One of the main problems that we can find when going from Windows to Linux is with the lack of our favorite programs. Many programs, like Office or Photoshop, are not available for distros like Ubuntu. And the same happens with games, since although we can install Steam, and other stores, the number of titles that work on Linux is very limited. This is due to the absence of libraries and Windows dependencies within this operating system. And this is exactly what Wine is trying to solve.
Wine was initially intended to be a Windows emulator for Linux. However, WineHQ does not “emulate” a complete Windows environment within Linux, but simply provides the necessary libraries and instructions to load and process the compiled binaries for the Microsoft system. Therefore, the acronym of this software changed to “Wine Is Not an Emulator”.

This software is capable of loading applications from Windows 3.x to Windows 10, both in 16 and 32 or 64 bits. It has practically all the official libraries of the Microsoft system, and it allows us to import our own libraries easily in case we have to make a program with special dependencies. It also has a graphics acceleration system that allows from drawing application windows to playing games.
Wine has become one of the essential programs for any user of Ubuntu, or any other Linux distro. And this is how we can install and configure it.
How to download and install Wine
The first thing we are going to have to do if we are using a 64-bit Ubuntu is to enable 32-bit support , since it is disabled by default. We can do this very easily by opening a terminal and executing the following command in it:
sudo dpkg --add-architecture i386
And then we will update the repositories (optional):
sudo apt update
The next step will be to import the WineHQ key into our system in order to add the repository and download the most recent versions of the software. Wine can be installed from many repositories, although we strongly recommend that you always use the official one. We download the key with the following command:
wget -nc https://dl.winehq.org/wine-builds/winehq.key
And to add the key to the system we will execute the following command in the same terminal:
sudo apt-key add winehq.key
Now we are going to add the repository that corresponds to our version of Ubuntu. We have used the Ubuntu 20.04 repository, but if we use any other version (or another edition, such as Linux Mint) we must add the corresponding repository. These can be consulted from the Wine website .
Ubuntu 20.04 or Linux Mint 20.x
sudo add-apt-repository 'deb https://dl.winehq.org/wine-builds/ubuntu/ focal main'
Ubuntu 20.10
sudo add-apt-repository 'deb https://dl.winehq.org/wine-builds/ubuntu/ groovy main'
Old versions: Ubuntu 18.04 or Linux Mint 19.x
sudo add-apt-repository 'deb https://dl.winehq.org/wine-builds/ubuntu/ bionic main'
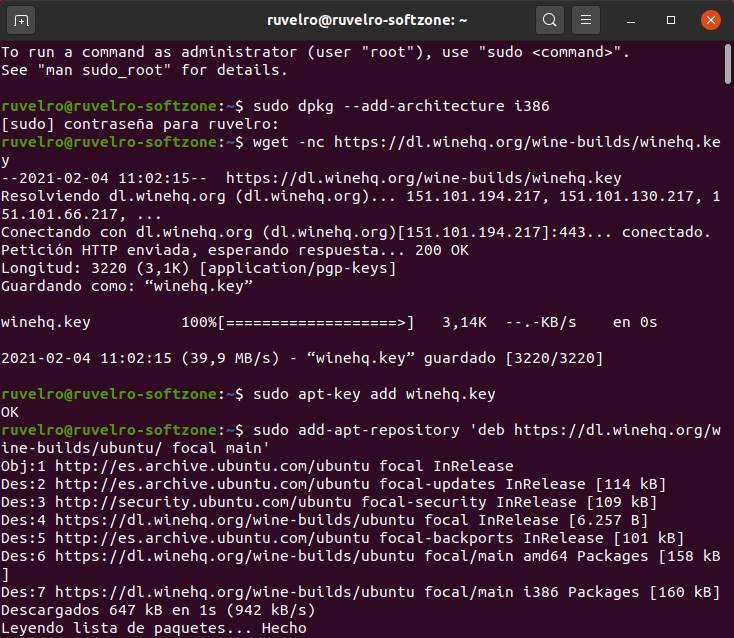
And we update the repositories of our system again with:
sudo apt update
We already have the software repositories ready. The only thing left to do is install the version we want . We recommend installing the stable branch, as it is much more debugged and gives fewer problems.
