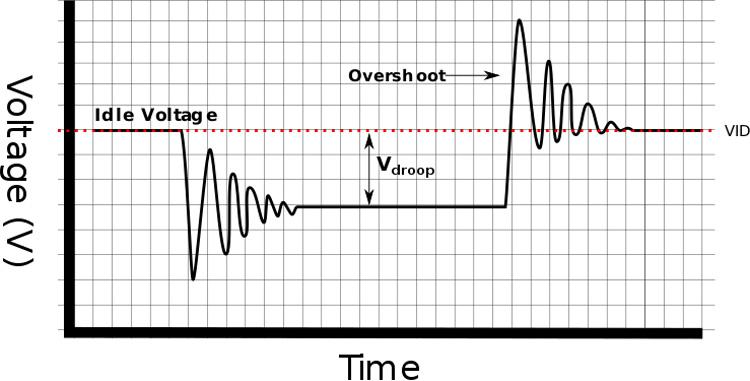
Passing the electrical current coming from the power supply through a greater number of phases reduces the risk of a voltage drop and increases stability, especially when the processor is operating at very high clock speeds in the face of overclocking.
The relationship between voltage and clock speed
The general and simplified formula to measure the energy consumption of a chip is the following:
Energy Consumption = c * f * v 2
In the formula: c is the capacity to maintain an electrical charge of the transistors, f is the frequency and therefore the clock speed and v is the voltage with which the chip is fed.
Although today the chips are designed to have several energy domains in such a way that certain parts of them can be turned off when they are not necessary or remain with a much lower consumption to make this entry understandable, to simplify we are going to assume that the chips all run under the same energy domain.
There is a direct relationship between voltage and clock speed: the higher the voltage, the higher the clock speed that can be achieved.
It happens that the same processor or memory reaches the same clock speed and with different voltages, which allows us to lower the voltage within the ranges accepted by the processor (the so-called undervolting) without losing performance, thus reducing energy consumption and increasing power. processor life.
In the same way, if we want to increase the clock speed, there will come a point where it will be necessary to increase the voltage that feeds the chip or memory.
This is where the so-called VRM (Voltage Regulator Modules) come in, which are responsible for correctly distributing the voltage to the different components and which we have explained in the previous section. For this reason the phases are important not only within a GPU but also in any electronic circuit of our computer, because they ensure that at the level of electrical current, the voltage is adequate at all times.