NVIDIA graphics cards have a really interesting feature for their use by users who purchase them. And it is that apart from certain proprietary technologies that improve graphics or performance, Huang’s have been developing a specific function called NVENC for many years, which has been updated after the jump from Pascal to Turing as an architecture and where Ampere is expected. be one more turn of the screw. But what have been the changes between these two current generations?
We start from the assumption that we already know exactly what NVENC is and exactly what it is used for thanks to our specific article. So it will be easier knowing this to understand why many users are more than happy with Turing versus Pascal and by the way, we will understand part of the outlay they make and that sometimes seems to be little justified.

Pascal left many graphics cards in the lurch, especially MX

As architecture and part of it, NVENC with Pascal reached its fourth generation where the changes are substantial. However, it requires that the SIP kernel be compatible with a brand-name driver due to the restrictions of the NVIDIA proprietary API, which is not open source.
The main novelty compared to Maxwell was the support of HEVC at 10 bits and something that is little said, lossless encoding and the so-called SAO (Sample Adaptive Offset) . It improves encoding and its performance in 4K under H.264 and supports HEVC 8K with a 4: 4: 4 chroma .
The controversy came with the so-called B-Frames, since Pascal could do it under H.264 but not with HEVC, where all the features seen were left out of the GT 1030, P500 and the entire MX range, including the MX350 that it is disabled at the factory.
The problem with Turing and its chips, why does NVIDIA segregate like this?
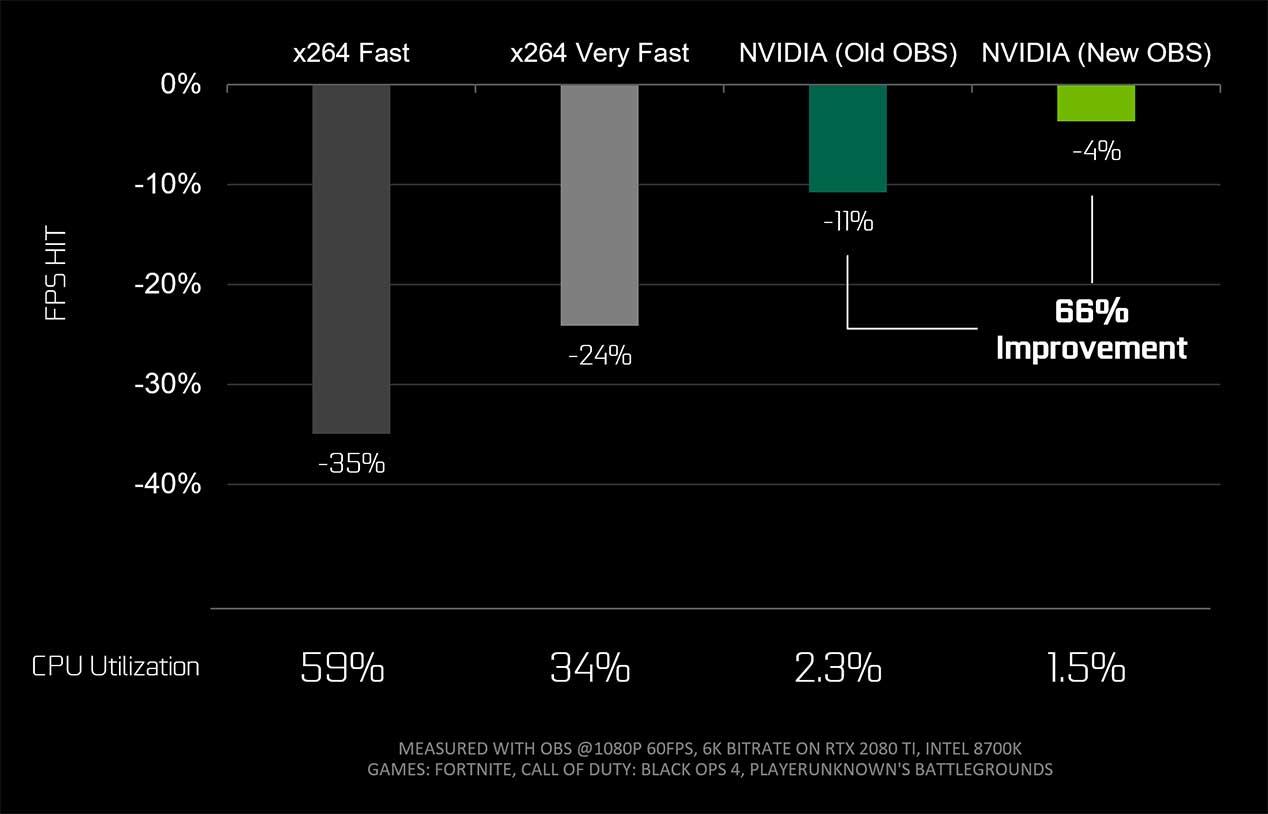
Not long ago we talked about the problems that users faced when choosing certain GPU models with a view to using NVENC. And it is that with Turing there are two generations of this function: the fifth and sixth generation.