Stable
sudo apt install --install-recommends winehq-stable
Development version
sudo apt install --install-recommends winehq-devel
Trial version
sudo apt install --install-recommends winehq-staging
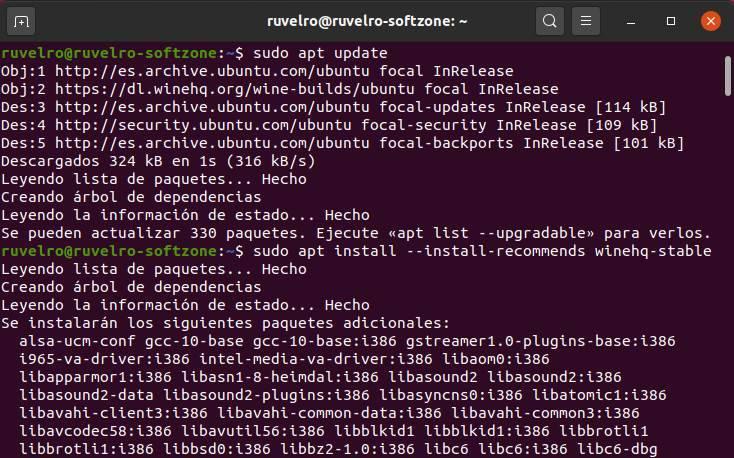
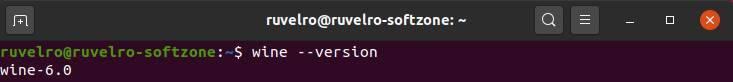
When the installation process is finished, we will have Wine ready on our PC. We can check that it is installed, and the version that has been installed, with the following command:
wine --version
Simple alternative
The above method is the recommended one to install this tool. However, if we prefer, we can use the version that comes in Ubuntu’s own repositories. We will simply execute the following command to download and install this version.
sudo apt install wine64
This will be installed automatically on our PC without having to do all of the above, although it is very easy to find an outdated version of Wine. Therefore, we recommend using the above method.
How to configure Wine
Initial setup
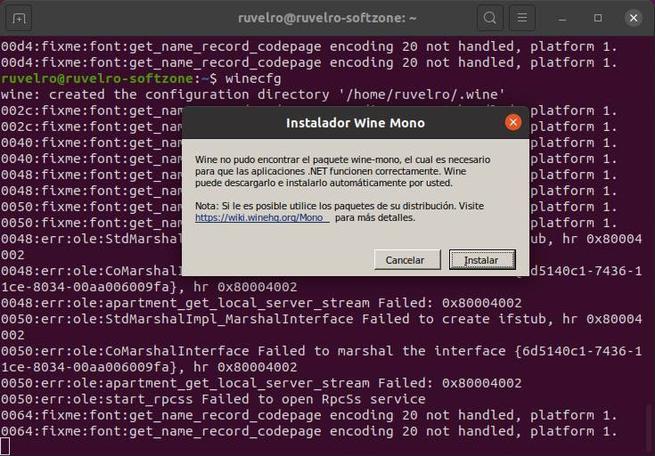
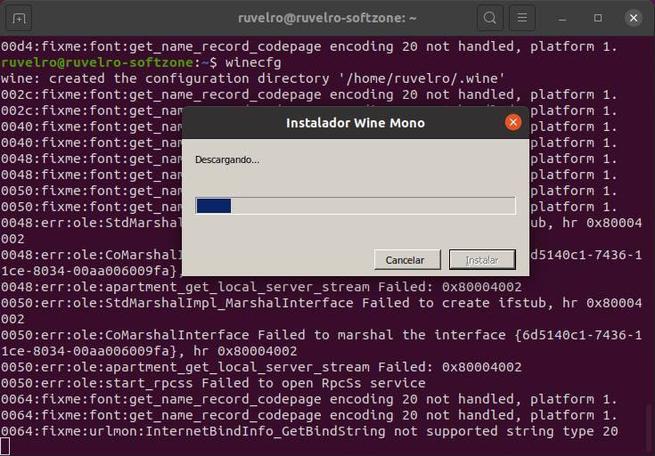
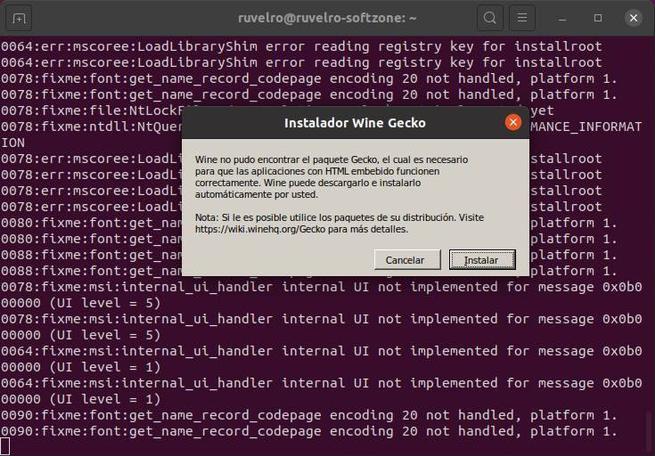
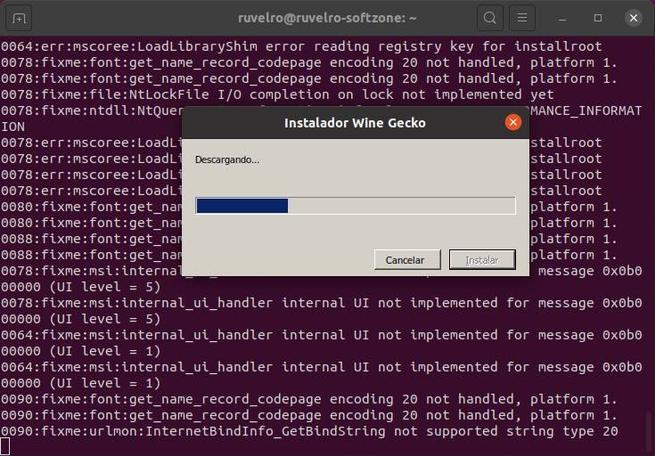
We already have Wine installed on our Ubuntu distro. But before starting to use it, you have to make a first configuration of the tool. In this configuration, the system will be prepared to be able to run Windows apps and certain components (such as Wine-Mono or Gecko) necessary for certain elements, such as .NET, to work, will be downloaded.
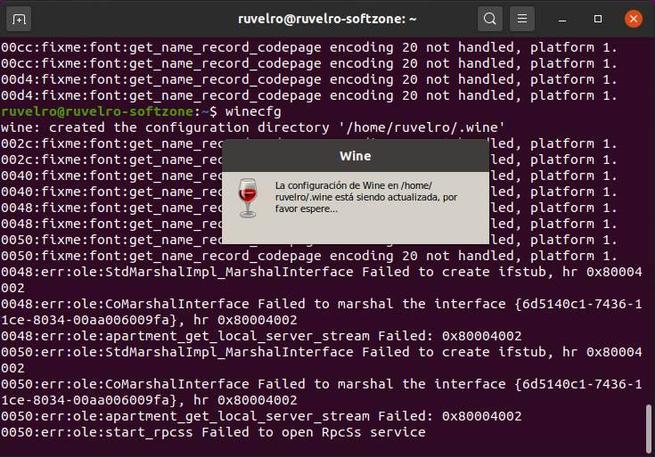
To start this initial configuration we will execute the following command:
winecfg
We will see a window that will indicate that the program is being configured. We wait for it to finish, or for us to see a window that asks us for permission to install dependencies. We click on the “Install” button of all of them so that the wizard itself takes care of downloading and copying everything necessary.
Wine Options
When the process is finished, and everything is ready on our PC, we will be able to see the Wine configuration window. This window has 7 tabs, through which we will be able to configure the different aspects of this tool.
Applications
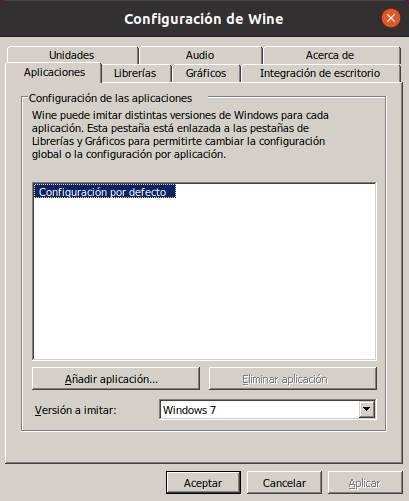
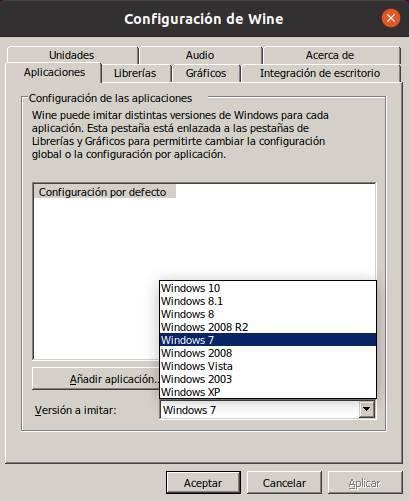
Wine allows us to simulate all versions of Windows. In this way, if we have software that can only be run on a specific version of Windows, we can load the libraries of that version, and supplant the version of the operating system, for each one of them. We can configure a default version, which will be used in all programs, and add specific EXE files to give each one a version.