The fifth is part of the Volta GV10X and the Turing TU117 chip, found in many GTX 1650s. Instead, the sixth includes all the other chips of the Turing architecture. The funny thing about this is that the fifth generation has a performance almost identical to that seen in Pascal, but the sixth brings many improvements.
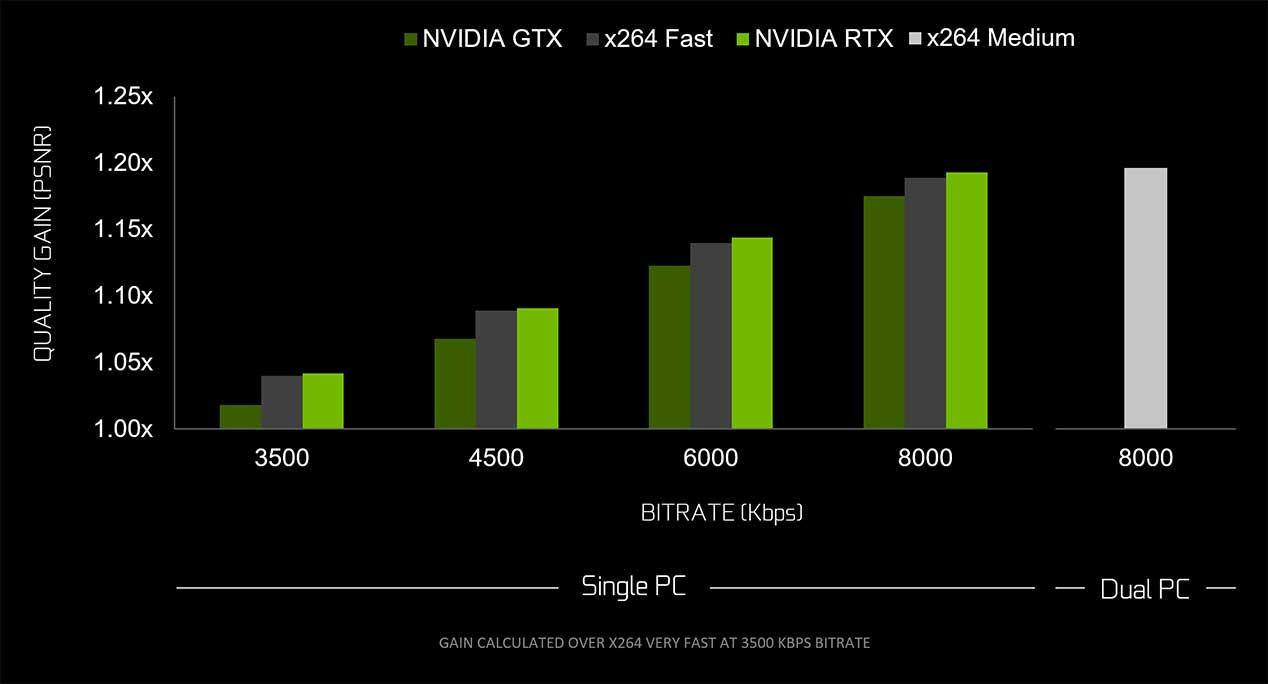
Starting with the inclusion and support of HEVC B-Frames and HEVC 8K at 30 FPS , something unthinkable just two years ago and ending with a gain of up to 25% in bitrate with HEVC and 15% with H.264. This means that it will be on average 20% faster in encoding than Pascal and his NVENC, where in addition many users claim that it is not only the fact that it takes less time, but that the final image quality is much better in Turing.
Unfortunately, at Ampere we do not yet have data on its capabilities, but some rumors claim that it could be compatible with AV1 , mainly due to the global push to this codec.