Bookstores
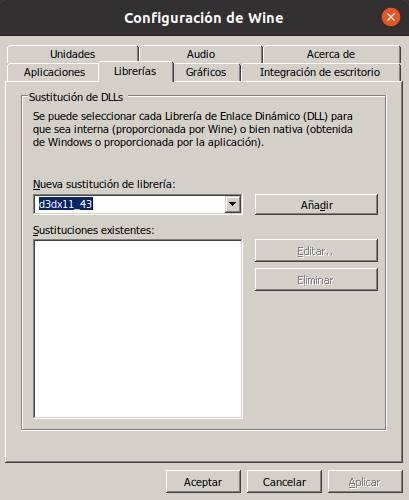
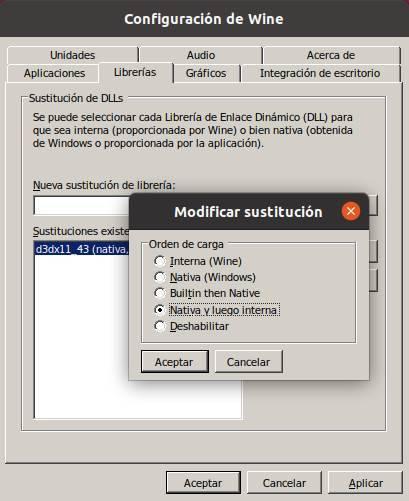
From this section we will be able to configure how we want the libraries to be used. We can let the own ones that Wine provides be used by default, or let each program use its own (if it has them) or the libraries that we copy from a Windows version or Internet downloads.
Graphics
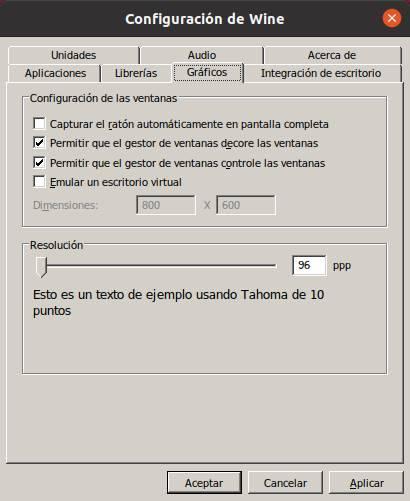
From this section we can configure how we want the windows or graphics of the applications we run to be drawn. We can choose if we want the mouse to be captured inside, emulate a virtual Windows desktop so that the program runs on it, and even window decorations. We can also choose the font size.
Desktop integration
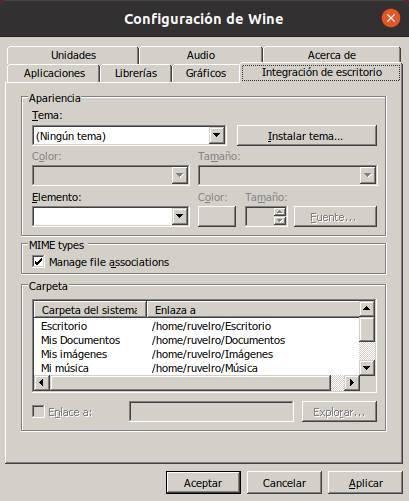
It allows us to install and configure different desktop themes, as well as configure the typical personal folders of the operating system where the data generated from these programs opened from Wine will be saved.
Units
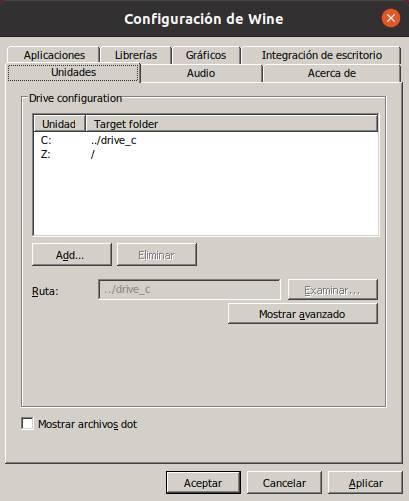
From this section we can configure the different mount points that we want the Wine applications to recognize. Each of these mount points (which can be drives or just folders) will be recognized as hard drives connected to the PC.
Audio
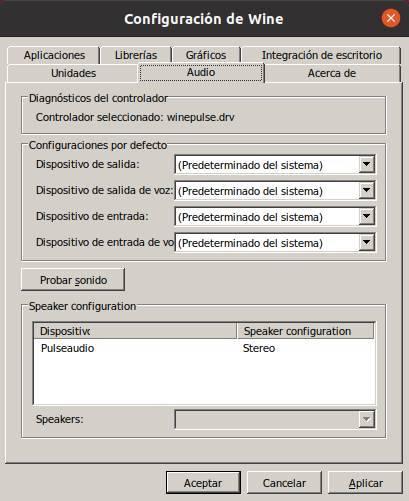
It allows us to control the sound driver used and configure the audio input and output devices.
About
As its name indicates, this tab will allow us to see the version of the program that we have installed. It is not used to configure anything.
Open a Windows program in Linux
Now that we have Wine installed, and we know how to configure it, we only have to know how to use it. By default, this program will be integrated into Ubuntu so that it automatically recognizes the .exe and .msi files and opens them by double clicking on them. Same as in Windows. We can also open these files from the context menu, by right clicking on them.
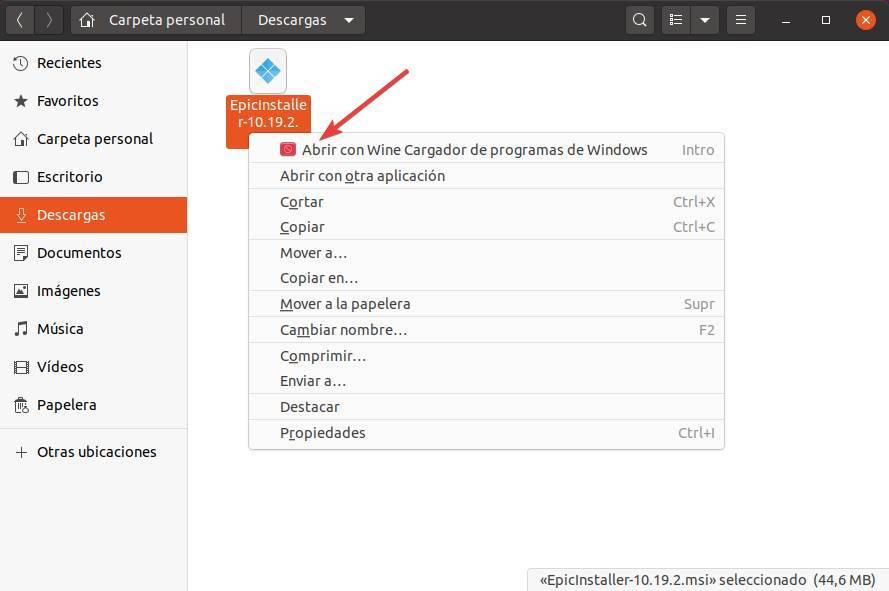
Wine will take care of everything. We will have to follow the wizard as if we were installing the program in Windows and, when it is finished, we will have the software ready to run.

Uninstall Wine
Wine is very useful, but it must also be admitted that it is quite a heavy program . And if we install many dependencies on the PC (such as .NET, for example), it can also take up a lot of space. Therefore, if we are not going to use this program, we will be able to uninstall it easily. To do this, all we have to do is execute the following command (changing “stable” to the version that we have previously installed):
sudo apt-get remove –purge winehq-stable
The system itself will take care of completely deactivating and deleting the entire program. Also, we need to delete the following cache and configuration folders by hand to free up space. We must make sure to show the hidden files with the keyboard shortcut Control + R.
- .wine (inside our personal folder)
- ./.wine
- ./.config/menus/applications-merged/ (any directory that starts with “wine”)
- ./.local/share/applications/wine
- /.local/share/desktop-directories/wine*
- ./.local/share/icons/ (all .xmp files)
Once we have eliminated all these files we must execute the following commands, in order, to finish deleting Wine from the PC:
sudo apt update sudo apt autoclean sudo apt clean sudo apt autoremove
And finally, we can manually delete the repository that we have added from the software sources of this Linux.